Java新特性
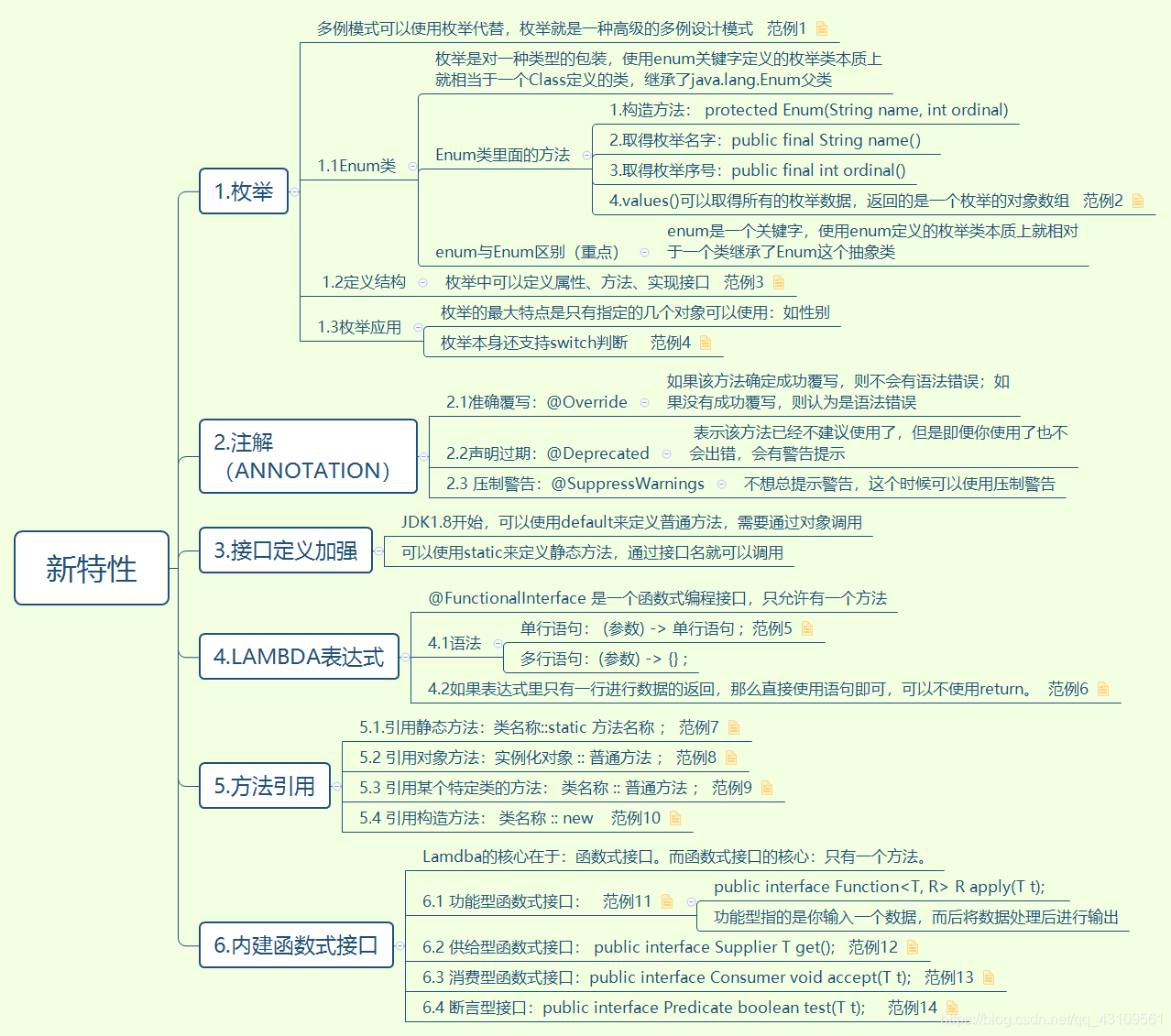
备注:
范例:
1.枚举实现多例设计模式 范例1:
enum Color {
RED,GREEN,BLUE
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Color.BLUE);
}
}2.values()可以取得所有的枚举数据,返回的是一个枚举的对象数组 范例2:
enum Color {
RED,GREEN,BLUE
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Color temp : Color.values()) {
System.out.println(temp.ordinal()+" = " +temp.name());
//0 = RED
//1 = GREEN
//2 = BLUE
}
}
}3.枚举中可以定义属性、方法、实现接口 范例3:
interface IColor {
public String getColor() ;
}
enum Color implements IColor{
RED("红色"),GREEN("绿色"),BLUE("蓝色") ; // 如果定义有很多内容,枚举对象必须写在第一行
private String title ;
private Color(String title) { // 构造方法私有化
this.title = title ;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.title ;
}
@Override
public String getColor() {
return this.title ;
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IColor iColor = Color.BLUE ;
System.out.println(iColor.getColor());
}
}4. 枚举支持switch判断 范例4:
enum Sex {
MALE,FEMALE
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
switch(Sex.MALE) {
case MALE :
System.out.println("男人");
break ;
case FEMALE :
System.out.println("女人");
break ;
}
}
}5.Lambda表达式单行、多行语句 范例5:
@FunctionalInterface // 是一个函数式编程接口,只允许有一个方法
interface IMessage {
public void print() ; // 这是一个接口,接口中的抽象方法必须由子类覆写。
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 函数式编程的使用,目的还是输出一句话
IMessage message = () -> System.out.println("Hello World");
/*
//多行
IMessage message = () -> {
System.out.println("Hello ");
System.out.println("World");
};
*/
message.print();
}
}6.Lambda表达式里只有一行进行数据的返回,那么直接使用语句即可,可以不使用return。 范例6:
interface IMath {
public int add(int x,int y) ;
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 函数式编程的使用,目的还是输出一句话
IMath msg = (p1,p2) -> p1+p2 ; // 只有一行返回
System.out.println(msg.add(10, 20));
}
}7.方法引用-引用静态方法:类名称::static 方法名称 ; 范例7:
@FunctionalInterface // 是一个函数式编程接口,只允许有一个方法
interface IUtil<P,R> {
public R switchPara(P p) ;
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IUtil<Integer,String> iu = String :: valueOf ; //进行方法引用
String str = iu.switchPara(1000) ; // 相当于调用了String.valueOf(1000)
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}8.方法引用-引用对象方法:实例化对象 :: 普通方法 ; 范例8:
IUtil<String> iu = "hello" :: toUpperCase ; // 进行方法引用9.方法引用- 引用某个特定类的方法: 类名称 :: 普通方法 ; 范例9:
IUtil<Integer,String> iu = String :: compareTo ;10.方法引用- 引用构造方法: 类名称 :: new 范例10:
IUtil<Person,String,Integer> iu = Person :: new;
System.out.println(iu.createPerson("yuisama", 25)); // 相当于调用Person类的构造方法11.内建函数式接口-功能型函数式接口: public interface Function<T, R> R apply(T t); 范例11:
//如果现在确定操作的数据是int,则可以使用IntFunction接口。
import java.util.function.IntFunction;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntFunction<String> fun = String :: valueOf ;
System.out.println(fun.apply(1000));
}
}12.内建函数式接口-供给型函数式接口: public interface Supplier T get(); 范例12:
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Supplier<String> sup = "hello"::toUpperCase ;
System.out.println(sup.get());
}
}13.内建函数式接口-消费型函数式接口:public interface Consumer void accept(T t); 范例13:
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Consumer<String> cons = System.out :: println ;
cons.accept("哈哈");
}
}14.内建函数式接口-断言型接口:public interface Predicate boolean test(T t); 范例14:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<String> pre = "##123shdbs" :: startsWith ;
System.out.println(pre.test("##"));
}
}