使用Python Numpy 做一些有趣的例子
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
埃拉托斯特尼筛法生成质数序列
a = np.arange(1, 101)
n_max = int(np.sqrt(len(a)))
is_prime = np.ones(len(a), dtype=bool)
is_prime[0] = False
for i in range(2, n_max):
if i in a[is_prime]:
is_prime[(i**2 - 1)::i] = False
print(a[is_prime])
[ 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 31 37 41 43 47 53 59 61 67 71 73 79 83 89
97]
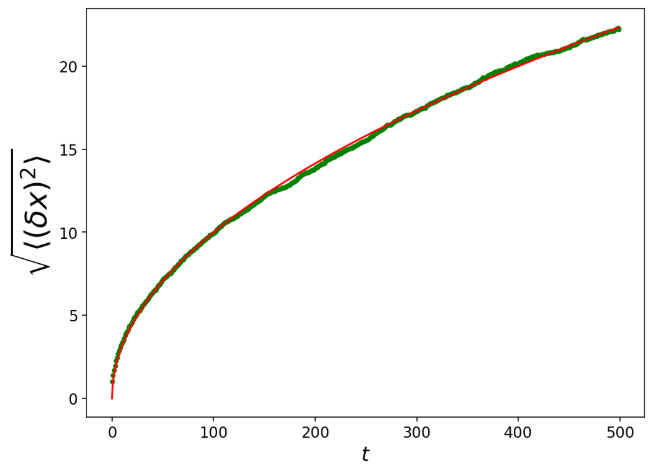
随机漫步算法
n_person = 2000
n_times = 500
t = np.arange(n_times)
steps = 2 * np.random.randint(2, size=(n_person, n_times)) - 1
amount = np.cumsum(steps, axis=1)
sd_amount = amount ** 2
mean_sd_amount = sd_amount.mean(axis=0)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.xlabel(r"$t$", fontsize=16)
plt.tick_params(labelsize=12)
plt.ylabel(r"$\sqrt{\langle (\delta x)^2 \rangle}$", fontsize=24)
plt.plot(t, np.sqrt(mean_sd_amount), 'g.', t, np.sqrt(t), 'r-');
多项式拟合
Numpy 提供的 np.ployfit() 函数可以用多项式对数据进行拟合。
n_dots = 20
n_order = 3
x = np.linspace(0, 1, n_dots)
y = np.sqrt(x) + 0.2*np.random.rand(n_dots)
p = np.poly1d(np.polyfit(x, y, n_order))
print(p.coeffs)
t = np.linspace(0, 1, 200)
#plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12), dpi=200)
plt.plot(x, y, 'ro', t, p(t), '-')

蒙特卡罗方法求圆周率
使用Numpy 求圆周率
的值。
使用的算法是蒙特卡法(Monte Carlo method)。
其主要的思想是,在一个正方形内,用正方形的变长画出一个
圆的扇形,
假设圆的半径为
,则正方向的面积为
,圆的面积为
,它们的面积之比是
。
n_dots = 1000000
x = np.random.random(n_dots)
y = np.random.random(n_dots)
distance = np.sqrt(x ** 2 + y ** 2)
in_circle = distance[distance < 1]
pi = 4 * float(len(in_circle)) / n_dots
print(pi)
3.141524
