字节流
字节输出流
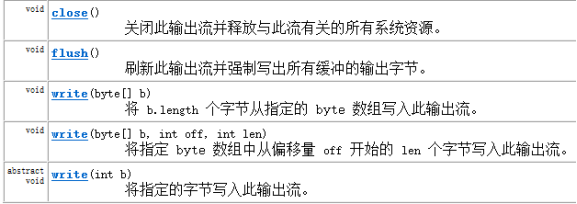
OutputStream:OutputStream定义了输出字节流的基本共性功能方法,
* FileOutputStream创建对象调用构造方法的时候 * 如果文件存在会被覆盖 * 如果不存在会加上 * 字节流操作的单位是字节,write方法一次只能写入一个字节 * 100代表ascii值里面的d * * 步骤: * 1.创建流子类对象,绑定数据 * 2.调用write方法 * 3.关闭流对象,调用close方法,释放资源 * */ File f=new File("e:\\java\\demo.txt"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(f,true); //fos.write(49); //若传入的是负数,就走汉字 // byte[]b={97,98}; // fos.write(b); // fos.write(b, 'a', 'b'); //需求:传hello fos.write("\r\nhello".getBytes()); fos.close(); }
这是比较简单的字节流输出
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class input { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub FileInputStream fis=null; try{ fis=new FileInputStream("e:\\java\\demo.txt"); // byte[] b=new byte[3]; // int a=fis.read(b);//返回值代表的是有效字节数 // for(byte b1:b){System.out.println(b1);} int len=0; while((len=fis.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)len); } // byte[]b=new byte[1024]; // int l=0; // while((l=fis.read(b))!=-1){ // String str=new String(b,0,l); // System.out.println(str); //} }catch(IOException ex){ ex.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(); }finally{ try{ if(fis!=null){ fis.close(); } }catch(IOException ex){ ex.printStackTrace(); } } } }
这是字节流输入的几种方法,用byte数组效率会高一点,记得一定要抛异常