NIO同步阻塞与同步非阻塞
一:BIO与NIO区别:
本质就是阻塞和非阻塞的区别
阻塞概念:程序在获取网络数据时,网络延迟,会一直等待。直到传输完毕为止。
非阻塞概念:应用程序可以直接获取已经准备好的数据,无需等待。
一:BIO与NIO区别:
本质就是阻塞和非阻塞的区别
阻塞概念:程序在获取网络数据时,网络延迟,会一直等待。直到传输完毕为止。
非阻塞概念:应用程序可以直接获取已经准备好的数据,无需等待。
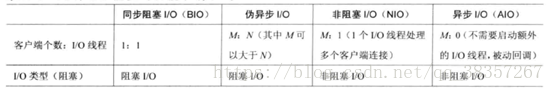
二:IO为同步阻塞形式,NIO为非同步阻塞形。
NIO:起初并没有实现异步,在jdk1.7后支持异步非阻塞。
BIO(IO):同步阻塞式IO,服务器实现模式为一个连接,一个线程。
客户发送的连接请求,都会注册到多路复用器上。
多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求时才启动一个线程处理。
AIO:异步非阻塞式IO,服务器实现模式为:一个有效请求对应一个线程。
客户端的I/O请求都是由OS先完成了再通知服务器应用启动线程处理。
NIO:起初并没有实现异步,在jdk1.7后支持异步非阻塞。
BIO(IO):同步阻塞式IO,服务器实现模式为一个连接,一个线程。
客户发送的连接请求,都会注册到多路复用器上。
多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求时才启动一个线程处理。
AIO:异步非阻塞式IO,服务器实现模式为:一个有效请求对应一个线程。
客户端的I/O请求都是由OS先完成了再通知服务器应用启动线程处理。
三:同步时,应用程序会直接参与IO读写操作,并且我们的应用程序会直接阻塞
到某一个方法上,直到数据准备就绪,或轮询策略实时监测数据的就绪状态
若为就绪状态则获取数据。
到某一个方法上,直到数据准备就绪,或轮询策略实时监测数据的就绪状态
若为就绪状态则获取数据。
四:异步时,所有IO读写操作交给操作系统,与我们的应用程序没有直接关系。
等到操作系统完成IO读写操作,会给我们应用程序发送通知,应用程序直接
拿走数据就ok。
等到操作系统完成IO读写操作,会给我们应用程序发送通知,应用程序直接
拿走数据就ok。
五:伪异步:
后端使用线程池来处理多个客户端的请求。
线程池可以灵活调配线程资源,设置线程最大数,防止高并发导致线程耗尽。
六:原理:
当有新客户端连接时,将客户端的Socket封装成一个Task(实现Runnable接口)
投递到后端线程处理。线程池可以设置消息队列大小及线程池大最大值。资源占用
可控,支持高并发。
后端使用线程池来处理多个客户端的请求。
线程池可以灵活调配线程资源,设置线程最大数,防止高并发导致线程耗尽。
六:原理:
当有新客户端连接时,将客户端的Socket封装成一个Task(实现Runnable接口)
投递到后端线程处理。线程池可以设置消息队列大小及线程池大最大值。资源占用
可控,支持高并发。
使用多线程支持多个请求:
//tcp服务器端...
class TcpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("socket tcp服务器端启动....");
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
// 等待客户端请求
try {
while (true) {
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream inputStream = accept.getInputStream();
// 转换成string类型
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(buf);
String str = new String(buf, 0, len);
System.out.println("服务器接受客户端内容:" + str);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}).start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
serverSocket.close();
}
}
}
public class TcpClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
System.out.println("socket tcp 客户端启动....");
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8080);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("我是盖世英雄".getBytes());
socket.close();
}
}
使用线程池管理线程:
package com.xuyuedu.NIO;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
//tcp服务器端...
class TcpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("socket tcp服务器端启动....");
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
// 等待客户端请求
try {
while (true) {
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream inputStream = accept.getInputStream();
// 转换成string类型
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(buf);
String str = new String(buf, 0, len);
System.out.println("服务器接受客户端内容:" + str);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}).start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
serverSocket.close();
}
}
}
public class TcpClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
System.out.println("socket tcp 客户端启动....");
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8080);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("我是你的盖世英雄".getBytes());
socket.close();
}
}
socket tcp服务器端启动....
服务器接受客户端内容:我是你的盖世英雄IO模型关系:
NIO非阻塞代码:
package com.xuyuedu.NIO;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
//nio 异步非阻塞
class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("客户端已经启动....");
// 1.创建网络通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080));
// 2.切换为异步非阻塞
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 3.指定缓冲区大小
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scanner= new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
String str=scanner.next();
byteBuffer.put((new Date().toString()+"\n"+str).getBytes());
// 4.切换读取模式
byteBuffer.flip();
sChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
//5.关闭通道
sChannel.close();
}
}
// nio
class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务器端已经启动....");
// 1.创建服务器端通道
ServerSocketChannel sChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 2.切换异步非阻塞
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 3.绑定连接
sChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 4.获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 5.将通道注册到选择器 "并且指定监听接受事件"
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 6. 轮训式获取选择 "已经准备就绪"的事件
while (selector.select() > 0) {
// 7.获取当前选择器所有注册的"选择键(已经就绪的监听事件)"
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
// 8.获取准备就绪的事件
SelectionKey sk = it.next();
// 9.判断事件准备就绪
if (sk.isAcceptable()) {
// 10.若"接受就绪",获取客户端连接
SocketChannel socketChannel = sChannel.accept();
// 11.设置阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 12.将该通道注册到服务器上
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (sk.isReadable()) {
// 13.获取当前选择器"就绪" 状态的通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel();
// 14.读取数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = 0;
while ((len = socketChannel.read(buf)) > 0) {
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
buf.clear();
}
}
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
选择KEY :
1、SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT
2、SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT
3、SelectionKey.OP_READ
4、SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
Netty:
解决传统NIO非阻塞代码BUG,进行封装,事件驱动。
netty框架是一个通讯框架,NIO框架也是一个通讯框架。
netty底层对NIO进行封装。
Netty特征:
1.是一个异步通讯框架.(底层创建线程)。
2.异步非阻塞
3.高可用
4.事件驱动。
netty应用场景:
1.分布式开源框架中dubbo,Zookeeper,RocketMQ底层rpc通讯使用netty框架。
netty底层NIO。
2.游戏开发中,服务器端底层使用netty通讯。
解决传统NIO非阻塞代码BUG,进行封装,事件驱动。
netty框架是一个通讯框架,NIO框架也是一个通讯框架。
netty底层对NIO进行封装。
Netty特征:
1.是一个异步通讯框架.(底层创建线程)。
2.异步非阻塞
3.高可用
4.事件驱动。
netty应用场景:
1.分布式开源框架中dubbo,Zookeeper,RocketMQ底层rpc通讯使用netty框架。
netty底层NIO。
2.游戏开发中,服务器端底层使用netty通讯。
为什么选择netty?
解决NIO代码复杂问题,容错机制。
解决NIO代码复杂问题,容错机制。
Netty服务器端:
package com.xuyuedu.netty;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.Channels;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import org.jboss.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelPipelineFactory;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelStateEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ExceptionEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.MessageEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.SimpleChannelHandler;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannelFactory;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
class ServerHanlder extends SimpleChannelHandler {
// 通道被关闭的时候会触发
@Override
public void channelClosed(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelStateEvent e) throws Exception {
super.channelClosed(ctx, e);
System.out.println("channelClosed");
}
// 必须要建立连接,关闭通道的时候才会触发
@Override
public void channelDisconnected(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelStateEvent e) throws Exception {
super.channelDisconnected(ctx, e);
System.out.println("channelDisconnected");
}
// 接受出现异常
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ExceptionEvent e) throws Exception {
super.exceptionCaught(ctx, e);
System.out.println("exceptionCaught");
}
// 接受客户端数据..
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
super.messageReceived(ctx, e);
System.out.println("messageReceived");
System.out.println("服务器获取客户端发来的参数:" + e.getMessage());
ctx.getChannel().write("你好啊!");
}
}
// netty 服务器端
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.创建服务对象
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
// 2.创建两个线程池 第一个 监听端口号 nio监听
ExecutorService boos = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ExecutorService wook = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 3.将线程池放入工程
serverBootstrap.setFactory(new NioServerSocketChannelFactory(boos, wook));
// 4.设置管道工程
serverBootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
// 设置管道
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = org.jboss.netty.channel.Channels.pipeline();
// 传输数据的时候直接为string类型
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
// 设置事件监听类
pipeline.addLast("serverHanlder", new ServerHanlder());
return pipeline;
}
});
// 绑定端口号
serverBootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
System.out.println("服务器端已经被启动.....");
// while (true) {
// try {
// Thread.sleep(500);
// } catch (Exception e) {
// // TODO: handle exception
// }
// System.out.println("每隔0.五秒打印.....");
//
// }
}
}
Netty客户端:
package com.xuyuedu.netty;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import org.jboss.netty.bootstrap.ClientBootstrap;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelPipelineFactory;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelStateEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ExceptionEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.MessageEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.SimpleChannelHandler;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioClientSocketChannelFactory;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
class ClientHanlder extends SimpleChannelHandler{
// 通道被关闭的时候会触发
@Override
public void channelClosed(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelStateEvent e) throws Exception {
super.channelClosed(ctx, e);
System.out.println("channelClosed");
}
// 必须要建立连接,关闭通道的时候才会触发
@Override
public void channelDisconnected(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelStateEvent e) throws Exception {
super.channelDisconnected(ctx, e);
System.out.println("channelDisconnected");
}
// 接受出现异常
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ExceptionEvent e) throws Exception {
super.exceptionCaught(ctx, e);
System.out.println("exceptionCaught");
}
// 接受客户端数据..
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
super.messageReceived(ctx, e);
System.out.println("messageReceived");
System.out.println("服务器向客户端回复的内容:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
//netty客户端
public class NettyClinet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.创建服务对象
ClientBootstrap clientBootstrap = new ClientBootstrap();
// 2.创建两个线程池 第一个 监听端口号 nio监听
ExecutorService boos = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ExecutorService wook = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 3.将线程池放入工程
clientBootstrap.setFactory(new NioClientSocketChannelFactory(boos, wook));
// 4.设置管道工程
clientBootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
// 设置管道
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = org.jboss.netty.channel.Channels.pipeline();
// 传输数据的时候直接为string类型
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
// 设置事件监听类
pipeline.addLast("clientHanlder", new ClientHanlder());
return pipeline;
}
});
// 绑定端口号
ChannelFuture connect = clientBootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080));
Channel channel = connect.getChannel();
System.out.println("client start");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入内容:");
channel.write(scanner.next());
}
}
}
Maven坐标:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0.Final</version>
</dependency>测试结果:
client start
请输入内容:
你是我的盖世英雄
请输入内容:
messageReceived
服务器向客户端回复的内容:你好啊!服务器端已经被启动.....
messageReceived
服务器获取客户端发来的参数:你是我的盖世英雄
补充:直缓冲区与非直接缓冲区的区别:
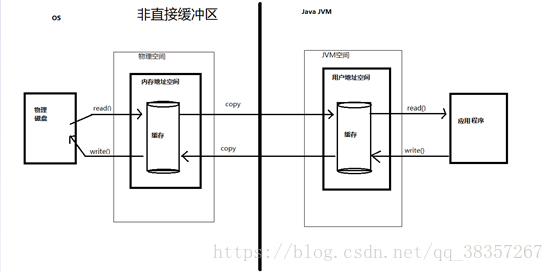
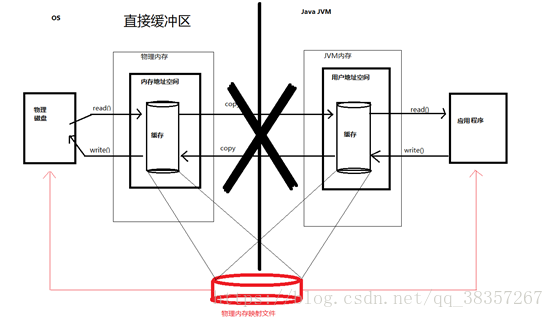
非直接缓冲区:通过 allocate() 方法分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在 JVM 的内存中。
直接缓冲区:通过 allocateDirect() 方法分配直接缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在物理内存中。可以提高效率。
直接缓冲区与非直接缓冲耗时计算:
package com.xuyuedu.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel.MapMode;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
import org.junit.Test;
public class Test003 {
@Test
//直接缓冲区
public void test002() throws Exception {
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
//创建管道
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("F:\\第八节(多线程运行状态).mp4"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("F:\\第1节(多线程运行状态).mp4"),StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
MappedByteBuffer inMap = inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY,0, inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMap = outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size());
//直接对缓冲区操作
byte[] dsf=new byte [inMap.limit()];
inMap.get(dsf);
outMap.put(dsf);
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("直接操作直接缓冲区耗时时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"ms");
}
@Test
//非直接缓冲区
public void test001() throws Exception{
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
//读入流
FileInputStream fst = new FileInputStream("F:\\第八节(多线程运行状态).mp4");
//写入流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("F:\\第1节(多线程运行状态).mp4");
//创建读入流通道
FileChannel inChannel = fst.getChannel();
//创建写入流通道
FileChannel outChannel = fos.getChannel();
//分配指定大小缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(inChannel.read(buffer)!=-1) {
//开启读取模式
buffer.flip();
//将数据写入到通道中
outChannel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
}
//关闭通道,关闭连接
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
fos.close();
fst.close();
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("非直接操作直接缓冲区耗时时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"ms");
}
}
测试结果:
非直接操作直接缓冲区耗时时间:3554ms
直接操作直接缓冲区耗时时间:289ms分散读取与聚集写入:
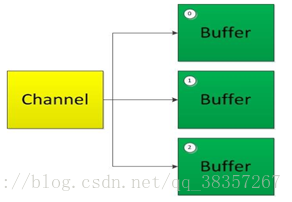
分散读取(scattering Reads):将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区中
聚集写入(gathering Writes):将多个缓冲区的数据聚集到通道中
测试代码:
package com.xuyuedu.nio;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* 分散读取,聚集写入
分散读取:将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区。
聚集写入:将多个缓冲区的数据聚集到通道中。
* @author DELL
*
*/
public class Test004 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//随机访问
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("test.txt", "rw");
//获取NIO通道
FileChannel channel = raf.getChannel();
//分配指定大小缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//分散读取
ByteBuffer[]buffers= {buffer1,buffer2};
channel.read(buffers);
for(ByteBuffer byteBuffer:buffers) {
//切换成读模式
byteBuffer.flip();
}
System.out.println(new String(buffers[0].array(),0,buffers[0].limit()));
System.out.println("*****************");
System.out.println(new String(buffers[1].array(),1,buffers[1].limit()));
System.out.println("-----聚集读取-----");
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile=new RandomAccessFile("test2.txt", "rw");
//获取通道
FileChannel channel2 = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
channel2.write(buffers);
//关闭
randomAccessFile.close();
raf.close();
}
}
测试结果:
sdcdcdc地方v发v发v发v方法发v发v发反盗版的
太皇太后你跟隔壁隔壁
提高人�
*****************
�放过他吧