HashMap
HashMap是Java集合中重要的一个数据结构,作为key-value形式的存在,被广泛使用
虽在平常开发中经常使用HashMap来存放数据,并且很多框架也使用了Map,但对HashMap的了解一直不够深入
HashMap在JDK 1.7中的实现
1.7中的数据结构
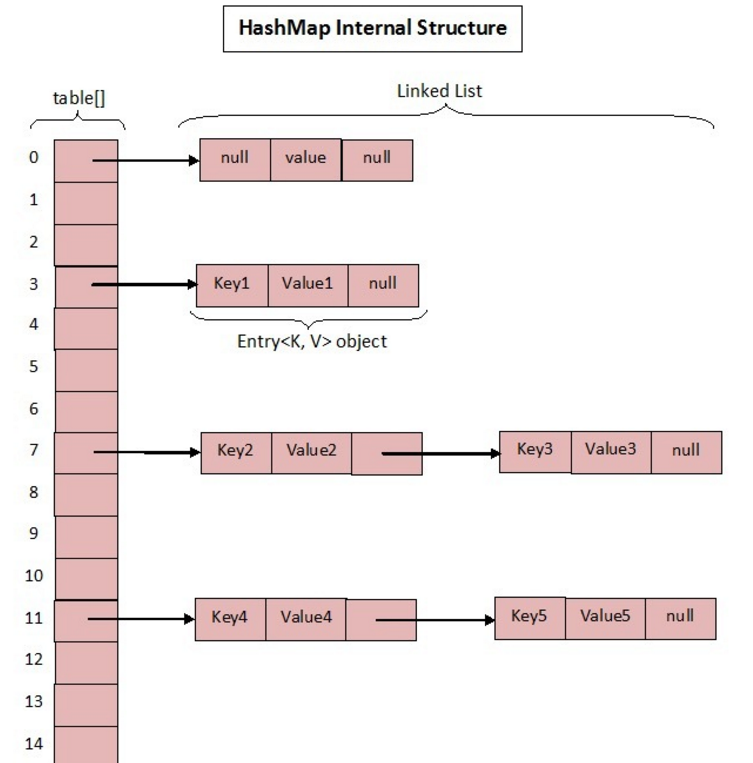
1.7中HashMap几个关键的成员变量

- 初始化桶大小,因为底层是数组,所以这是数组默认的大小。
- 桶最大值。
- 默认的负载因子(0.75)
table真正存放数据的数组。Map存放数量的大小。- 桶大小,可在初始化时显式指定。
- 负载因子,可在初始化时显式指定
负载因子
给定的默认容量为 16,负载因子为 0.75。Map 在使用过程中不断的往里面存放数据,当数量达到了 16 * 0.75 = 12 就需要将当前 16 的容量进行扩容,而扩容这个过程涉及到 rehash、复制数据等操作
Entry类
Entry 是 HashMap 中的一个内部类,从他的成员变量很容易看出:
- key 就是写入时的键。
- value 自然就是值。
- 开始的时候就提到 HashMap 是由数组和链表组成,所以这个 next 就是用于实现链表结构。
- hash 存放的是当前 key 的 hashcode。
put 方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}put 操作的流程
- 判断当前数组是否需要初始化。
- 如果 key 为空,则 put 一个空值进去。
- 根据 key 计算出 hashcode。
- 根据计算出的 hashcode 定位出所在桶。
- 如果桶是一个链表则需要遍历判断里面的 hashcode、key 是否和传入 key 相等,如果相等则进行覆盖,并返回原来的值。
- 如果桶是空的,说明当前位置没有数据存入;新增一个 Entry 对象写入当前位置。
get 方法
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}- 首先也是根据 key 计算出 hashcode,然后定位到具体的桶中。
- 判断该位置是否为链表。
- 不是链表就根据
key、key 的 hashcode是否相等来返回值。 - 为链表则需要遍历直到 key 及 hashcode 相等时候就返回值。
- 啥都没取到就直接返回 null
HashMap在JDK 1.8中的实现
1.7中HashMap有一个问题就是,当Hash严重冲突时,链表就会越来越长,查找的效率就会越来越低
因此在1.8中就优化了这个问题
1.8中的数据结构
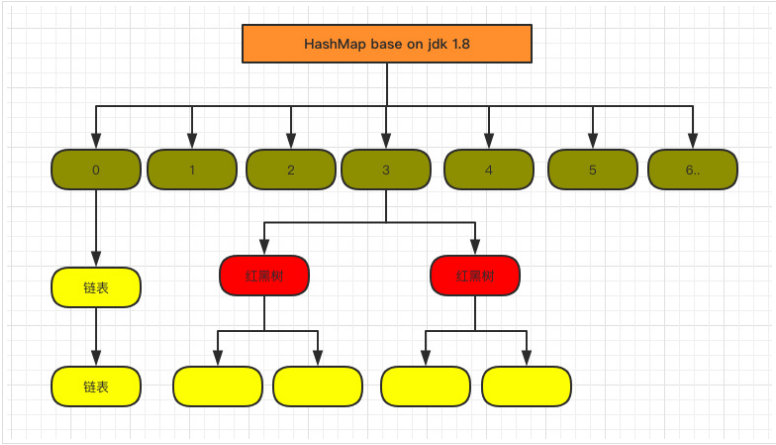
1.8中HashMap关键成员变量
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used
* for keySet() and values().
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size;和1.7中的区别
TREEIFY_THRESHOLD用于判断是否需要将链表转换为红黑树的阈值。- HashEntry 修改为
Node,Node核心组成和1.7中的Entry一致
put 方法
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}- 判断当前桶是否为空,空的就需要初始化(resize 中会判断是否进行初始化)。
- 根据当前 key 的 hashcode 定位到具体的桶中并判断是否为空,为空表明没有 Hash 冲突就直接在当前位置创建一个新桶即可。
- 如果当前桶有值( Hash 冲突),那么就要比较当前桶中的
key、key 的 hashcode与写入的 key 是否相等,相等就赋值给e,在第 8 步的时候会统一进行赋值及返回。 - 如果当前桶为红黑树,那就要按照红黑树的方式写入数据。
- 如果是个链表,就需要将当前的 key、value 封装成一个新节点写入到当前桶的后面(形成链表)。
- 接着判断当前链表的大小是否大于预设的阈值,大于时就要转换为红黑树。
- 如果在遍历过程中找到 key 相同时直接退出遍历。
- 如果
e != null就相当于存在相同的 key,那就需要将值覆盖。 - 最后判断是否需要进行扩容
get 方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}- 首先将 key hash 之后取得所定位的桶。
- 如果桶为空则直接返回 null 。
- 否则判断桶的第一个位置(有可能是链表、红黑树)的 key 是否为查询的 key,是就直接返回 value。
- 如果第一个不匹配,则判断它的下一个是红黑树还是链表。
- 红黑树就按照树的查找方式返回值。
- 不然就按照链表的方式遍历匹配返回值。
HashMap存在的问题
HashMap问题之一就是在并发情况下可能会出现死循环
final HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
map.put(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), "");
}
}).start();
}HashMap的遍历方式
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entryIterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (entryIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> next = entryIterator.next();
System.out.println("key=" + next.getKey() + " value=" + next.getValue());
}
Iterator<String> iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
String key = iterator.next();
System.out.println("key=" + key + " value=" + map.get(key));
}建议使用第一种方式遍历,可以一次取出key和value