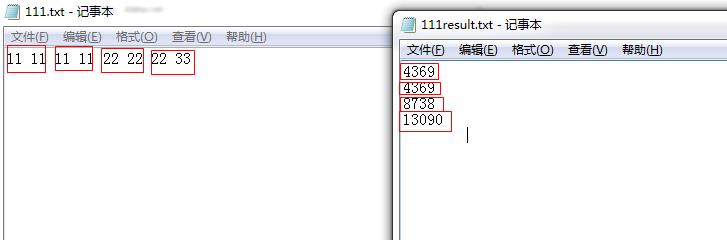
以前都是处理bin文件,突然处理text文件,不专业,方法不适用
主要处理效果如下:
程序处理时将数据保存为小端形式到txt文件。现在需要将其转换为10进制有符号的数据,分析其规律。原理很简单,代码很简单,记录下
其中值类型和字节类型的转换必须掌握(以下为:由低位、高位组成的byte[],直接转为有符号的int值类型)。
var b =
new
byte
[] { 0xeb, 0x1f };//low high
BitConverter.ToInt16(
new
byte
[] { b[1], b[0] }, 0);
Convert.ToInt16((b[0].ToString(
"X2"
) + b[1].ToString(
"X2"
)), 16);
(Int16)Convert.ToUInt16((b[0] << 8) + b[1]);
代码如图:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
namespace HandleData
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string line = string.Empty;
HandleData.Program.ReadData("E:\\language\\python\\file\\data.txt", "E:\\language\\python\\file\\dataResult.txt");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void ReadData(string filepath,string filepathw)
{
string strData = File.ReadAllText(filepath);
FileStream fs = File.Open(filepathw, FileMode.Create);
string[] str = strData.Split(' ','\r','\n');
StreamWriter wr = new StreamWriter(fs);
for (int k=0;k<str.Count()-2;k+=2)
{
string strA = str[k] +" "+ str[k+1];
int low;
//
if (str[k] == "")
{
k++;
}
low = Convert.ToInt16(str[k], 16);
if (str[k + 1] == "")
{
k++;
}
int high = Convert.ToInt16(str[k + 1], 16);
byte[] bytearr= { (byte)low, (byte)high };
int result = BitConverter.ToInt16(bytearr,0);//运算出来为已处理好的小端形式的有符号十进制数据
wr.WriteLine(result);
//byte[] byteArray = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetBytes(strA);
}
wr.Flush();
wr.Close();
// 关闭文件
fs.Close();
Console.WriteLine(strData);
}
}
}
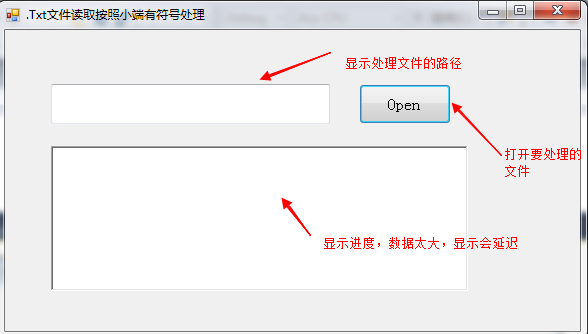
界面:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading;
namespace HandleTxtData
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog ofd = new OpenFileDialog();
ofd.Filter = "文本文件(*.txt)|*.txt|所有文件(*.*)|*.*";
ofd.ValidateNames = true;
ofd.CheckPathExists = true;
ofd.CheckFileExists = true;
string strFileName="";
if (ofd.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
strFileName = ofd.FileName;
}
textBox1.Text = strFileName;
string path = Path.GetDirectoryName(strFileName);
string fileName = Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(strFileName);
string strFileNameW = path +"\\"+fileName+ "result.txt";
ReadData(strFileName,strFileNameW);
}
public void ReadData(string filepath, string filepathw)
{
string strData = File.ReadAllText(filepath);
FileStream fs = File.Open(filepathw, FileMode.OpenOrCreate);
string[] str = strData.Split(' ', '\r', '\n');
StreamWriter wr = new StreamWriter(fs);
richTextBox1.Text = "开始处理数据\n";
for (int k = 0; k < str.Count() - 2; k += 2)
{
string strA = str[k] + " " + str[k + 1];
int low;
//
if (str[k] == "")
{
k++;
}
low = Convert.ToInt16(str[k], 16);
if (str[k + 1] == "")
{
k++;
}
int high = Convert.ToInt16(str[k + 1], 16);
byte[] bytearr = { (byte)low, (byte)high };
int result = BitConverter.ToInt16(bytearr, 0);
wr.WriteLine(result);
//byte[] byteArray = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetBytes(strA);
richTextBox1.Text = ".";
}
richTextBox1.Text = "\n数据处理完成";
wr.Flush();
wr.Close();
// 关闭文件
fs.Close();
Console.WriteLine(strData);
}
}
}
用python语言试一下,发现处理数据更快,代码如下:
#encoding=utf-8
import re
file_open=open('data.txt')
file_write=open('handle_data.txt','w')
listfile=file_open.read()
listf=re.split('[ \n\r]',listfile)
i=0
while i<len(listf)-2:
intlow=int(listf[i],16)
inthigh=int(listf[i+1],16)
i=i+2
num2=intlow+(inthigh<<8)
if (inthigh>>7)&0x01==0x01:
num2-=65536
file_write.write(str(num2));
file_write.write("\n");
#listf中的数据类型为字符串,需要转为16进制对应的数据
file_open.close()
file_write.close()
print "数据处理完成"将.py修改为可以添加参数的脚本,在cmd路径在,输入python,拖入.py文件,再拖入要处理的data.txt,会在同一路径下生成Result.txt结果文件.代码如下
#encoding=utf-8
import re
import os
import sys
file_open=open(sys.argv[1])#处理输入的文件参数
filewritepath=os.path.dirname(sys.argv[1])+"\\Result.txt"
file_write=open(filewritepath,'w')
#file_open=open('data.txt')
#file_write=open('handle_data.txt','w')
listfile=file_open.read()
listf=re.split('[ \n\r]',listfile)
i=0
while i<len(listf)-2:
intlow=int(listf[i],16)
inthigh=int(listf[i+1],16)
i=i+2
num2=intlow+(inthigh<<8)
if (inthigh>>7)&0x01==0x01:
num2-=65536
file_write.write(str(num2)+'\n');
#file_write.write("\n");
#listf中的数据类型为字符串,需要转为16进制对应的数据
file_open.close()
file_write.close()
print("Data processing is completed")
.