C++ 基础入门 之 程序流程结构-选择结构if三目switch/循环结构while/dowhile/for/跳转结构break/continue/goto
目录
一、简单介绍
C++ 开发的一些知识整理,方便后期遇到类似的问题,能够及时查阅使用。
本节介绍,程序流程结构,C/C++支持最基本的三种程序运行结构:顺序结构、选择结构、循环结构,包括 选择结构if三目switch/循环结构while/dowhile/for/跳转结构break/continue/goto 以及注意事项。如果有不足之处,欢迎指出,或者你有更好的方法,欢迎留言。
* 顺序结构:程序按顺序执行,不发生跳转
* 选择结构:依据条件是否满足,有选择的执行相应功能
* 循环结构:依据条件是否满足,循环多次执行某段代码
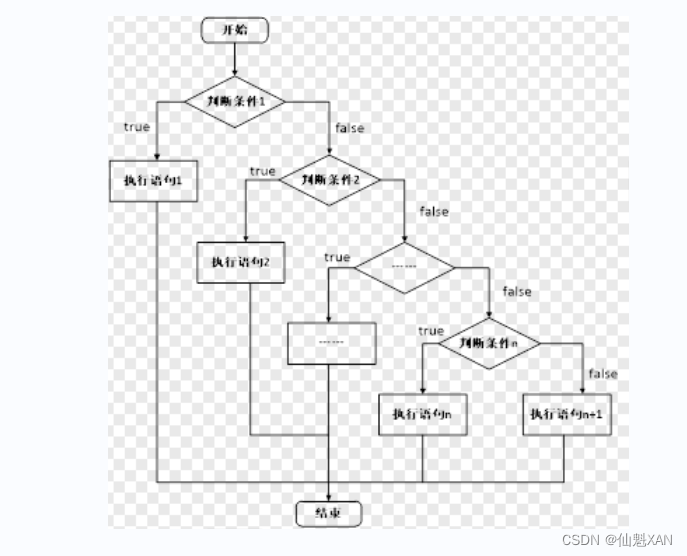
二、选择结构
1、 if 语句
作用:执行满足条件的语句
if 语句的三种形式
- 单行格式if语句
- 多行格式if语句
- 多条件的if语句
1)单行格式 if 语句:`if(条件){ 条件满足执行的语句 }`

代码:
提示:if条件表达式后不用加分号
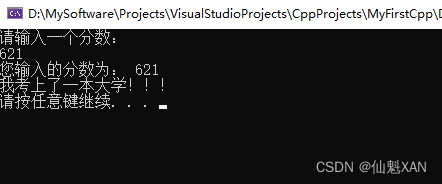
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//选择结构-单行if语句
//输入一个分数,如果分数大于589分,视为考上一本大学,并在屏幕上打印
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入一个分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您输入的分数为: " << score << endl;
//if语句
//注意事项,在if判断语句后面,不要加分号
if (score > 589)
{
cout << "我考上了一本大学!!!" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 
2) 多行格式if语句:`if(条件){ 条件满足执行的语句 }else{ 条件不满足执行的语句 };`

代码:
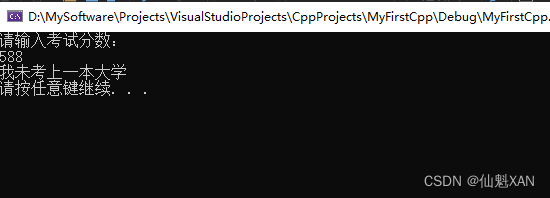
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入考试分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
if (score > 589)
{
cout << "我考上了一本大学" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "我未考上一本大学" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3)多条件的if语句:`if(条件1){ 条件1满足执行的语句 }else if(条件2){条件2满足执行的语句}... else{ 都不满足执行的语句}`
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入考试分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
if (score > 589)
{
cout << "我考上了一本大学" << endl;
}
else if (score > 498)
{
cout << "我考上了二本大学" << endl;
}
else if (score > 211)
{
cout << "我考上了三本大学" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "我未考上本科" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4)嵌套if语句:在if语句中,可以嵌套使用if语句,达到更精确的条件判断
代码案例:
- 提示用户输入一个高考考试分数,根据分数做如下判断
- 分数如果大于600分视为考上一本,大于500分考上二本,大于400考上三本,其余视为未考上本科;
- 在一本分数中,如果大于700分,考入北大,大于650分,考入清华,大于600考入人大。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入考试分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
if (score > 600)
{
cout << "我考上了一本大学" << endl;
if (score > 700)
{
cout << "我考上了北大" << endl;
}
else if (score > 650)
{
cout << "我考上了清华" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "我考上了人大" << endl;
}
}
else if (score > 500)
{
cout << "我考上了二本大学" << endl;
}
else if (score > 400)
{
cout << "我考上了三本大学" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "我未考上本科" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、三目运算符 xx ? xx : xx;
作用: 通过三目运算符实现简单的判断
语法:`表达式1 ? 表达式2 :表达式3`
说明:
- 如果表达式1的值为真,执行表达式2,并返回表达式2的结果;
- 如果表达式1的值为假,执行表达式3,并返回表达式3的结果。
- 和 if 语句比较,三目运算符优点是短小整洁,缺点是如果用嵌套,结构不清晰
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 0;
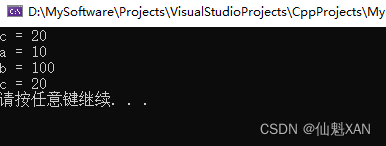
c = a > b ? a : b;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
//C++中三目运算符返回的是变量,可以继续赋值
(a > b ? a : b) = 100;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3、switch 语句
作用:执行多条件分支语句
形式:
switch(表达式)
{
case 结果1:执行语句;break;
case 结果2:执行语句;break;
...
default:执行语句;break;
}说明:
- switch语句中表达式类型只能是整型或者字符型
- case里如果没有break,那么程序会一直向下执行
- 与if语句比,对于多条件判断时,switch的结构清晰,执行效率高,缺点是switch不可以判断区间
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
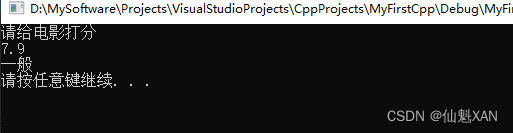
//请给电影评分
//10 ~ 9 经典
// 8 ~ 7 非常好
// 6 ~ 5 一般
// 5分以下 烂片
int score = 0;
cout << "请给电影打分" << endl;
cin >> score;
switch (score)
{
case 10:
case 9:
cout << "经典" << endl;
break;
case 8:
cout << "非常好" << endl;
break;
case 7:
case 6:
cout << "一般" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "烂片" << endl;
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
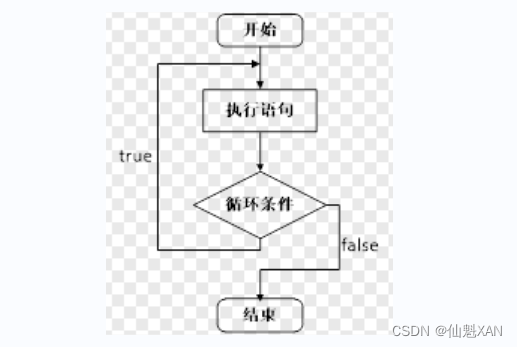
三、循环结构
1、while 循环语句
作用:满足循环条件,执行循环语句
形式:` while(循环条件){ 循环语句 }`
说明:
- 只要循环条件的结果为真,就执行循环语句
- 在执行循环语句时候,程序必须提供跳出循环的出口,否则出现死循环

代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
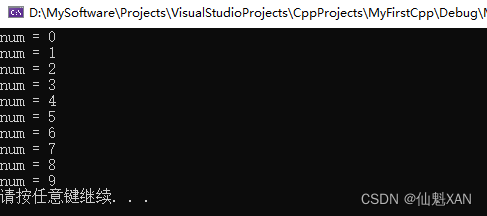
int num = 0;
while (num < 10)
{
cout << "num = " << num << endl;
num++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
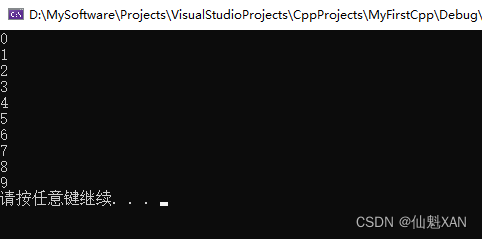
2、do...while 循环语句
作用:满足循环条件,执行循环语句
语法: `do{ 循环语句 } while(循环条件);`
说明:
- 与while的区别在于,do...while会先执行一次循环语句,再判断循环条件
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num = 0;
do
{
cout << num << endl;
num++;
} while (num < 10);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
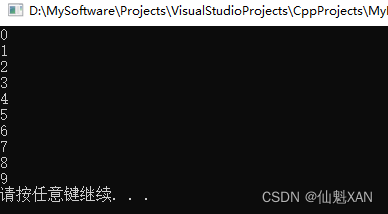
3、for循环语句
作用:满足循环条件,执行循环语句
形式:` for(起始表达式;条件表达式;末尾循环体) { 循环语句; }`
说明:
- 注意:for循环中的表达式,要用分号进行分隔
- 总结:while , do...while, for都是开发中常用的循环语句,for循环结构比较清晰,比较常用

代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4、嵌套循环
作用:在循环体中再嵌套一层循环,解决一些实际问题
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//外层循环执行1次,内层循环执行1轮
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
cout << "*" << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
四、跳转语句
1、break语句
作用:用于跳出==选择结构==或者==循环结构==
break 使用的说明 :
- 出现在switch条件语句中,作用是终止case并跳出switch
- 出现在循环语句中,作用是跳出当前的循环语句
- 出现在嵌套循环中,跳出最近的内层循环语句
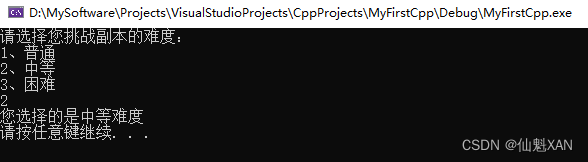
1)switch 中使用的代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、在switch 语句中使用break
cout << "请选择您挑战副本的难度:" << endl;
cout << "1、普通" << endl;
cout << "2、中等" << endl;
cout << "3、困难" << endl;
int num = 0;
cin >> num;
switch (num)
{
case 1:
cout << "您选择的是普通难度" << endl;
break;
case 2:
cout << "您选择的是中等难度" << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "您选择的是困难难度" << endl;
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
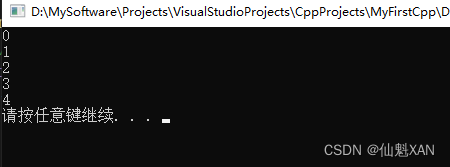
2)for 中使用的代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//2、在循环语句中用break
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (i == 5)
{
break; //跳出循环语句
}
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3) for 嵌套循环中使用代码:
int main() {
//在嵌套循环语句中使用break,退出内层循环
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
if (j == 5)
{
break;
}
cout << "*" << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、continue语句
作用:在循环语句中,跳过本次循环中余下尚未执行的语句,继续执行下一次循环
说明:
- continue并没有使整个循环终止,而是不执行后面的代码,从头开始新的循环,区别于 break 会跳出循环
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
continue;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3、goto语句
作用:可以无条件跳转语句
形式:`goto 标记;`
说明:
- 如果标记的名称存在,执行到goto语句时,会跳转到标记的位置
- 在程序中不建议使用goto语句,以免造成程序流程混乱
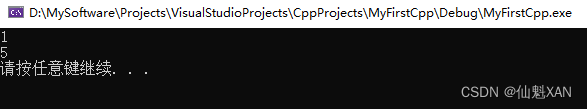
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "1" << endl;
goto FLAG;
cout << "2" << endl;
cout << "3" << endl;
cout << "4" << endl;
FLAG:
cout << "5" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}