比较玩具数据集异常检测的异常检测算法
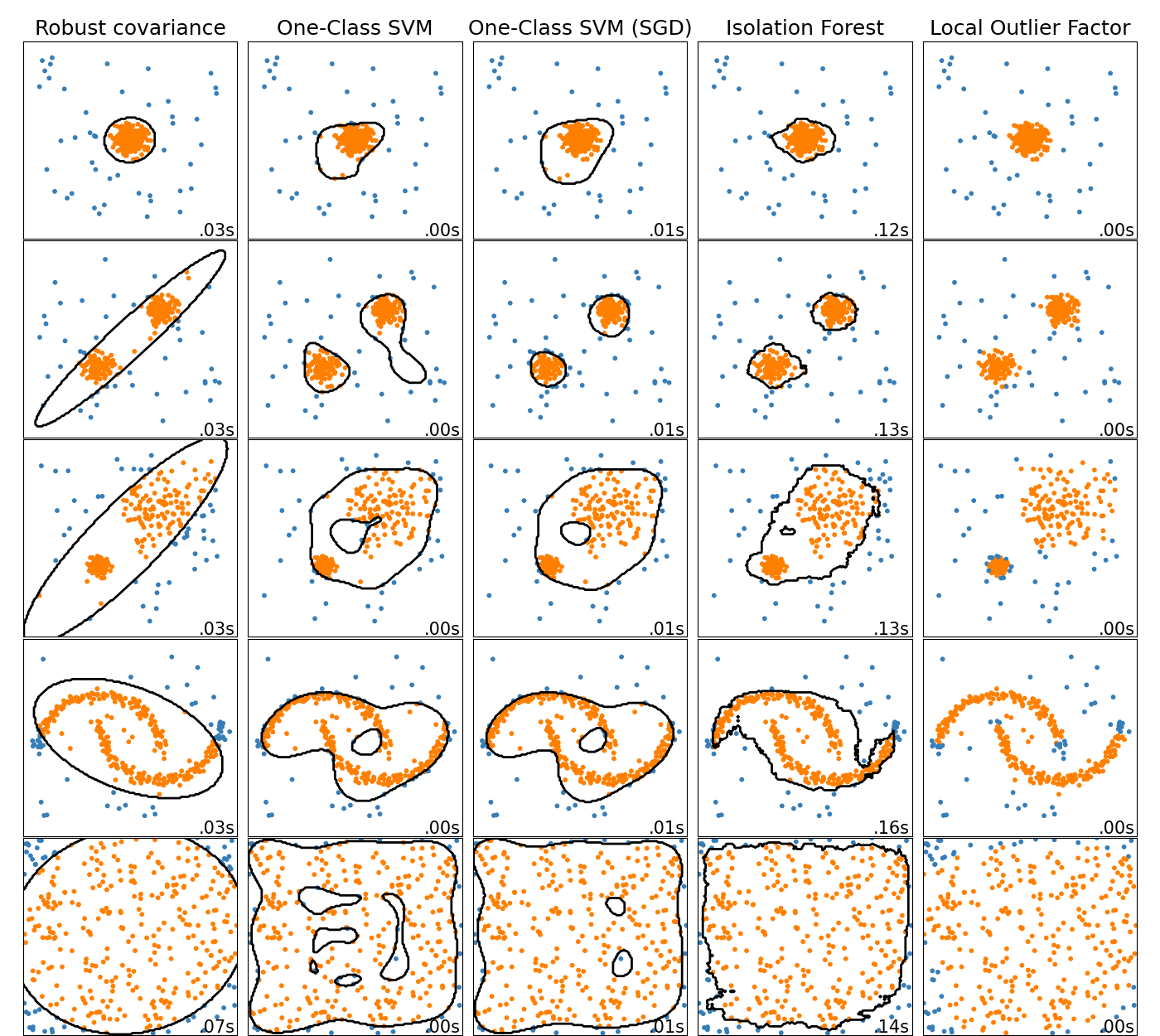
此示例显示了2D数据集上不同异常检测算法的特征。 数据集包含一种或两种模式(高密度区域),以说明算法处理多模态数据的能力。
对于每个数据集,15%的样本被生成为随机均匀噪声。 该比例是给予OneClassSVM的nu参数的值和其他异常值检测算法的污染参数。 除了局部异常因子(LOF)之外,内部和异常值之间的决策边界以黑色显示,因为当用于异常值检测时,它没有预测方法应用于新数据。
已知sklearn.svm.OneClassSVM对异常值敏感,因此对异常值检测的效果不佳。 当训练集未被异常值污染时,该估计器最适合于新颖性检测。 也就是说,高维中的离群检测,或者对上层数据的分布没有任何假设是非常具有挑战性的,并且单类SVM可能在这些情况下根据其超参数的值给出有用的结果。
sklearn.covariance.EllipticEnvelope假设数据是高斯数并学习椭圆。 因此,当数据不是单峰时,它会降级。 但请注意,此估算器对异常值很稳健。
sklearn.ensemble.IsolationForest和sklearn.neighbors.LocalOutlierFactor似乎对多模态数据集表现得相当好。 对于第三个数据集,显示了sklearn.neighbors.LocalOutlierFactor优于其他估计器的优点,其中两个模式具有不同的密度。 这一优势可以通过LOF的局部方面来解释,这意味着它只将一个样本的异常得分与其邻居的得分进行比较。
最后,对于最后一个数据集,很难说一个样本比另一个样本更异常,因为它们均匀分布在超立方体中。 除了稍微适应的sklearn.svm.OneClassSVM之外,所有估算器都为这种情况提供了不错的解决方案。 在这种情况下,更仔细地观察样本的异常分数是明智的,因为良好的估计器应该为所有样本分配相似的分数。
虽然这些例子给出了一些关于算法的直觉,但这种直觉可能不适用于非常高维的数据。
最后,请注意模型的参数已经在这里精心挑选,但实际上它们需要进行调整。 在没有标记数据的情况下,问题完全没有监督,因此模型选择可能是一个挑战。

# Author: Alexandre Gramfort <[email protected]>
# Albert Thomas <[email protected]>
# License: BSD 3 clause
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_blobs
from sklearn.covariance import EllipticEnvelope
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
from sklearn.neighbors import LocalOutlierFactor
print(__doc__)
matplotlib.rcParams['contour.negative_linestyle'] = 'solid'
# Example settings
n_samples = 300
outliers_fraction = 0.15
n_outliers = int(outliers_fraction * n_samples)
n_inliers = n_samples - n_outliers
# define outlier/anomaly detection methods to be compared
anomaly_algorithms = [
("Robust covariance", EllipticEnvelope(contamination=outliers_fraction)),
("One-Class SVM", svm.OneClassSVM(nu=outliers_fraction, kernel="rbf",
gamma=0.1)),
("Isolation Forest", IsolationForest(behaviour='new',
contamination=outliers_fraction,
random_state=42)),
("Local Outlier Factor", LocalOutlierFactor(
n_neighbors=35, contamination=outliers_fraction))]
# Define datasets
blobs_params = dict(random_state=0, n_samples=n_inliers, n_features=2)
datasets = [
make_blobs(centers=[[0, 0], [0, 0]], cluster_std=0.5,
**blobs_params)[0],
make_blobs(centers=[[2, 2], [-2, -2]], cluster_std=[0.5, 0.5],
**blobs_params)[0],
make_blobs(centers=[[2, 2], [-2, -2]], cluster_std=[1.5, .3],
**blobs_params)[0],
4. * (make_moons(n_samples=n_samples, noise=.05, random_state=0)[0] -
np.array([0.5, 0.25])),
14. * (np.random.RandomState(42).rand(n_samples, 2) - 0.5)]
# Compare given classifiers under given settings
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-7, 7, 150),
np.linspace(-7, 7, 150))
plt.figure(figsize=(len(anomaly_algorithms) * 2 + 3, 12.5))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=.02, right=.98, bottom=.001, top=.96, wspace=.05,
hspace=.01)
plot_num = 1
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
for i_dataset, X in enumerate(datasets):
# Add outliers
X = np.concatenate([X, rng.uniform(low=-6, high=6,
size=(n_outliers, 2))], axis=0)
for name, algorithm in anomaly_algorithms:
t0 = time.time()
algorithm.fit(X)
t1 = time.time()
plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(anomaly_algorithms), plot_num)
if i_dataset == 0:
plt.title(name, size=18)
# fit the data and tag outliers
if name == "Local Outlier Factor":
y_pred = algorithm.fit_predict(X)
else:
y_pred = algorithm.fit(X).predict(X)
# plot the levels lines and the points
if name != "Local Outlier Factor": # LOF does not implement predict
Z = algorithm.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linewidths=2, colors='black')
colors = np.array(['#377eb8', '#ff7f00'])
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=10, color=colors[(y_pred + 1) // 2])
plt.xlim(-7, 7)
plt.ylim(-7, 7)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.text(.99, .01, ('%.2fs' % (t1 - t0)).lstrip('0'),
transform=plt.gca().transAxes, size=15,
horizontalalignment='right')
plot_num += 1
plt.show()