fastJson对于json格式字符串的解析主要用到了一下三个类:
JSON:fastJson的解析器,用于JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间的转换。
JSONObject:fastJson提供的json对象。
JSONArray:fastJson提供json数组对象。
我们可以把JSONObject当成一个Map<String,Object>来看,只是JSONObject提供了更为丰富便捷的方法,方便我们对于对象属性的操作。我们看一下源码。

同样我们可以把JSONArray当做一个List<Object>,可以把JSONArray看成JSONObject对象的一个集合。

此外,由于JSONObject和JSONArray继承了JSON,所以说也可以直接使用两者对JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间做转换,不过为了避免混淆我们还是使用JSON。
首先定义三个json格式的字符串,作为我们的数据源。
//json字符串-简单对象型 private static final String JSON_OBJ_STR = "{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12}"; //json字符串-数组类型 private static final String JSON_ARRAY_STR = "[{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12},{\"studentName\":\"lucy\",\"studentAge\":15}]"; //复杂格式json字符串 private static final String COMPLEX_JSON_STR = "{\"teacherName\":\"crystall\",\"teacherAge\":27,\"course\":{\"courseName\":\"english\",\"code\":1270},\"students\":[{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12},{\"studentName\":\"lucy\",\"studentAge\":15}]}";
示例1:JSON格式字符串与JSON对象之间的转换。
示例1.1-json字符串-简单对象型与JSONObject之间的转换
/** * json字符串-简单对象型与JSONObject之间的转换 */ public static void testJSONStrToJSONObject(){ JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR); //JSONObject jsonObject1 = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR); //因为JSONObject继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); }
示例1.2-json字符串-数组类型与JSONArray之间的转换
/** * json字符串-数组类型与JSONArray之间的转换 */ public static void testJSONStrToJSONArray(){ JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR); //JSONArray jsonArray1 = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR);//因为JSONArray继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 //遍历方式1 int size = jsonArray.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){ JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i); System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); } //遍历方式2 for (Object obj : jsonArray) { JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) obj; System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); } }
示例1.3-复杂json格式字符串与JSONObject之间的转换
/** * 复杂json格式字符串与JSONObject之间的转换 */ public static void testComplexJSONStrToJSONObject(){ JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR); //JSONObject jsonObject1 = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR);//因为JSONObject继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 String teacherName = jsonObject.getString("teacherName"); Integer teacherAge = jsonObject.getInteger("teacherAge"); JSONObject course = jsonObject.getJSONObject("course"); JSONArray students = jsonObject.getJSONArray("students"); }
示例2:JSON格式字符串与javaBean之间的转换。
首先,我们针对数据源所示的字符串,提供三个javaBean。
public class Student { private String studentName; private Integer studentAge; public String getStudentName() { return studentName; } public void setStudentName(String studentName) { this.studentName = studentName; } public Integer getStudentAge() { return studentAge; } public void setStudentAge(Integer studentAge) { this.studentAge = studentAge; } }
public class Course { private String courseName; private Integer code; public String getCourseName() { return courseName; } public void setCourseName(String courseName) { this.courseName = courseName; } public Integer getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Integer code) { this.code = code; } }
public class Teacher { private String teacherName; private Integer teacherAge; private Course course; private List<Student> students; public String getTeacherName() { return teacherName; } public void setTeacherName(String teacherName) { this.teacherName = teacherName; } public Integer getTeacherAge() { return teacherAge; } public void setTeacherAge(Integer teacherAge) { this.teacherAge = teacherAge; } public Course getCourse() { return course; } public void setCourse(Course course) { this.course = course; } public List<Student> getStudents() { return students; } public void setStudents(List<Student> students) { this.students = students; } }
json字符串与javaBean之间的转换推荐使用 TypeReference<T> 这个类,使用泛型可以更加清晰,当然也有其它的转换方式,这里就不做探讨了。
示例2.1-json字符串-简单对象型与javaBean之间的转换
/** * json字符串-简单对象与JavaBean_obj之间的转换 */ public static void testJSONStrToJavaBeanObj(){ Student student = JSON.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, new TypeReference<Student>() {}); //Student student1 = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, new TypeReference<Student>() {});//因为JSONObject继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 System.out.println(student.getStudentName()+":"+student.getStudentAge()); }
示例2.2-json字符串-数组类型与javaBean之间的转换
/** * json字符串-数组类型与JavaBean_List之间的转换 */ public static void testJSONStrToJavaBeanList(){ ArrayList<Student> students = JSON.parseObject(JSON_ARRAY_STR, new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {}); //ArrayList<Student> students1 = JSONArray.parseObject(JSON_ARRAY_STR, new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {});//因为JSONArray继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 for (Student student : students) { System.out.println(student.getStudentName()+":"+student.getStudentAge()); } }
示例2.3-复杂json格式字符串与与javaBean之间的转换
/** * 复杂json格式字符串与JavaBean_obj之间的转换 */ public static void testComplexJSONStrToJavaBean(){ Teacher teacher = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {}); //Teacher teacher1 = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});//因为JSONObject继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 String teacherName = teacher.getTeacherName(); Integer teacherAge = teacher.getTeacherAge(); Course course = teacher.getCourse(); List<Student> students = teacher.getStudents(); }
对于TypeReference<T>,由于其构造方法使用 protected 进行修饰,所以在其他包下创建其对象的时候,要用其实现类的子类:new TypeReference<Teacher>() {}
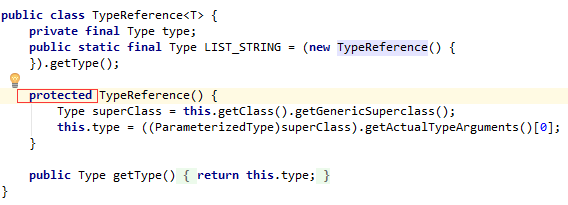
此外的:
1,对于JSON对象与JSON格式字符串的转换可以直接用 toJSONString()这个方法。
2,javaBean与JSON格式字符串之间的转换要用到:JSON.toJSONString(obj);
3,javaBean与json对象间的转换使用:JSON.toJSON(obj),然后使用强制类型转换,JSONObject或者JSONArray。
Jackson转换java对象与json对象
一、导入jar包:
(因为之前使用的是jackson 1.x的jar包,所以在把json转换成list时候没有objectMapper.getTypeFactory()这个方法,而使用jackson 2.x的jar包会有)
jackson 1.x:jackson-all-1.7.6.jar(1个核心文件)
jackson 2.x:jackson-annotations-2.5.0.jar、jackson-core-2.5.0.jar、jackson-databind-2.5.0.jar(3个核心文件)
二、建立java对象User:
 View Code
View Code
三、测试jackson 2.x的使用方法:
package com.cn.jackson.test; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import com.cn.jackson.entity.User; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonEncoding; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JavaType; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; public class Test_2_x { public static void main(String[] args) { try { ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); JsonGenerator jsonGenerator = objectMapper.getJsonFactory() .createJsonGenerator(System.out, JsonEncoding.UTF8); //对象转JSON User user = new User("张三", 23, "深圳市"); System.out.println("ObjectMapper方式"); objectMapper.writeValue(System.out, user);//直接输出到控制台 String userJsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);//返回字符串,输出 System.out.println(userJsonStr); System.out.println("JsonGenerator方式"); jsonGenerator.writeObject(user); System.out.println(); //map转JSON Map<String , Object> map = new HashMap<String ,Object>(); map.put("one", new User("张", 12, "深圳")); map.put("two", new User("李", 22, "武汉")); map.put("three", new User("王", 32, "北京")); System.out.println("ObjectMapper方式"); objectMapper.writeValue(System.out, map); //JsonGenerator方式同上 //list转JSON List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>(); list.add(new User("张", 12, "深圳")); list.add(new User("李", 22, "武汉")); list.add(new User("王", 32, "北京")); System.out.println("ObjectMapper方式"); objectMapper.writeValue(System.out, list); //JsonGenerator方式同上 //JSON转java对象: String json = "{\"name\":\"张三\",\"age\":23,\"address\":\"深圳市\"}"; User zhang = objectMapper.readValue(json, User.class); System.out.println(zhang.getName()+"\n"+zhang.getAge()+"\n"+zhang.getAddress()); //JSON转list String listJson = "[{\"name\":\"张三\",\"age\":21,\"address\":\"深圳\"}," + "{\"name\":\"李四\",\"age\":11,\"address\":\"武汉\"}," + "{\"name\":\"王五\",\"age\":31,\"address\":\"北京\"}]"; JavaType javaType1 = objectMapper.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(ArrayList.class, User.class); List<User> userList = (List<User>)objectMapper.readValue(listJson, javaType1); for (User user1 : userList) { System.out.println(user1.getName()+"\t"+user1.getAge()+"\t"+user1.getAddress()); } //JSON转map String mapJson = "{\"one\":{\"name\":\"张三\",\"age\":21,\"address\":\"深圳\"}," + "\"two\":{\"name\":\"李四\",\"age\":11,\"address\":\"武汉\"}," + "\"three\":{\"name\":\"王五\",\"age\":31,\"address\":\"北京\"}}"; JavaType javaType2 = objectMapper.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(HashMap.class, String.class, User.class); Map<String,User> userMap = (Map<String,User>)objectMapper.readValue(mapJson, javaType2); User one = userMap.get("one"); User two = userMap.get("two"); User three = userMap.get("three"); System.out.println(one.getName()+"\t"+one.getAge()+"\t"+one.getAddress()); System.out.println(two.getName()+"\t"+two.getAge()+"\t"+two.getAddress()); System.out.println(three.getName()+"\t"+three.getAge()+"\t"+three.getAddress()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
四、测试jackson 1.x的使用方法:
package com.cn.jackson.test; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.codehaus.jackson.map.ObjectMapper; import org.codehaus.jackson.type.TypeReference; import com.cn.jackson.entity.User; public class Test_1_x { public static void main(String[] args) { try { //后面几种转换同Test_2_x一样 //对象转JSON //map转JSON //list转JSON //JSON转java对象 //JSON转list ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); String listJson = "[{\"name\":\"张三\",\"age\":21,\"address\":\"深圳\"}," + "{\"name\":\"李四\",\"age\":11,\"address\":\"武汉\"}," + "{\"name\":\"王五\",\"age\":31,\"address\":\"北京\"}]"; List<User> userList = objectMapper.readValue(listJson, new TypeReference<List<User>>() {}); for (User user1 : userList) { System.out.println(user1.getName()+"\t"+user1.getAge()+"\t"+user1.getAddress()); } //JSON转map String mapJson = "{\"one\":{\"name\":\"张三\",\"age\":21,\"address\":\"深圳\"}," + "\"two\":{\"name\":\"李四\",\"age\":11,\"address\":\"武汉\"}," + "\"three\":{\"name\":\"王五\",\"age\":31,\"address\":\"北京\"}}"; Map<String,User> userMap = objectMapper.readValue(mapJson, new TypeReference<Map<String,User>>() {}); User one = userMap.get("one"); User two = userMap.get("two"); User three = userMap.get("three"); System.out.println(one.getName()+"\t"+one.getAge()+"\t"+one.getAddress()); System.out.println(two.getName()+"\t"+two.getAge()+"\t"+two.getAddress()); System.out.println(three.getName()+"\t"+three.getAge()+"\t"+three.getAddress()); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } } }
转载地址:
https://www.cnblogs.com/songzhen/p/5794494.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/cdf-opensource-007/p/7106018.html
