1、首先我在Mysql中准备了一条数据
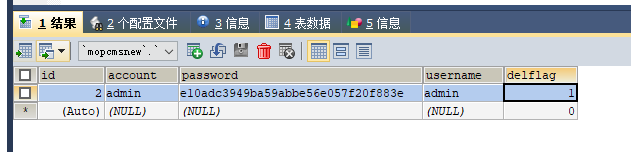
2、简单粗暴的开始测试了
1、我们的目的是需要把delflag修改为0 简单的准备一下sql
<update id="test">
UPDATE tbl_users set delflag='0' where account='admin'
</update>
2、我们先来测试一下@Transactional 代码如下 大家都知道2/0必会抛出异常
@Override
@Transactional
public Ret test(){
int i = articleMapper.test();
int a = 2/0;
if(i > 0){
ResultUtil.success();
}
return ResultUtil.error();
}
3、执行测试 i=1说明更新成功 别着急咱们继续断点往下面走
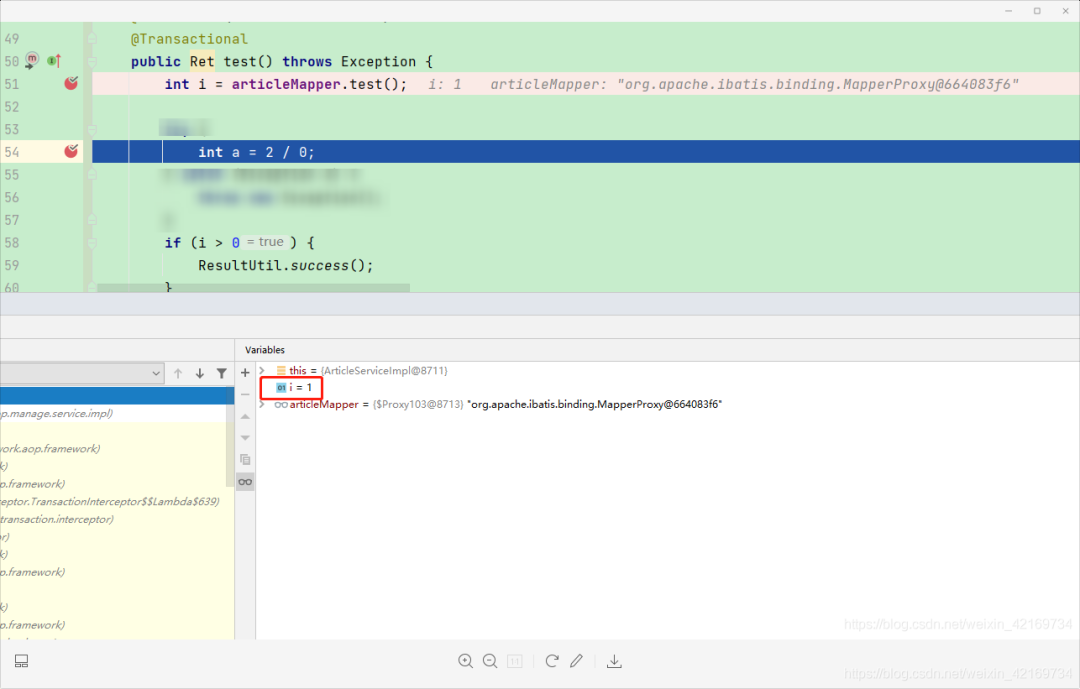 4、果然不出所料 执行到第54行的时候报错了 出现了
4、果然不出所料 执行到第54行的时候报错了 出现了java.lang.ArithmeticException: /by zero
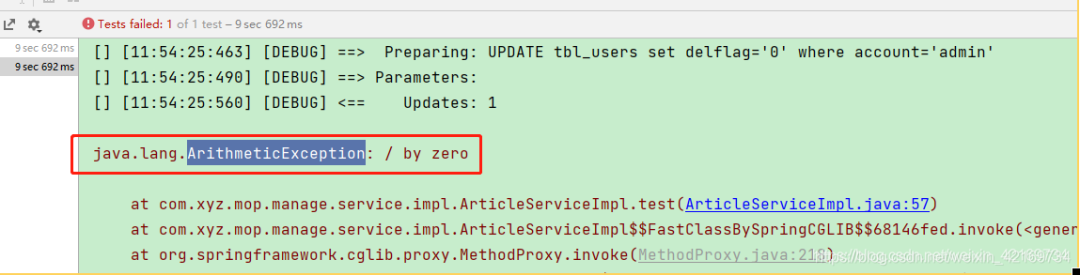 5、细心的同学会发现
5、细心的同学会发现ArithmeticException这个异常类是继承了RuntimeException的
而@Transactional默认回滚的的异常就是RuntimeException
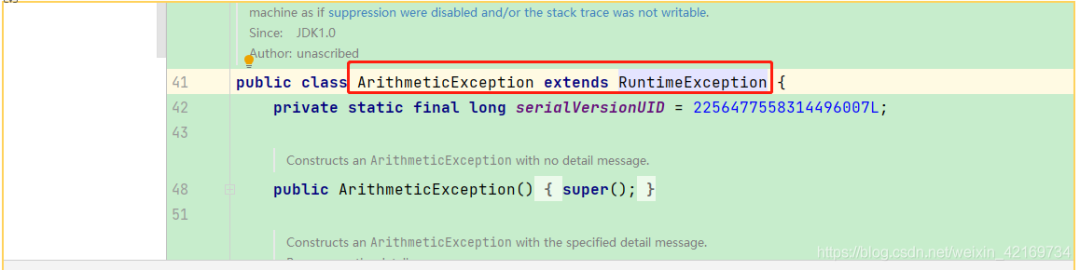 6、我们在点进去
6、我们在点进去RuntimeException这个类里面一探究竟 我们发现RuntimeException又是继承Exception的
而所有的异常类基本都是继承RuntimeException包括刚才上面的java.lang.ArithmeticException异常
所以只要是RuntimeException和RuntimeException下面的子类抛出的异常 @Transactional都可以回滚的
 7、这个时候我们去看一下数据库的值到底有没有修改成功 很显然数据是被回滚了 并没有修改成0
7、这个时候我们去看一下数据库的值到底有没有修改成功 很显然数据是被回滚了 并没有修改成0
1、下面我们在试试@Transactional不能过滚的异常 代码如下
我们直接先用try catch来捕获异常 然后在catch里面自定义抛出Exception异常
@Override
@Transactional
public Ret test() throws Exception {
int i = articleMapper.test();
try {
int a = 2 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception();
}
if (i > 0) {
ResultUtil.success();
}
return ResultUtil.error();
}
2、ok直接 抛出的异常是我们指定的java.lang.Exception异常 我们去看看数据库

3、数据库被更新成0了 说明@Transactional并不能回滚Exception异常
总结一下
@Transactional只能回滚RuntimeException和RuntimeException下面的子类抛出的异常 不能回滚Exception异常
如果需要支持回滚Exception异常请用@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
这里如果是增删改的时候我建议大家都使用@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
Transactional失效场景介绍
第一种 Transactional注解标注方法修饰符为非public时,@Transactional注解将会不起作用。例如以下代码。
定义一个错误的@Transactional标注实现,修饰一个默认访问符的方法
@Component
public class TestServiceImpl {
@Resource
TestMapper testMapper;
@Transactional
void insertTestWrongModifier() {
int re = testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));
if (re > 0) {
throw new NeedToInterceptException("need intercept");
}
testMapper.insert(new Test(210,20,30));
}
}
在同一个包内,新建调用对象,进行访问。
@Component
public class InvokcationService {
@Resource
private TestServiceImpl testService;
public void invokeInsertTestWrongModifier(){
//调用@Transactional标注的默认访问符方法
testService.insertTestWrongModifier();
}
}
测试用例
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Resource
InvokcationService invokcationService;
@Test
public void testInvoke(){
invokcationService.invokeInsertTestWrongModifier();
}
}
以上的访问方式,导致事务没开启,因此在方法抛出异常时,testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));操作不会进行回滚。如果TestServiceImpl#insertTestWrongModifier方法改为public的话将会正常开启事务,testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));将会进行回滚。
第二种
在类内部调用调用类内部@Transactional标注的方法。这种情况下也会导致事务不开启。示例代码如下。
设置一个内部调用
@Component
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Resource
TestMapper testMapper;
@Transactional
public void insertTestInnerInvoke() {
//正常public修饰符的事务方法
int re = testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));
if (re > 0) {
throw new NeedToInterceptException("need intercept");
}
testMapper.insert(new Test(210,20,30));
}
public void testInnerInvoke(){
//类内部调用@Transactional标注的方法。
insertTestInnerInvoke();
}
}
测试用例。
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Resource
TestServiceImpl testService;
/**
* 测试内部调用@Transactional标注方法
*/
@Test
public void testInnerInvoke(){
//测试外部调用事务方法是否正常
//testService.insertTestInnerInvoke();
//测试内部调用事务方法是否正常
testService.testInnerInvoke();
}
}
上面就是使用的测试代码,运行测试知道,外部调用事务方法能够征程开启事务,testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30))操作将会被回滚;
然后运行另外一个测试用例,调用一个方法在类内部调用内部被@Transactional标注的事务方法,运行结果是事务不会正常开启,testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30))操作将会保存到数据库不会进行回滚。
第三种
事务方法内部捕捉了异常,没有抛出新的异常,导致事务操作不会进行回滚。示例代码如下。
@Component
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Resource
TestMapper testMapper;
@Transactional
public void insertTestCatchException() {
try {
int re = testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));
if (re > 0) {
//运行期间抛异常
throw new NeedToInterceptException("need intercept");
}
testMapper.insert(new Test(210,20,30));
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("i catch exception");
}
}
}
测试用例代码如下。
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Resource
TestServiceImpl testService;
@Test
public void testCatchException(){
testService.insertTestCatchException();
}
}
运行测试用例发现,虽然抛出异常,但是异常被捕捉了,没有抛出到方法 外, testMapper.insert(new Test(210,20,30))操作并没有回滚。
以上三种就是@Transactional注解不起作用,@Transactional注解失效的主要原因。下面结合spring中对于@Transactional的注解实现源码分析为何导致@Transactional注解不起作用。
@Transactional注解不起作用原理分析
第一种
@Transactional注解标注方法修饰符为非public时,@Transactional注解将会不起作用。这里分析 的原因是,@Transactional是基于动态代理实现的,@Transactional注解实现原理中分析了实现方法,在bean初始化过程中,对含有@Transactional标注的bean实例创建代理对象,这里就存在一个spring扫描@Transactional注解信息的过程,不幸的是源码中体现,标注@Transactional的方法如果修饰符不是public,那么就默认方法的@Transactional信息为空,那么将不会对bean进行代理对象创建或者不会对方法进行代理调用
@Transactional注解实现原理中,介绍了如何判定一个bean是否创建代理对象,大概逻辑是。根据spring创建好一个aop切点BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例,遍历当前bean的class的方法对象,判断方法上面的注解信息是否包含@Transactional,如果bean任何一个方法包含@Transactional注解信息,那么就是适配这个BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor切点。则需要创建代理对象,然后代理逻辑为我们管理事务开闭逻辑。
spring源码中,在拦截bean的创建过程,寻找bean适配的切点时,运用到下面的方法,目的就是寻找方法上面的@Transactional信息,如果有,就表示切点BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor能够应用(canApply)到bean中,
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
//遍历class的方法对象
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
classes.add(targetClass);
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null &&
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) ||
//适配查询方法上的@Transactional注解信息
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
我们可以在上面的方法打断点,一步一步调试跟踪代码,最终上面的代码还会调用如下方法来判断。在下面的方法上断点,回头看看方法调用堆栈也是不错的方式跟踪。
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#getTransactionAttribute
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#computeTransactionAttribute
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
// Don't allow no-public methods as required.
//非public 方法,返回@Transactional信息一律是null
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
//后面省略.......
}
不创建代理对象
所以,如果所有方法上的修饰符都是非public的时候,那么将不会创建代理对象。以一开始的测试代码为例,如果正常的修饰符的testService是下面图片中的,经过cglib创建的代理对象。
如果class中的方法都是非public的那么将不是代理对象。
不进行代理调用
考虑一种情况,如下面代码所示。两个方法都被@Transactional注解标注,但是一个有public修饰符一个没有,那么这种情况我们可以预见的话,一定会创建代理对象,因为至少有一个public修饰符的@Transactional注解标注方法。
创建了代理对象,insertTestWrongModifier就会开启事务吗?答案是不会。
@Component
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Resource
TestMapper testMapper;
@Override
@Transactional
public void insertTest() {
int re = testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));
if (re > 0) {
throw new NeedToInterceptException("need intercept");
}
testMapper.insert(new Test(210,20,30));
}
@Transactional
void insertTestWrongModifier() {
int re = testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));
if (re > 0) {
throw new NeedToInterceptException("need intercept");
}
testMapper.insert(new Test(210,20,30));
}
}
原因是在动态代理对象进行代理逻辑调用时,在cglib创建的代理对象的拦截函数中CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept,有一个逻辑如下,目的是获取当前被代理对象的当前需要执行的method适配的aop逻辑。
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
而针对@Transactional注解查找aop逻辑过程,相似地,也是执行一次
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#getTransactionAttribute
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#computeTransactionAttribute
也就是说还需要找一个方法上的@Transactional注解信息,没有的话就不执行代理@Transactional对应的代理逻辑,直接执行方法。没有了@Transactional注解代理逻辑,就无法开启事务,这也是上一篇已经讲到的。
第二种
在类内部调用调用类内部@Transactional标注的方法。这种情况下也会导致事务不开启。
经过对第一种的详细分析,对这种情况为何不开启事务管理,原因应该也能猜到;
既然事务管理是基于动态代理对象的代理逻辑实现的,那么如果在类内部调用类内部的事务方法,这个调用事务方法的过程并不是通过代理对象来调用的,而是直接通过this对象来调用方法,绕过的代理对象,肯定就是没有代理逻辑了。
其实我们可以这样玩,内部调用也能实现开启事务,代码如下。
@Component
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Resource
TestMapper testMapper;
@Resource
TestServiceImpl testServiceImpl;
@Transactional
public void insertTestInnerInvoke() {
int re = testMapper.insert(new Test(10,20,30));
if (re > 0) {
throw new NeedToInterceptException("need intercept");
}
testMapper.insert(new Test(210,20,30));
}
public void testInnerInvoke(){
//内部调用事务方法
testServiceImpl.insertTestInnerInvoke();
}
}
上面就是使用了代理对象进行事务调用,所以能够开启事务管理,但是实际操作中,没人会闲的蛋疼这样子玩~
第三种
事务方法内部捕捉了异常,没有抛出新的异常,导致事务操作不会进行回滚。
这种的话,可能我们比较常见,问题就出在代理逻辑中,我们先看看源码里卖弄动态代理逻辑是如何为我们管理事务的。
TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction
代码如下。
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation)
throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
//开启事务
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
//反射调用业务方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
//异常时,在catch逻辑中回滚事务
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
//提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
//....................
}
}
所以看了上面的代码就一目了然了,事务想要回滚,必须能够在这里捕捉到异常才行,如果异常中途被捕捉掉,那么事务将不会回滚。
总结了以上几种情况。