文章目录
一、Room#Migration 迁移工具简介
1、Room 中的迁移工具 Migration 简介
使用 Room 访问数据库时 , 应用程序 的 数据模型 发生 改变 , 数据库版本进行升级 , 数据库表的字段 , 数据结构 , 发生了变化 , 需要进行更新 , 可以使用 Migration 迁移工具 升级数据库 ;
迁移 是指 将 数据库的结构 从一个版本 更改为 另一个版本 , 以适应新的数据模型 ;
Room 提供了强大的 迁移工具 Migration , 使开发人员能够 管理和执行 数据库迁移 操作 ;
使用 Room 操作数据库升级 ,
- 从 数据库版本 1 升级为 数据库版本 2 , 只需要 执行 Migration(1, 2) 即可 ;
- 从 数据库版本 1 升级为 数据库版本 3 , 先执行 Migration(1, 2) , 再执行 Migration(2, 3) ;
Room 提供了简便的方式来 处理 Android 应用程序中的本地数据库,并且 在数据模型发生变化时,提供了强大的 迁移工具 Migration ,使开发人员能够 有效地管理数据库结构的更改。
2、Migration 迁移工具使用步骤
在 Room 中使用 Migration 迁移工具 升级数据库步骤 :
- 更新数据模型 : 如果要 更改数据库的结构 ,
- 更新 Entity 实体类 , 修改实体类就是修改数据库表结构 ;
- 修改 Dao 数据库访问接口对象 , 包括添加 / 删除 / 修改 表 / 列 / 索引 ;
- 创建迁移类 : 创建一个用于执行数据库迁移的 迁移类 Migration , Migration 迁移类应 实现 Room 的 Migration 接口 , 并 定义数据库从旧版本迁移到新版本的操作 ;
- 指定迁移规则 : 在 Room 数据库的构建器中 , 使用 addMigrations 方法指定迁移规则 , 该方法接受一组 Migration 迁移对象 , 每个 Migration 迁移对象 代表一个数据库版本之间的迁移操作 ;
- 执行迁移 : 当应用程序启动并访问数据库时,Room 将自动检测数据库版本并执行适当的迁移操作 , 应用程序可以无缝地将旧版本的数据库迁移到新版本,而不会丢失现有的数据。
注意 : 执行迁移 有风险,特别是在 修改表结构 或 删除数据 时。
在进行迁移之前,强烈建议先备份数据库,以防出现意外情况。
二、Room#Migration 迁移工具使用要点
本章节中以新增一个数据库表字段为例 , 在 【Jetpack】Room + ViewModel + LiveData 综合使用 ( 核心要点说明 | 组合方式 | 代码示例 ) 博客的代码示例基础上 , 为 student 数据库表 , 新增 性别 sex 字段 ;
1、修改 Entity 实体类 - 更改数据模型
首先 , 要在 Entity 实体类中加入新的数据库字段 .
/**
* 性别字段
* 数据库表中的列名为 sex
* 数据库表中的类型为 INTEGER 文本类型
*/
@ColumnInfo(name = "sex", typeAffinity = ColumnInfo.INTEGER)
var sex: Int = 0
修改了该 Entity 实体类 , 就意味着 修改了 数据库中的数据库表 ;
2、创建 Migration 迁移类
然后 , 在 RoomDatabase 中 , 定义 final 静态的 Migration 类 , 如果是 Kotlin 中 , 则定义在 伴生对象 companion object 中 ;
这里使用 匿名内部类 的方式 定义 Migration 迁移类 ;
companion object {
/**
* 数据库版本 1 升级到 版本 2 的迁移类实例对象
*/
val MIGRATION_1_2: Migration = object : Migration(1, 2) {
override fun migrate(database: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
Log.i("StudentDatabase", "数据库版本 1 升级到 版本 2")
database.execSQL("alter table student add column sex integer not null default 1")
}
}
}
上述 Migration 迁移类中 , 使用了 SQL 语句 :
alter table student add column sex integer not null default 1
该 SQL 语句的作用是 向 “student” 表中添加一个名为 “sex” 的整数类型列 , 该列不允许为空 , 并且默认值为 1 ; 可以使用类似的 ALTER TABLE 语句来修改表结构,添加、修改或删除列等操作 ;
alter table student 表示对 student 数据库表 进行修改 ;
add column sex integer 表示 要添加的新列名为 “sex” , 数据类型为 integer , 即整数类型 ;
not null 表示该新列不允许为空值,即在插入或更新数据时,必须为该列提供非空值。
default 1 表示新列的默认值为 1 ; 当插入新行时 , 如果没有显式提供 “sex” 列的值 , 将使用默认值 1 ;
3、修改数据库版本
数据库的版本 在 RoomDatabase 的抽象实现类 中的 @Database 注解上修改 ,
@Database(entities = [Student::class], version = 1, exportSchema = false)
abstract class StudentDatabase: RoomDatabase() {
修饰 RoomDatabase 抽象类的 @Database 注解中的 version 参数 , 就是数据库的版本号 ;
上面定义的 Migration(1, 2) 迁移类 , 就是从 @Database 注解 的 version = 1 版本 , 迁移到 version = 2 版本 ;
/**
* 数据库版本 1 升级到 版本 2 的迁移类实例对象
*/
val MIGRATION_1_2: Migration = object : Migration(1, 2)
4、数据库更新的情况
如果之前运行了 【Jetpack】Room + ViewModel + LiveData 综合使用 ( 核心要点说明 | 组合方式 | 代码示例 ) 博客的代码示例 ;
然后再 修改 Entity 实体类 , 即更改数据模型 , 创建 Migration 迁移类 并 修改数据库版本 ,
此时运行 , 手机应用中已经创建了 版本 1 的数据库 , 在该数据库的基础上 , 运行 带 Migration(1, 2) 的应用 ;
如果检测到了 版本 1 数据库 , 就会在最开始 , 先更新数据库 , 然后再运行后续 Room 操作数据库代码 ;
首次执行 版本 1 数据库代码 , 也就是 【Jetpack】Room + ViewModel + LiveData 综合使用 ( 核心要点说明 | 组合方式 | 代码示例 ) 博客的代码 ;
执行结果如下 :
2023-05-31 11:45:56.981 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: []
2023-05-31 11:45:57.416 I/Room_MainActivity: 插入数据 S1 : Student(id=0, name='Tom', age=18)
2023-05-31 11:45:57.425 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=1, name='Tom', age=18)]
2023-05-31 11:45:57.920 I/Room_MainActivity: 插入数据 S2 : Student(id=0, name='Jerry', age=16)
2023-05-31 11:45:57.922 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=1, name='Tom', age=18), Student(id=2, name='Jerry', age=16)]
2023-05-31 11:45:58.422 I/Room_MainActivity: 更新数据 S2 : Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)
2023-05-31 11:45:58.424 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=1, name='Tom', age=18), Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)]
2023-05-31 11:45:58.930 I/Room_MainActivity: 删除数据 id = 1
2023-05-31 11:45:58.931 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)]
2023-05-31 11:45:59.432 I/Room_MainActivity: 主动查询 : LiveData : androidx.room.RoomTrackingLiveData@8726677 , 实际数据 : null
2023-05-31 11:45:59.437 I/Room_MainActivity: 主动查询2 : [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)]
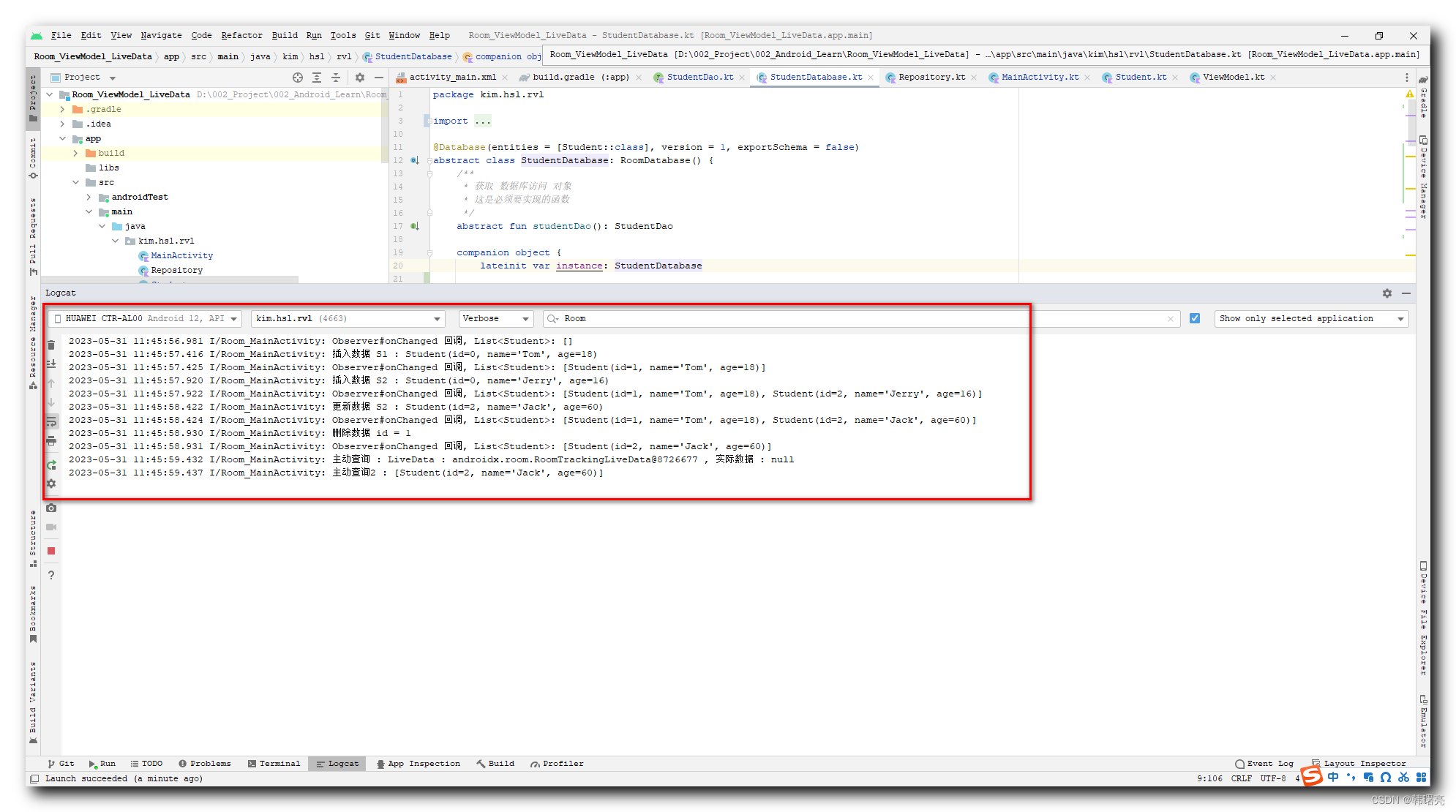
此时 , 手机中已经运行了 数据库版本 1 的程序 , 手机中该应用的存储区域已经有一个数据库了 ;
修改 Entity 实体类 , 即更改数据模型 , 创建 Migration 迁移类 并 修改数据库版本 version = 2 , 不卸载原来的应用 , 直接再次运行新程序 ;
2023-05-31 11:50:09.745 I/Room_StudentDatabase: 数据库版本 1 升级到 版本 2
2023-05-31 11:50:09.834 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)]
2023-05-31 11:50:10.216 I/Room_MainActivity: 插入数据 S1 : Student(id=0, name='Tom', age=18)
2023-05-31 11:50:10.233 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60), Student(id=3, name='Tom', age=18)]
2023-05-31 11:50:10.723 I/Room_MainActivity: 插入数据 S2 : Student(id=0, name='Jerry', age=16)
2023-05-31 11:50:10.733 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60), Student(id=3, name='Tom', age=18), Student(id=4, name='Jerry', age=16)]
2023-05-31 11:50:11.241 I/Room_MainActivity: 更新数据 S2 : Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)
2023-05-31 11:50:11.253 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60), Student(id=3, name='Tom', age=18), Student(id=4, name='Jerry', age=16)]
2023-05-31 11:50:11.744 I/Room_MainActivity: 删除数据 id = 1
2023-05-31 11:50:12.250 I/Room_MainActivity: 主动查询 : LiveData : androidx.room.RoomTrackingLiveData@b23c326 , 实际数据 : null
2023-05-31 11:50:12.274 I/Room_MainActivity: 主动查询2 : [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60), Student(id=3, name='Tom', age=18), Student(id=4, name='Jerry', age=16)]
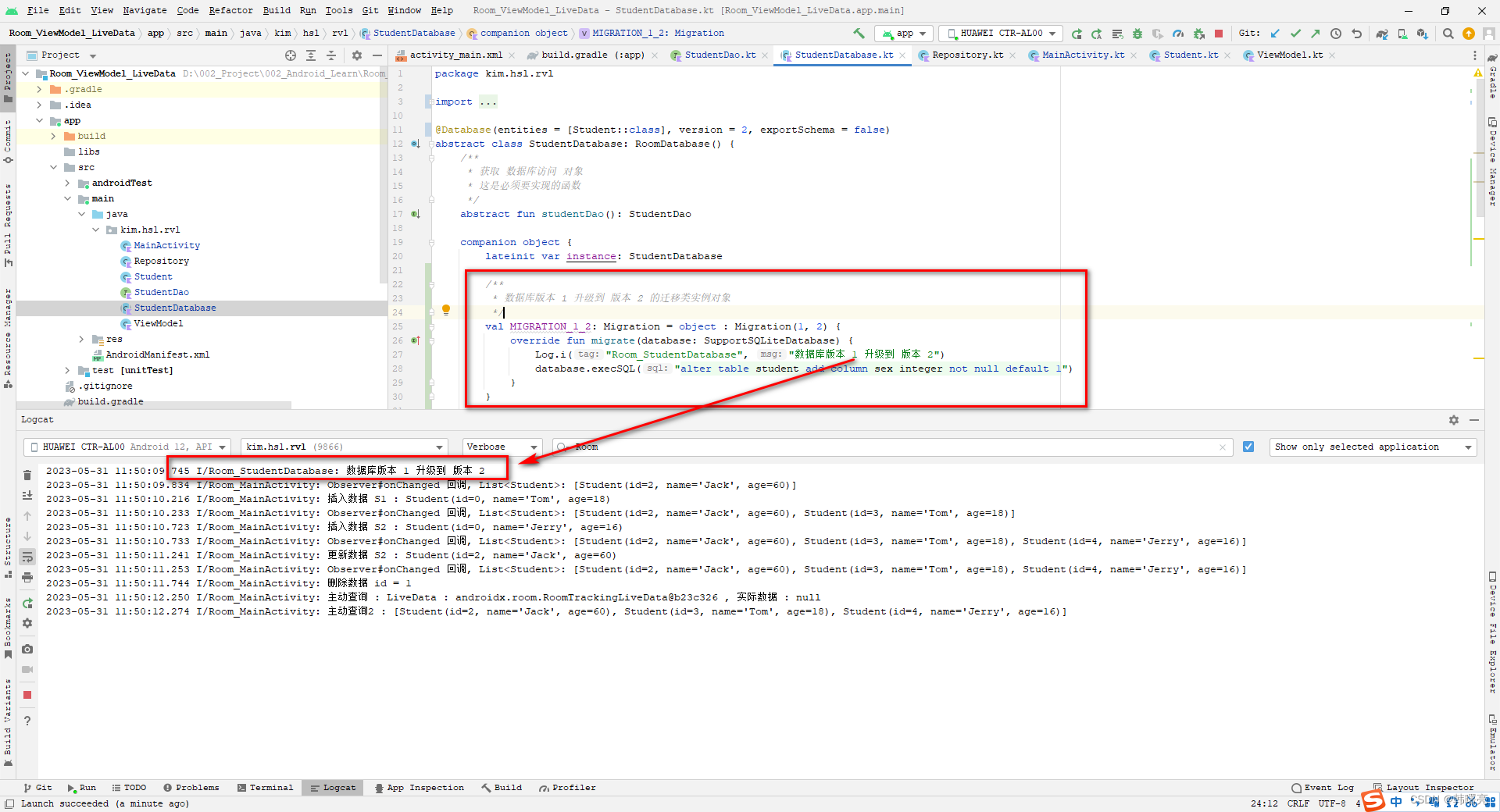
5、直接安装最新数据库的情况
卸载原来的应用 , 直接安装 数据库版本 2 的新应用 ;
数据库直接创建最新版本的数据库 , 不涉及 版本 1 的老数据库 ;
2023-05-31 11:52:15.946 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: []
2023-05-31 11:52:16.248 I/Room_MainActivity: 插入数据 S1 : Student(id=0, name='Tom', age=18)
2023-05-31 11:52:16.252 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=1, name='Tom', age=18)]
2023-05-31 11:52:16.756 I/Room_MainActivity: 插入数据 S2 : Student(id=0, name='Jerry', age=16)
2023-05-31 11:52:16.758 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=1, name='Tom', age=18), Student(id=2, name='Jerry', age=16)]
2023-05-31 11:52:17.258 I/Room_MainActivity: 更新数据 S2 : Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)
2023-05-31 11:52:17.260 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=1, name='Tom', age=18), Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)]
2023-05-31 11:52:17.760 I/Room_MainActivity: 删除数据 id = 1
2023-05-31 11:52:17.762 I/Room_MainActivity: Observer#onChanged 回调, List<Student>: [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)]
2023-05-31 11:52:18.261 I/Room_MainActivity: 主动查询 : LiveData : androidx.room.RoomTrackingLiveData@8726677 , 实际数据 : null
2023-05-31 11:52:18.264 I/Room_MainActivity: 主动查询2 : [Student(id=2, name='Jack', age=60)]
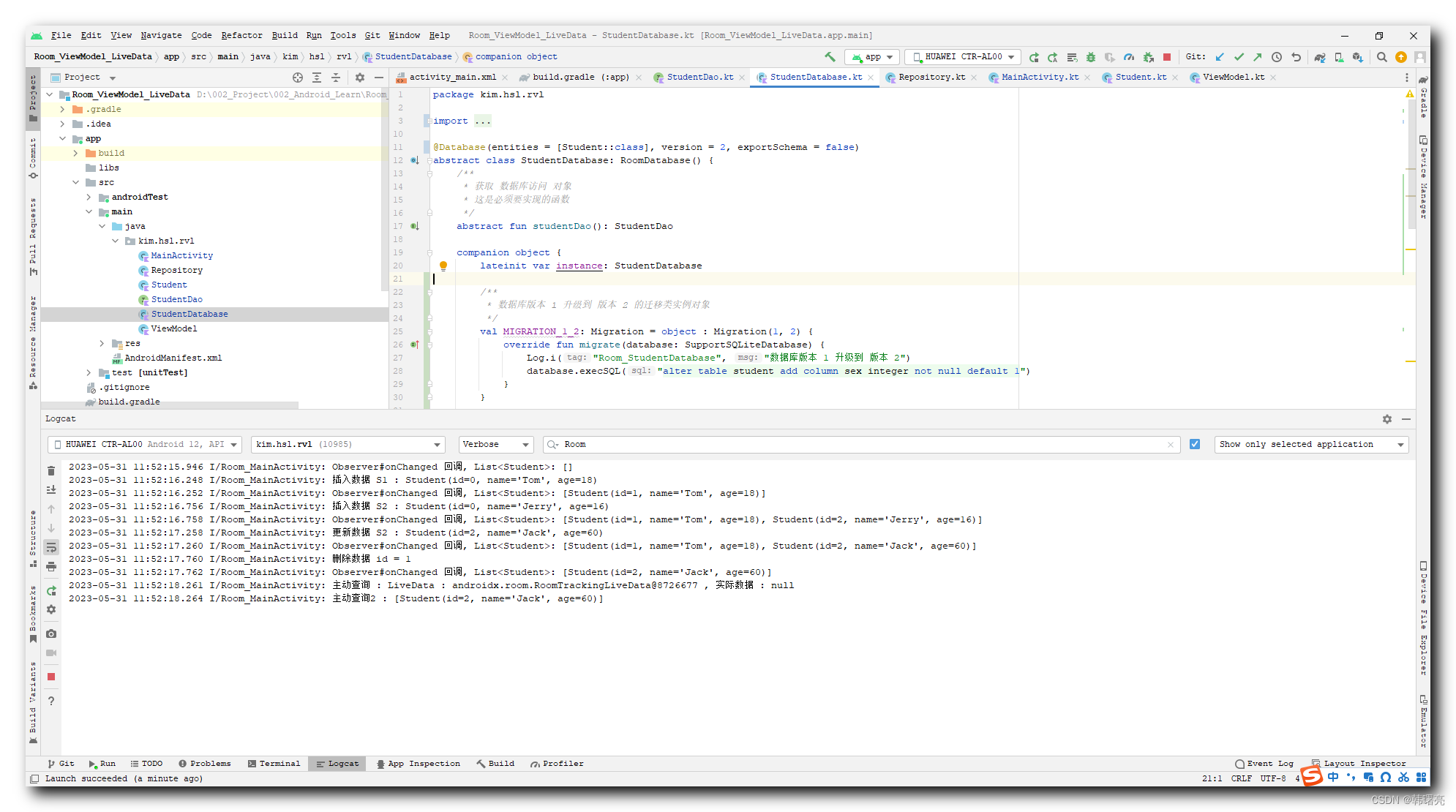
三、Room#Migration 迁移工具完整代码示例
本章节完整代码示例在 【Jetpack】Room + ViewModel + LiveData 综合使用 ( 核心要点说明 | 组合方式 | 代码示例 ) 博客的代码示例基础上进行修改 ;
代码地址 : https://github.com/han1202012/Room_ViewModel_LiveData
1、Entity 实体类修改后的完整代码
Entity 实体类中加入新的数据库字段 sex 字段 ;
完整代码 :
package kim.hsl.rvl
import androidx.room.ColumnInfo
import androidx.room.Entity
import androidx.room.Ignore
import androidx.room.PrimaryKey
/**
* 定义数据库表 Entity 实体 / 同时定义数据库表 和 对鹰的实体类
* 设置该数据类对应数据库中的一张数据表, 表名为 student
* 该数据库表中的数据对应一个 Student 类实例对象
*/
@Entity(tableName = "student")
class Student {
/**
* @PrimaryKey 设置主键 autoGenerate 为自增
* @ColumnInfo name 设置列名称 / typeAffinity 设置列类型
*/
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
@ColumnInfo(name = "id", typeAffinity = ColumnInfo.INTEGER)
var id: Int = 0
/**
* 姓名字段
* 数据库表中的列名为 name
* 数据库表中的类型为 TEXT 文本类型
*/
@ColumnInfo(name = "name", typeAffinity = ColumnInfo.TEXT)
lateinit var name: String
/**
* 年龄字段
* 数据库表中的列名为 age
* 数据库表中的类型为 INTEGER 文本类型
*/
@ColumnInfo(name = "age", typeAffinity = ColumnInfo.INTEGER)
var age: Int = 0
/**
* 性别字段
* 数据库表中的列名为 sex
* 数据库表中的类型为 INTEGER 文本类型
*/
@ColumnInfo(name = "sex", typeAffinity = ColumnInfo.INTEGER)
var sex: Int = 0
/**
* 有些属性用于做业务逻辑
* 不需要插入到数据库中
* 使用 @Ignore 注解修饰该属性字段
*/
@Ignore
lateinit var studentInfo: String
/**
* 默认的构造方法给 Room 框架使用
*/
constructor(id: Int, name: String, age: Int) {
this.id = id
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
/**
* 使用 @Ignore 标签标注后
* Room 就不会使用该构造方法了
* 这个构造方法是给开发者使用的
*/
@Ignore
constructor(name: String, age: Int) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
/**
* 使用 @Ignore 标签标注后
* Room 就不会使用该构造方法了
* 这个构造方法是给开发者使用的
*/
@Ignore
constructor(id: Int) {
this.id = id
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "Student(id=$id, name='$name', age=$age)"
}
}
2、Migration 迁移类创建以及数据库版本修改代码示例
在 RoomDatabase 中 , 定义 final 静态的 Migration 类 , 如果是 Kotlin 中 , 则定义在 伴生对象 companion object 中 ;
这里使用 匿名内部类 的方式 定义 Migration 迁移类 ;
修饰 RoomDatabase 抽象类的 @Database 注解中的 version 参数 , 就是数据库的版本号 ;
完整代码示例 :
package kim.hsl.rvl
import android.content.Context
import android.util.Log
import androidx.room.Database
import androidx.room.Room
import androidx.room.RoomDatabase
import androidx.room.migration.Migration
import androidx.sqlite.db.SupportSQLiteDatabase
@Database(entities = [Student::class], version = 2, exportSchema = false)
abstract class StudentDatabase: RoomDatabase() {
/**
* 获取 数据库访问 对象
* 这是必须要实现的函数
*/
abstract fun studentDao(): StudentDao
companion object {
lateinit var instance: StudentDatabase
/**
* 数据库版本 1 升级到 版本 2 的迁移类实例对象
*/
val MIGRATION_1_2: Migration = object : Migration(1, 2) {
override fun migrate(database: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
Log.i("Room_StudentDatabase", "数据库版本 1 升级到 版本 2")
database.execSQL("alter table student add column sex integer not null default 1")
}
}
fun inst(context: Context): StudentDatabase {
if (!::instance.isInitialized) {
synchronized(StudentDatabase::class) {
// 创建数据库
instance = Room.databaseBuilder(
context.applicationContext,
StudentDatabase::class.java,
"student_database.db")
.addMigrations(MIGRATION_1_2)
.allowMainThreadQueries() // Room 原则上不允许在主线程操作数据库
// 如果要在主线程操作数据库需要调用该函数
.build()
}
}
return instance;
}
}
}