本文为美国爱荷华大学(作者:Qiaohan Guo)的博士论文,共260页。
化学计量学是一门利用数学和统计工具从测量数据中提取化学信息的化学学科。借助于化学计量方法,红外光谱已成为一种应用广泛的定量分析工具。本文探讨了化学计量学方法在红外光谱中的两个具有挑战性的应用:(1)被动傅里叶变换(FT)遥感和(2)近红外(NIR)光谱过程监测。被动红外遥感为探测室外环境中的气态物质提供了一种测量方法。该方法在定量分析中的应用受到两个主要障碍的限制:(1)温度和浓度对测量光谱强度的影响;(2)收集用于校准的参考数据的难度和成本。为了解决这些问题,设计了一个基于辐射模型的定量分析方案来开发综合校准数据。合成数据作为偏最小二乘(PLS)回归的输入,以构建用于估算乙醇和甲醇浓度的模型。利用实验室和野外遥感数据对该方法进行了检验。
近红外光谱技术由于样品制备的简单性和与水溶液的相容性,在过程监测中引起了人们极大的兴趣。为了在过程监控中使用,需要进行稳健的校准。近红外光谱领域的一个挑战是,弱的、宽的和高度重叠的光谱带使得从被测光谱中提取有用的化学信息变得困难。在这种情况下,信号处理方法可以有助于去除不需要的信号,从而揭示有用的信息。在将信号处理作为光谱预处理工具和回归分析用于建立定量校准模型时,优化指定方法细节的参数至关重要。在本研究中,粒子群优化是一种基于群体的优化方法。评估了数字滤波和小波处理方法作为光谱预处理工具的实用性。研究了毕赤酵母的泵控流动系统和生物反应器运行。在研究生物反应器运行时,由于参考数据不足,采用PLS校准方法存在困难。相反,由于只需要分析物和背景矩阵的纯组分或合成光谱,而不需要已知分析物浓度的大量混合样品,因此应用了增强的经典最小二乘建模技术。
Chemometrics is a discipline of chemistrywhich uses mathematical and statistical tools to help in the extraction ofchemical information from measured data. With the assistance of chemometricmethods, infrared (IR) spectroscopy has become a widely applied quantitativeanalysis tool. This dissertation explores two challenging applications of IRspectroscopy facilitated by chemometric methods: (1) passive Fourier transform(FT) remote sensing and (2) process monitoring by near-infrared (NIR)spectroscopy. Passive FT-IR remote sensing offers a measurement method todetect gaseous species in the outdoor environment. Two major obstacles limitthe application of this method in quantitative analysis: (1) the effect of bothtemperature and concentration on the measured spectral intensities and (2) thedifficulty and cost of collecting reference data for use in calibration. Toaddress these problems, a quantitative analysis protocol was designed based onthe use of a radiance model to develop synthetic calibration data. Thesynthetic data served as the input to partial least-squares (PLS) regression inorder to construct models for use in estimating ethanol and methanolconcentrations. The methodology was tested with both laboratory and fieldremote sensing data. Near-infrared spectroscopy has attracted significantinterest in process monitoring because of the simplicity in sample preparationand the compatibility with aqueous solutions. For use in process monitoring,the need exists for robust calibrations. A challenge in the NIR region is thatweak, broad and highly overlapped spectral bands make it difficult to extractuseful chemical information from measured spectra. In this case, signalprocessing methods can be helpful in removing unwanted signals and therebyuncovering useful information. When applying signal processing as a spectralpreprocessing tool and regression analysis for building a quantitativecalibration model, optimizing the parameters that specify the details of themethods is crucial. In this research, particle swarm optimization, apopulation-based optimization method was applied. Digital filtering and waveletprocessing methods were evaluated for their utility as spectral preprocessingtools. Both a pump-controlled flowing system and bioreactor runs involving theyeast, Pichia pastoris, were studied in this work. In investigating thebioreactor runs, insufficient reference data resulted in difficulties inemploying the PLS calibration method. Instead, the augmented classicalleast-squares modeling technique was applied since it requires onlypure-component or composite spectra of the analyte and background matrix ratherthan a large set of mixture samples of known analyte concentration.
- 引言
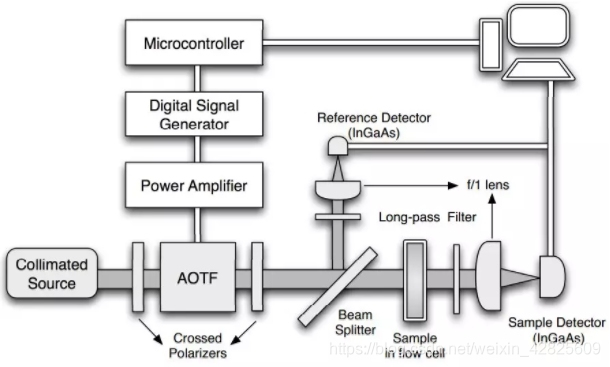
- 红外测量技术
- 信号处理与数据分析
- 被动傅里叶变换红外遥感合成校正光谱法测定甲醇和乙醇
- 基于粒子滤波和偏最小二乘模型参数的粒子群优化校正策略在近红外光谱连续监测葡萄糖中的应用
- 基于增广经典最小二乘法的生物反应器连续监测的信号处理方法
- 基于小波预处理的生物反应器连续监测自动校准协议
- 结论与未来工作展望
更多精彩文章请关注公众号:
