LLMs之Efficient-LLMs-Survey:Efficient-LLMs-Survey(高效大型语言模型综述)的简介、代表性算法论文及其代码之详细攻略
目录
LLMs:《Efficient Large Language Models: A Survey》翻译与解读
LLMs之Efficient-LLMs-Survey:Efficient-LLMs-Survey(高效大型语言模型综述)的简介、代表性算法论文及其代码之详细攻略
Efficient-LLMs-Survey(高效大型语言模型综述)的简介
Weight-Activation Co-Quantization
1.2.1、Mixed Precision Acceleration
1.2.3、Initialization Techniques
1.3.1、Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning
1.3.2、Memory Efficient Fine-Tuning
1.5.4、Transformer Alternative Architecture
三、System-Level Efficiency Optimization and LLM Frameworks
3.1、System-Level Efficiency Optimization
3.1.1、System-Level Pre-Training Efficiency Optimization
3.1.2、System-Level Inference Efficiency Optimization
3.1.3、System-Level Serving Efficiency Optimization
3.1.4、System-Level Efficient Architecture Optimization
相关文章
LLMs:《Efficient Large Language Models: A Survey》翻译与解读
https://yunyaniu.blog.csdn.net/article/details/135375631
LLMs之Efficient-LLMs-Survey:Efficient-LLMs-Survey(高效大型语言模型综述)的简介、代表性算法论文及其代码之详细攻略
https://yunyaniu.blog.csdn.net/article/details/135375804
Efficient-LLMs-Survey(高效大型语言模型综述)的简介
大语言模型(LLMs)在许多重要任务中展示了卓越的能力,并有潜力对我们的社会产生重大影响。然而,这种能力伴随着相当大的资源需求,突显了对开发有效技术来解决LLMs引发的效率挑战的强烈需求。在这份综述中,我们对高效LLMs研究进行了系统而全面的回顾。我们将文献分为三个主要类别,分别从模型中心、数据中心和框架中心的角度涵盖了不同但相互关联的高效LLMs主题。我们希望我们的综述和这个GitHub存储库能够作为有价值的资源,帮助研究人员和实践者系统地了解高效LLMs研究的发展,并激发他们为这一重要且令人兴奋的领域做出贡献。
我们将积极维护这个存储库,并通过引入新的研究来更新这份综述。
GitHub地址:GitHub - AIoT-MLSys-Lab/Efficient-LLMs-Survey: Efficient Large Language Models: A Survey
1、为什么需要高效LLMs?
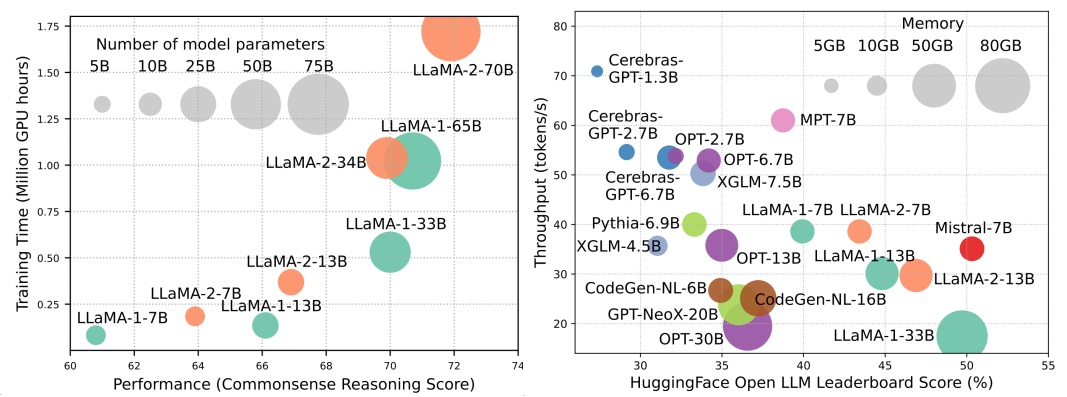
尽管LLMs引领着下一波人工智能革命,但LLMs卓越的能力是以巨大的资源需求为代价的。图1(左)以LLaMA系列为例,展示了模型性能与模型训练时间之间的关系,以GPU小时为单位,其中每个圆圈的大小与模型参数的数量成比例。如图所示,尽管较大的模型能够取得更好的性能,但用于训练它们的GPU小时随着模型规模的增加呈指数增长。除了训练之外,推断也对LLMs的操作成本产生了相当大的影响。图2(右)描述了模型性能与推断吞吐量之间的关系。类似地,增加模型大小可以实现更好的性能,但以降低推断吞吐量(更高的推断延迟)为代价,这对这些模型在以经济有效的方式扩展其覆盖范围到更广泛的客户群和各种应用中提出了挑战。LLMs的高资源需求强调了开发技术以提高LLMs效率的强烈需求。如图2所示,与LLaMA-1-33B相比,使用分组查询注意力和滑动窗口注意力来加速推断的Mistral-7B在性能上达到了可比较的水平,并且具有更高的吞吐量。这种优越性突显了为LLMs设计效率技术的可行性和重要性。
未完待续,更新中……
一、Model-Centric Methods
1.1、Model Compression
1.1.1、Quantization
Weight-Only Quantization
- GPTQ: Accurate Quantization for Generative Pre-trained Transformers, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- QuIP: 2-Bit Quantization of Large Language Models With Guarantees, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- AWQ: Activation-aware Weight Quantization for LLM Compression and Acceleration, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- OWQ: Lessons Learned from Activation Outliers for Weight Quantization in Large Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- SpQR: A Sparse-Quantized Representation for Near-Lossless LLM Weight Compression, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- FineQuant: Unlocking Efficiency with Fine-Grained Weight-Only Quantization for LLMs, NeurIPS-ENLSP, 2023 [Paper]
- LLM.int8(): 8-bit Matrix Multiplication for Transformers at Scale, NeurlPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Optimal Brain Compression: A Framework for Accurate Post-Training Quantization and Pruning, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
Weight-Activation Co-Quantization
- Intriguing Properties of Quantization at Scale, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper]
- ZeroQuant-V2: Exploring Post-training Quantization in LLMs from Comprehensive Study to Low Rank Compensation, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- ZeroQuant-FP: A Leap Forward in LLMs Post-Training W4A8 Quantization Using Floating-Point Formats, NeurIPS-ENLSP, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- OliVe: Accelerating Large Language Models via Hardware-friendly Outlier-Victim Pair Quantization, ISCA, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- RPTQ: Reorder-based Post-training Quantization for Large Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Outlier Suppression+: Accurate Quantization of Large Language Models by Equivalent and Optimal Shifting and Scaling, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- QLLM: Accurate and Efficient Low-Bitwidth Quantization for Large Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
- SmoothQuant: Accurate and Efficient Post-Training Quantization for Large Language Models, ICML, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- ZeroQuant: Efficient and Affordable Post-Training Quantization for Large-Scale Transformers, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper]
Quantization-Aware Training
- BitNet: Scaling 1-bit Transformers for Large Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
- LLM-QAT: Data-Free Quantization Aware Training for Large Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Compression of Generative Pre-trained Language Models via Quantization, ACL, 2022 [Paper]
1.1.2、Parameter Pruning
Structured Pruning
- LoRAShear: Efficient Large Language Model Structured Pruning and Knowledge Recovery, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
- LLM-Pruner: On the Structural Pruning of Large Language Models, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Sheared LLaMA: Accelerating Language Model Pre-training via Structured Pruning, NeurIPS-ENLSP, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- LoRAPrune: Pruning Meets Low-Rank Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
Unstructured Pruning
- SparseGPT: Massive Language Models Can Be Accurately Pruned in One-Shot, ICML, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- A Simple and Effective Pruning Approach for Large Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- One-Shot Sensitivity-Aware Mixed Sparsity Pruning for Large Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
1.1.3、Low-Rank Approximation
- TensorGPT: Efficient Compression of the Embedding Layer in LLMs based on the Tensor-Train Decomposition, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
- LoSparse: Structured Compression of Large Language Models based on Low-Rank and Sparse Approximation, ICML, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
1.1.4、Knowledge Distillation
White-Box KD
- Towards the Law of Capacity Gap in Distilling Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Baby Llama: Knowledge Distillation from an Ensemble of Teachers Trained on a Small Dataset with no Performance Penalty, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Knowledge Distillation of Large Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- GKD: Generalized Knowledge Distillation for Auto-regressive Sequence Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Propagating Knowledge Updates to LMs Through Distillation, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Less is More: Task-aware Layer-wise Distillation for Language Model Compression, ICML, 2023 [Paper]
- Token-Scaled Logit Distillation for Ternary Weight Generative Language Models, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
Black-Box KD
- Zephyr: Direct Distillation of LM Alignment, arXiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Instruction Tuning with GPT-4, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Lion: Adversarial Distillation of Closed-Source Large Language Model, arXiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Specializing Smaller Language Models towards Multi-Step Reasoning, ICML, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Distilling Step-by-Step! Outperforming Larger Language Models with Less Training Data and Smaller Model Sizes, ACL, 2023 [Paper]
- Large Language Models Are Reasoning Teachers, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- SCOTT: Self-Consistent Chain-of-Thought Distillation, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Symbolic Chain-of-Thought Distillation: Small Models Can Also "Think" Step-by-Step, ACL, 2023 [Paper]
- Distilling Reasoning Capabilities into Smaller Language Models, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- In-context Learning Distillation: Transferring Few-shot Learning Ability of Pre-trained Language Models, arXiv, 2022 [Paper]
- Explanations from Large Language Models Make Small Reasoners Better, arXiv, 2022 [Paper]
- DISCO: Distilling Counterfactuals with Large Language Models, arXiv, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
1.2、Efficient Pre-Training
1.2.1、Mixed Precision Acceleration
1.2.2、Scaling Models
1.2.3、Initialization Techniques
1.2.4、Optimization Strategies
1.3、Efficient Fine-Tuning
1.3.1、Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning
Adapter-based Tuning
Low-Rank Adaptation
Prefix Tuning
Prompt Tuning
1.3.2、Memory Efficient Fine-Tuning
1.4、Efficient Inference
1.4.1、Speculative Decoding
1.4.2、KV-Cache Optimization
1.5、Efficient Architecture
1.5.1、Efficient Attention
Sharing-based Attention
Feature Information Reduction
Kernelization or Low-Rank
Fixed Pattern Strategies
Learnable Pattern Strategies
1.5.2、Mixture of Experts
MoE-based LLMs
Algorithm-Level MoE Optimization
1.5.3、Long Context LLMs
Extrapolation and Interpolation
Recurrent Structure
Segmentation and Sliding Window
Memory-Retrieval Augmentation
1.5.4、Transformer Alternative Architecture
State Space Models
Other Sequential Models
二、Data-Centric Methods
2.1、Data Selection
Data Selection for Efficient Pre-Training
Data Selection for Efficient Fine-Tuning
2.2、Prompt Engineering
2.2.1、Few-Shot Prompting
Demonstration Organization
Demonstration Selection
Demonstration Ordering
Template Formatting
Instruction Generation
Multi-Step Reasoning
Parallel Generation
2.2.2、Prompt Compression
2.2.3、Prompt Generation
三、System-Level Efficiency Optimization and LLM Frameworks
3.1、System-Level Efficiency Optimization
3.1.1、System-Level Pre-Training Efficiency Optimization
3.1.2、System-Level Inference Efficiency Optimization
3.1.3、System-Level Serving Efficiency Optimization
3.1.4、System-Level Efficient Architecture Optimization
System-Level Attention Optimization
System-Level MoE Optimization
3.2、LLM Frameworks
| Efficient Training | Efficient Inference | Efficient Fine-Tuning | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSpeed [Code] | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Megatron [Code] | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Alpa [Code] | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| ColossalAI [Code] | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| FairScale [Code] | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Pax [Code] | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Composer [Code] | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| vLLM [Code] | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| OpenLLM [Code] | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Ray-LLM [Code] | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| MLC-LLM [Code] | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Sax [Code] | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Mosec [Code] | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| LLM-Foundry [Code] | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |