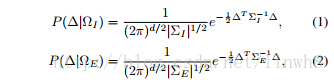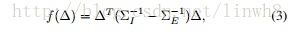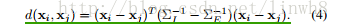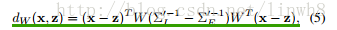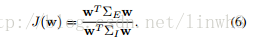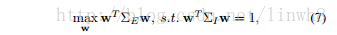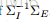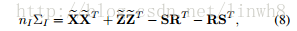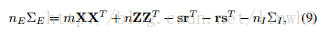版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/linwh8/article/details/78556771
注: 刚刚看完了这篇论文,顺便整理了一下这篇论文的思路,对论文的方法表示666
项目主页:http://www.cbsr.ia.ac.cn/users/scliao/projects/lomo_xqda/
论文解析
- 行人重识别有两个特别重要的问题:
- Feature representation
- Metric learning
在这篇论文中,作者采用的是LOMO的特征表示方法,以及XQDA的度量学习方法
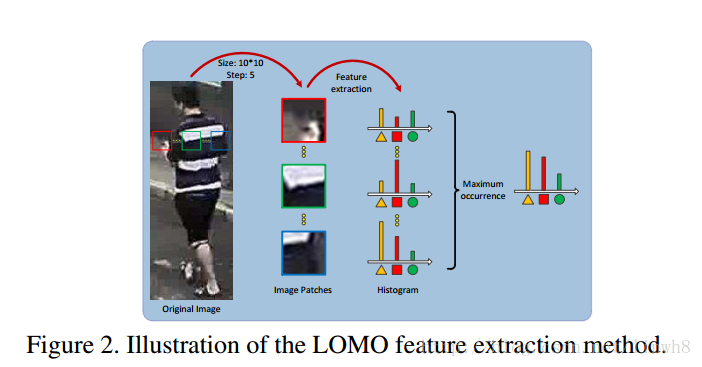
LOMO:Local Maximal Occurrence Representation, 工作原理如下:
- The LOMO feature analyze the horizontal occurrence of local features, and maximizes the occurrence to make a stable representation against viewpoint change. Besides, to handle illumination variations, we apply the Retinex transform and a scale invariant texture operator.
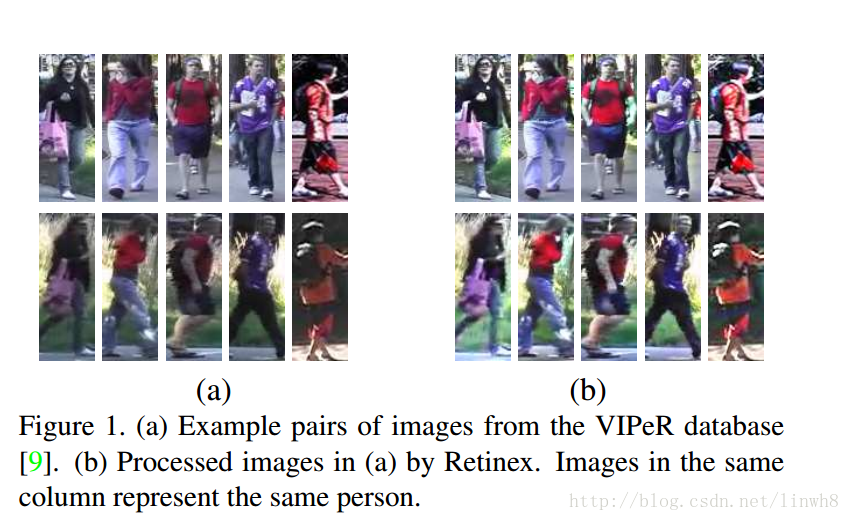
- 首先,使用Retinex algorithm 对图片进行预处理,减少光照对重识别带来的影响
- Retinex considers human lightness and color perception. It aims at producing a color image that is consistent to human observation of the scene
从效果图中可以看到,在a中不同view下illumination的差异在b中基本被消除了,这一定程度上减少了光照对重识别带来的影响
- 接着,对使用Retinex algorithm得到的Retinex image使用HSV color historgram提取颜色特征
- 除了color description, 作者还采用Scale Invariant Local Ternary Pattern(SILTP)的方法获得illuminaton invariant texture description
- 以上主要解决illumination change的问题,接下来要解决viewpoint change的问题
- 在之前的工作中,有论文proposed:equally divided a person image into six horizontal stripe, and a single histogram is comouted in each stripe.
- 虽然这种方法在一定程度上可以减轻viewpoint change带来的影响,但是这种方法可能会导致空间细节的丢失,进而影响其判别的能力
- 因此,作者提出使用silding windows来完成描述的工作:
- Specifically, we use a subwindow size of 10X10, with an overlapping step of 5 pixels to locate local patches in 128X48 images. Within each subwindow, we extract two scale of SILTP histograms, and an 8X8X8-bin joint HSV historgam. Each histogram bin represents the occurence probability of one pattern in a subwindow. (首先用10X10的silding windows,以步长为5进行滑动,然后对移动后的每一个subwindow提取三个直方图,直方图的每个bin代表对应pattern的出现概率)
- To address viewpoint change, we check all subwindows at the same horizontal location, and maximize the local occurence of each pattern among these subwindows.(接着,为了解决角度变化的问题,将位于同一水平的subwindow的直方图的同一个bin取最大值,然后组成新的直方图)
- The resulting histogram achieves some invariance to viewpoint changes, and at the same time captures local region characteristics of a person.(这些新获得的直方图不仅减轻了角度变化带来的影响,而且提取了图片局部的特征)
- To further consider the multi-scale information, we build a three-scale pyramid representation, which downsamples the original 128X48 image by 2X2 local average pooling operation, and repeats the above feature extraction procedure. So our final descriptor has (8*8*8\ colorbins+3^4*2 SILTP\ bins)*(24+11+5\ horizontal\ groups) = 26960\ demension (现在考虑multiscale的问题,将原图下采样获得另外两个尺寸的图片,每个尺寸图片的horizontal subgroup分别是24, 11, 5,然后进行前面步骤,得到26960维度的特征向量)
- Finally, we apply a log transform to suppress large bin values, and normalize both HSV and SILTP features to unit length.(最后,对直方图采用log运算并正规化, 然后就可以得到前面提到的26960维度向量)
XQDA:Cross-view Quadratic Discriminant Analysis, 工作原理如下:
- To learn a discriminant low dimensional subspace by cross-view quadratic discriminant analysis, and simultaneously, a QDA metric is learned on the derived subspace. We also present a practical computation method for XQDA, as well as its regularzation.
- XQDA是在KISSME Revisit与Bayesian Face的基础上提出的cross-view metric learning
- 首先使用高斯模型分别拟合类内与类间样本特征的差值分布
- 然后根据两个高斯分布的对数似然比推导出马氏距离
- 对数似然比:
- 马氏距离:
- 对数似然比:
- 接着定义子空间W,将(4)投影到该子空间W,得到距离
- 为了得到一个具有区分能力的目标子空间W, 即类内方差小,类外方差大,因此得到以下的优化函数:
- 其原型是:
J(w)=σE(w)/σI(w)
- 其原型是:
- 将这个优化函数进行最大化,得
- 最后得到解
但在实际计算中,协方差矩阵的计算复杂度较高,所以作者对公式进行了化简:
最后,再提一点,作者发现,取大于1有利于决定子空间维度。
- 介绍完该论文的特征表示以及距离度量学习的方法后,作者开始介绍他们的方法在四个数据集下的实验结果,以及与the state of the art(最先进技术)的比较,从实验结果可以看出,作者的方法的效果确实优于其它方法
- 作者还对自己的方法做了分析,说明方法是具有鲁棒性的。
- 最后作者做了总结并提出未来的可研究的方向
- 总结:We have proposed an effcient descriptor called LOMO, which is shown to be robust against viewpoint change and illumination variations. We have also proposed a subspace and metric learning approach called XQDA, which is formulated as a Generalized Rayleigh Quotient, and a closed-form soluton can be obtained by the generalized eigenvalue decomposition.
- 未来展望:It would be interesting to study other local features or feature coding approaches with the same LOMO idea for person re-identification.
以上内容皆为本人观点,欢迎大家提出批评和指导,我们一起探讨!