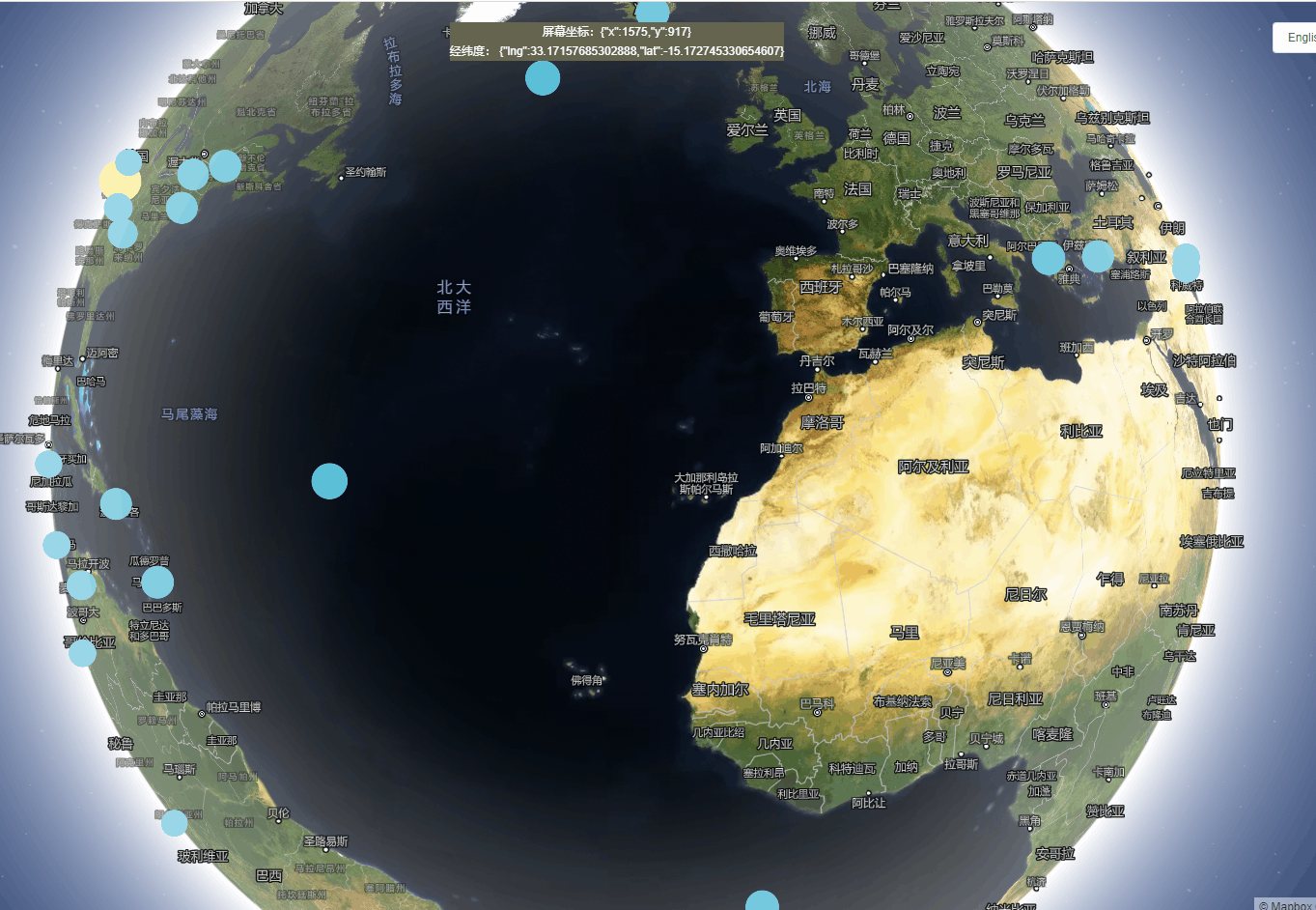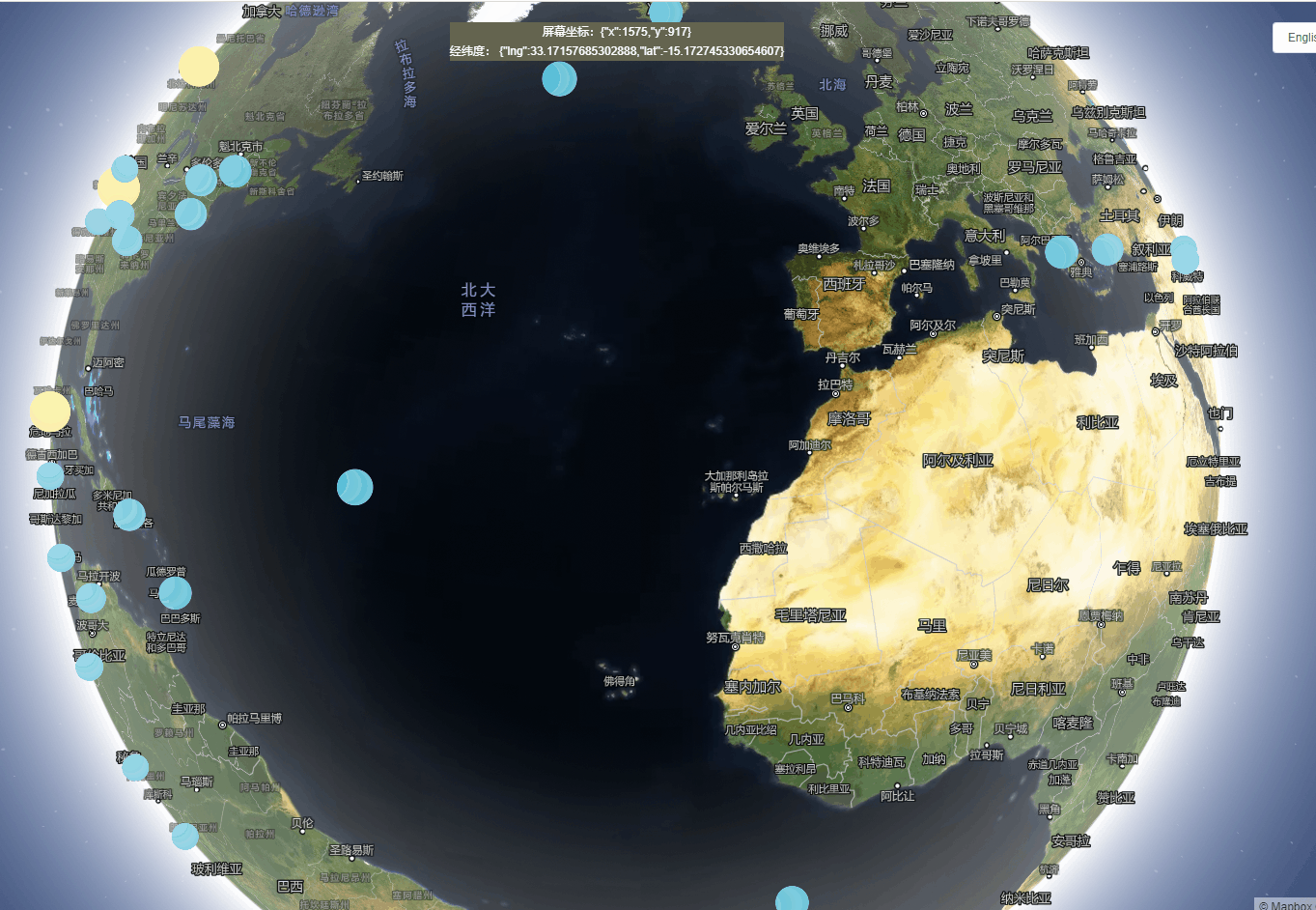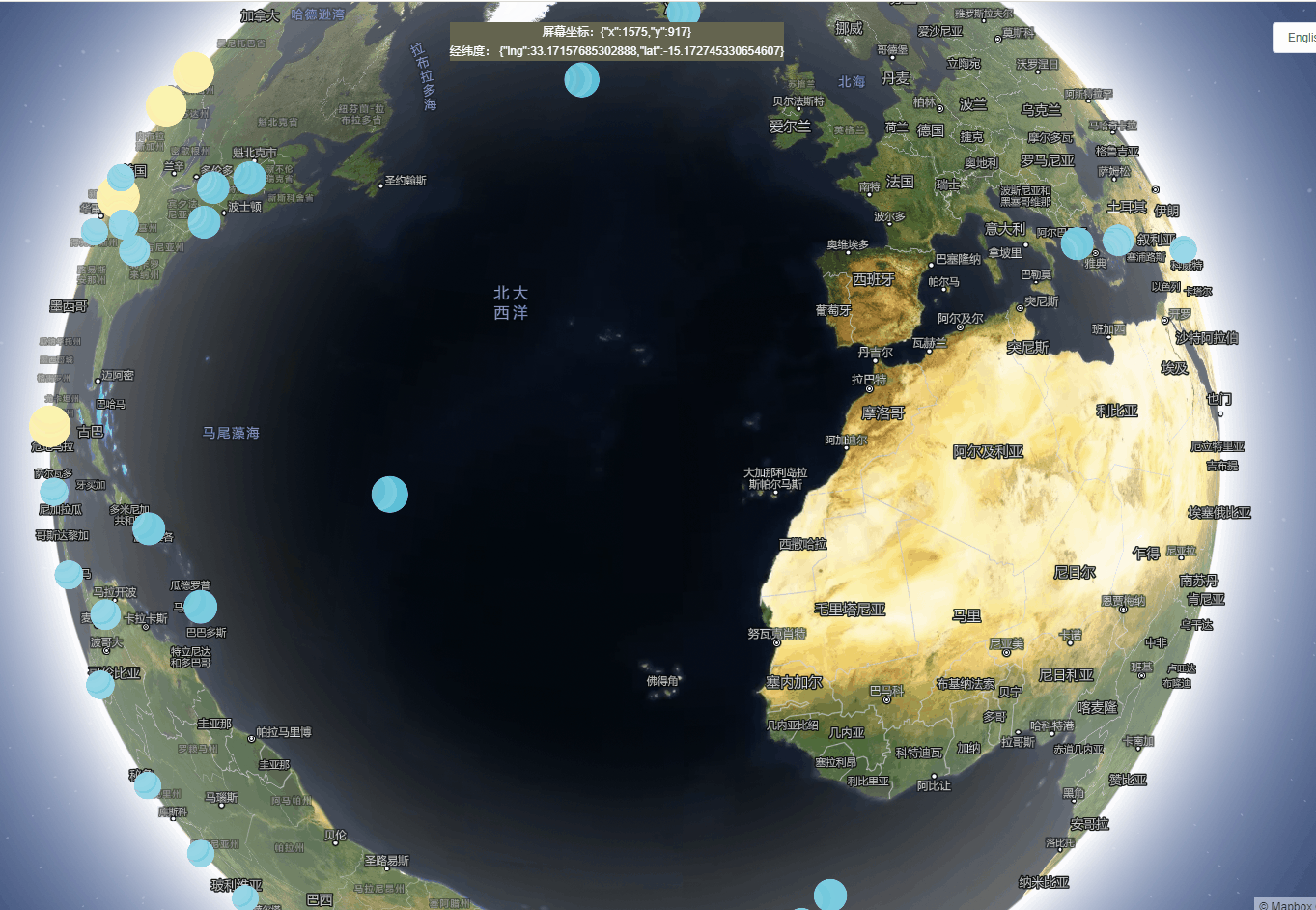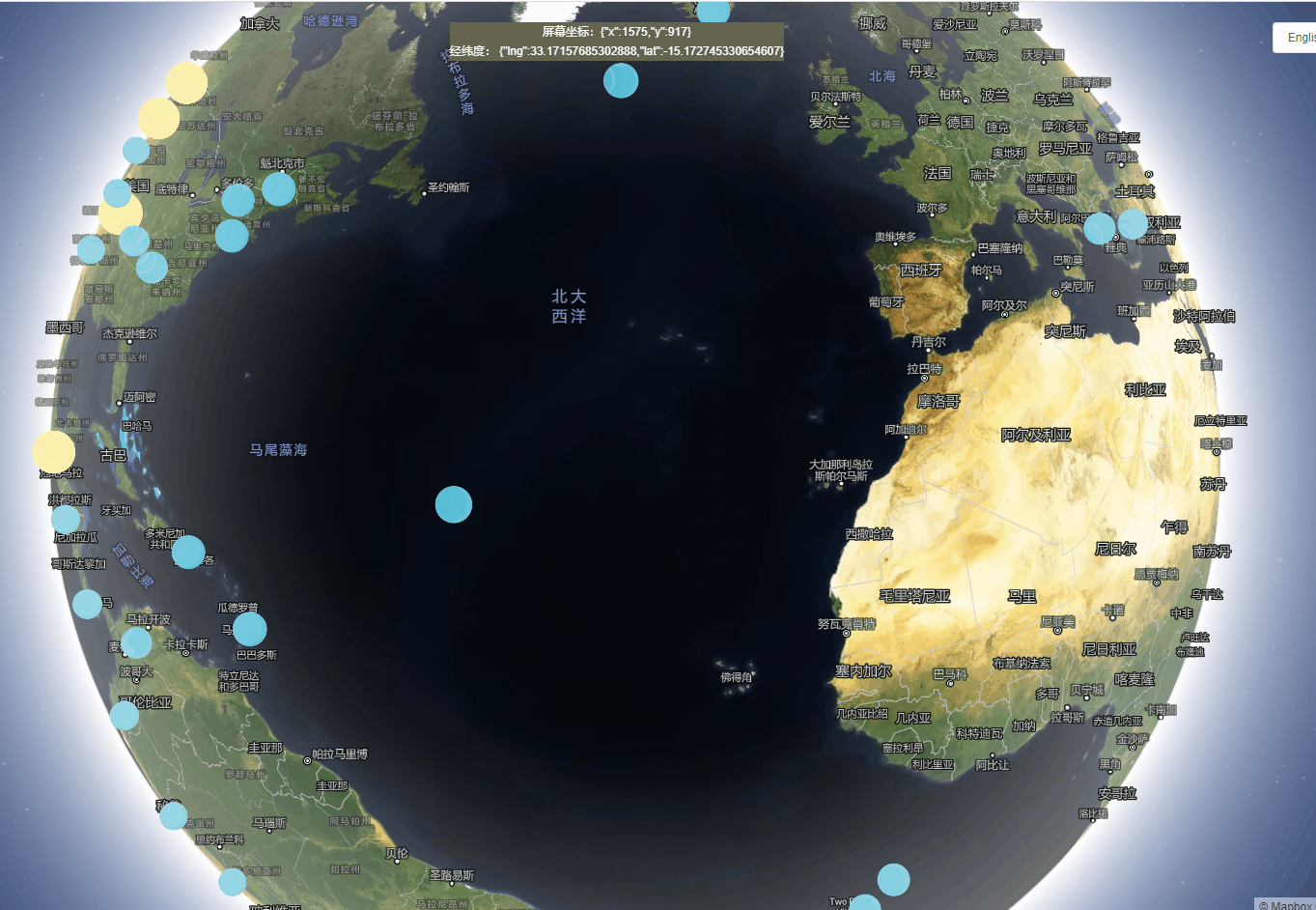
1、创建一个自动旋转的地球地图
实现功能:地球仪和camera动画结合在一起,创建旋转行星效果。
实现思路:通过在动画结束时调用easeTo,旋转动画将无限期地继续。旋转在用户交互时暂停,并且在高缩放级别时减慢到停止。
首先在dom中添加一个button:
<button id="btn-spin">Pause rotation</button>
实现代码:
map.on('style.load', () => {
map.setFog({
}); // Set the default atmosphere style
});
// The following values can be changed to control rotation speed:
// At low zooms, complete a revolution every two minutes.
const secondsPerRevolution = 120;
// Above zoom level 5, do not rotate.
const maxSpinZoom = 5;
// Rotate at intermediate speeds between zoom levels 3 and 5.
const slowSpinZoom = 3;
let userInteracting = false;
let spinEnabled = true;
function spinGlobe() {
const zoom = map.getZoom();
if (spinEnabled && !userInteracting && zoom < maxSpinZoom) {
let distancePerSecond = 360 / secondsPerRevolution;
if (zoom >
slowSpinZoom) {
// Slow spinning at higher zooms
const zoomDif =
(maxSpinZoom - zoom) / (maxSpinZoom - slowSpinZoom);
distancePerSecond *= zoomDif;
}
const center = map.getCenter();
center.lng -= distancePerSecond;
// Smoothly animate the map over one second.
// When this animation is complete, it calls a 'moveend' event.
map.easeTo({
center,
duration: 1000,
easing: (n) => n
});
}
}
// Pause spinning on interaction
map.on('mousedown', () => {
userInteracting = true;
});
// Restart spinning the globe when interaction is complete
map.on('mouseup', () => {
userInteracting = false;
spinGlobe();
});
// These events account for cases where the mouse has moved
// off the map, so 'mouseup' will not be fired.
map.on('dragend', () => {
userInteracting = false;
spinGlobe();
});
map.on('pitchend', () => {
userInteracting = false;
spinGlobe();
});
map.on('rotateend', () => {
userInteracting = false;
spinGlobe();
});
// When animation is complete, start spinning if there is no ongoing interaction
map.on('moveend', () => {
spinGlobe();
});
document.getElementById('btn-spin').addEventListener('click', (e) => {
spinEnabled = !spinEnabled;
if (spinEnabled) {
spinGlobe();
e.target.innerHTML = 'Pause rotation';
} else {
map.stop(); // Immediately end ongoing animation
e.target.innerHTML = 'Start rotation';
}
});
spinGlobe();
效果展示:
2、添加一个3D模型
使用three.js,首先three.js安装到项目中:
# three.js
npm install --save three
在项目中引入:
import * as THREE from 'three';
import {
GLTFLoader
} from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader.js';
使用带有three.js的自定义样式层将三维模型添加到地图中:
// parameters to ensure the model is georeferenced correctly on the map
const modelOrigin = [104.9819, 37.39847];
const modelAltitude = 0;
const modelRotate = [Math.PI / 2, 0, 0];
const modelAsMercatorCoordinate = this.$mapboxgl.MercatorCoordinate.fromLngLat(
modelOrigin,
modelAltitude
);
// transformation parameters to position, rotate and scale the 3D model onto the map
const modelTransform = {
translateX: modelAsMercatorCoordinate.x,
translateY: modelAsMercatorCoordinate.y,
translateZ: modelAsMercatorCoordinate.z,
rotateX: modelRotate[0],
rotateY: modelRotate[1],
rotateZ: modelRotate[2],
/* Since the 3D model is in real world meters, a scale transform needs to be
* applied since the CustomLayerInterface expects units in MercatorCoordinates.
*/
scale: modelAsMercatorCoordinate.meterInMercatorCoordinateUnits()
};
// const THREE = window.THREE;
// configuration of the custom layer for a 3D model per the CustomLayerInterface
const customLayer = {
id: '3d-model',
type: 'custom',
renderingMode: '3d',
onAdd: function (map, gl) {
this.camera = new THREE.Camera();
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
// create two three.js lights to illuminate the model
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff);
directionalLight.position.set(0, -70, 100).normalize();
this.scene.add(directionalLight);
const directionalLight2 = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff);
directionalLight2.position.set(0, 70, 100).normalize();
this.scene.add(directionalLight2);
// use the three.js GLTF loader to add the 3D model to the three.js scene
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(
'https://docs.mapbox.com/mapbox-gl-js/assets/34M_17/34M_17.gltf',
(gltf) => {
this.scene.add(gltf.scene);
}
);
this.map = map;
// use the Mapbox GL JS map canvas for three.js
this.renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
canvas: map.getCanvas(),
context: gl,
antialias: true
});
this.renderer.autoClear = false;
},
render: function (gl, matrix) {
const rotationX = new THREE.Matrix4().makeRotationAxis(
new THREE.Vector3(1, 0, 0),
modelTransform.rotateX
);
const rotationY = new THREE.Matrix4().makeRotationAxis(
new THREE.Vector3(0, 1, 0),
modelTransform.rotateY
);
const rotationZ = new THREE.Matrix4().makeRotationAxis(
new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1),
modelTransform.rotateZ
);
const m = new THREE.Matrix4().fromArray(matrix);
const l = new THREE.Matrix4()
.makeTranslation(
modelTransform.translateX,
modelTransform.translateY,
modelTransform.translateZ
)
.scale(
new THREE.Vector3(
modelTransform.scale,
-modelTransform.scale,
modelTransform.scale
)
)
.multiply(rotationX)
.multiply(rotationY)
.multiply(rotationZ);
this.camera.projectionMatrix = m.multiply(l);
// this.renderer.resetState();
this.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera);
this.map.triggerRepaint();
}
};
map.on('style.load', () => {
map.addLayer(customLayer, 'waterway-label');
});
上效果:
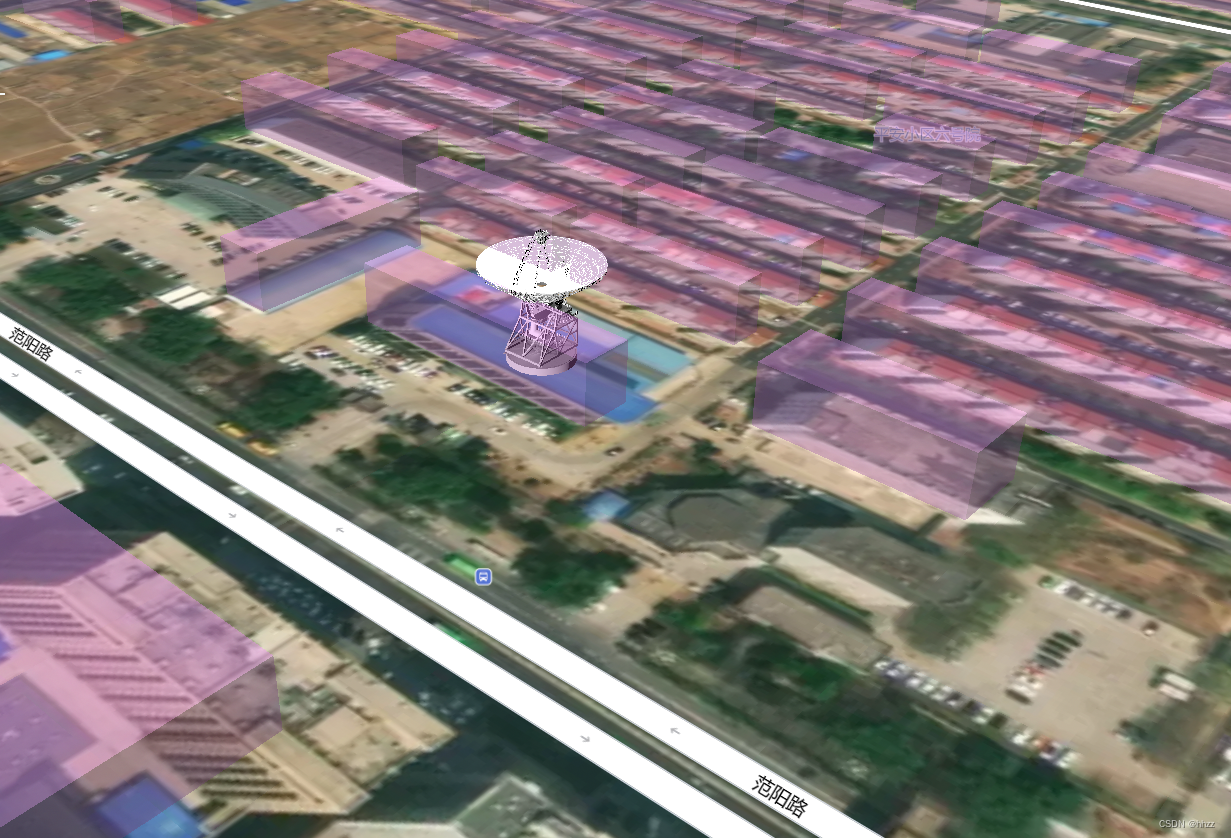
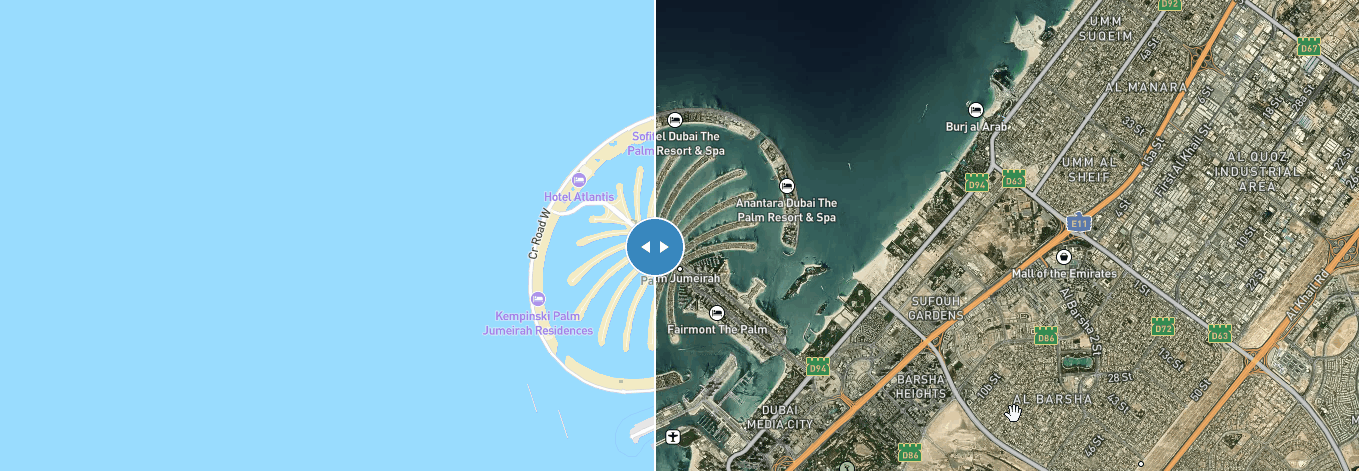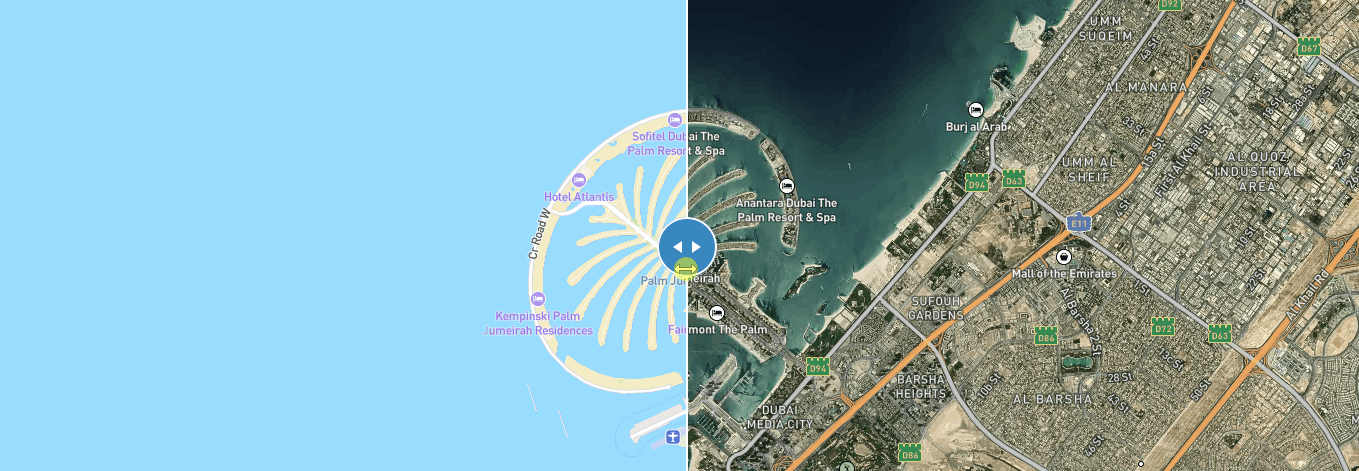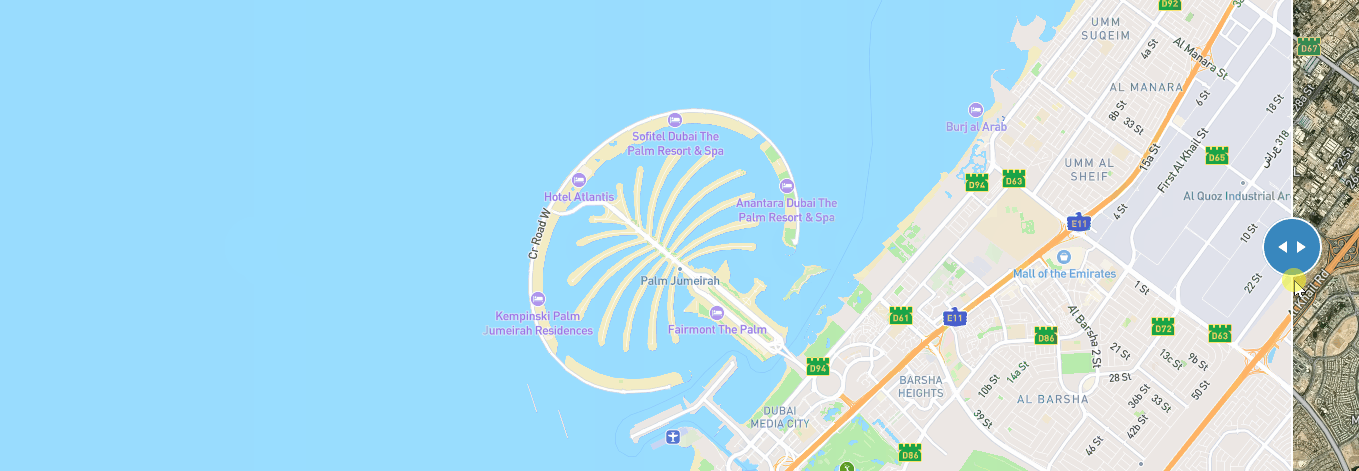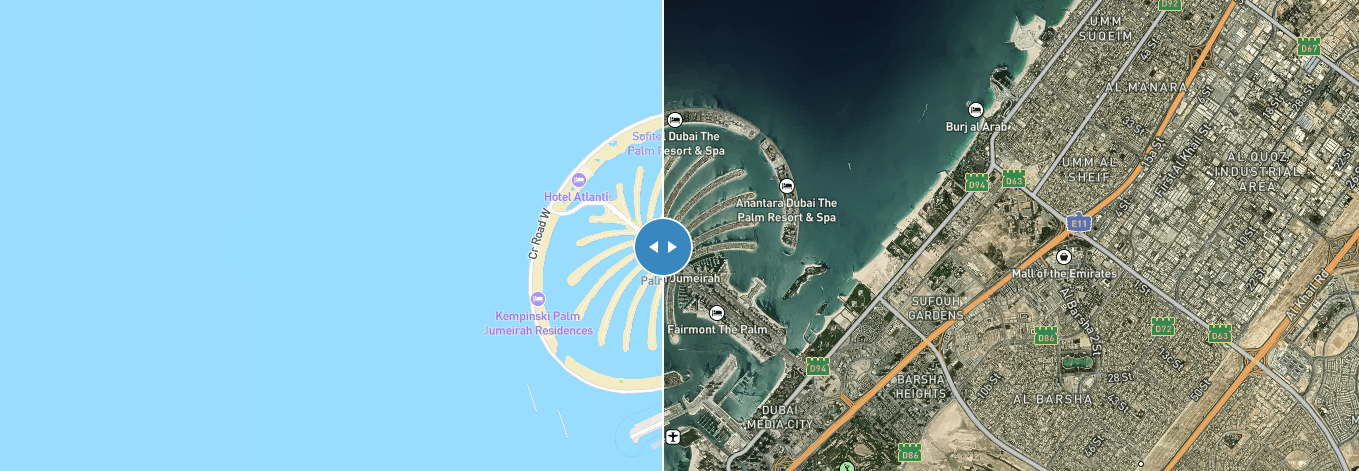
3、一个页面创建两个底图之间滑动
以通过左右滑动来比较两个地图
使用mapbox插件 mapbox-gl-compare
安装
npm i mapbox-gl-compare -D
npm i mapbox-gl-sync-move -D
导入
import mapboxgl from ‘mapbox-gl’
import Compare from ‘mapbox-gl-compare’
创建两个div:
<div id="comparison-container">
<div id="before" class="map"></div>
<div id="after" class="map"></div>
</div>
核心代码:
mapboxgl.accessToken = 'xxxxxxx';
const beforeMap = new mapboxgl.Map({
container: 'before',
// Choose from Mapbox's core styles, or make your own style with Mapbox Studio
style: 'mapbox://styles/mapbox/streets-v12',
center: [0, 0],
zoom: 0
});
const afterMap = new mapboxgl.Map({
container: 'after',
style: 'mapbox://styles/mapbox/satellite-streets-v12',
center: [0, 0],
zoom: 0
});
// A selector or reference to HTML element
const container = '#comparison-container';
const map = new mapboxgl.Compare(beforeMap, afterMap, container, {
// Set this to enable comparing two maps by mouse movement:
// mousemove: true
});
效果如下: