作者:一个喜欢猫咪的的程序员
专栏:《Leetcode》
喜欢的话:世间因为少年的挺身而出,而更加瑰丽。 ——《人民日报》
目录
KY11 二叉树遍历
描述
编一个程序,读入用户输入的一串先序遍历字符串,根据此字符串建立一个二叉树(以指针方式存储)。 例如如下的先序遍历字符串: ABC##DE#G##F### 其中“#”表示的是空格,空格字符代表空树。建立起此二叉树以后,再对二叉树进行中序遍历,输出遍历结果。
输入描述:
输入包括1行字符串,长度不超过100。
输出描述:
可能有多组测试数据,对于每组数据, 输出将输入字符串建立二叉树后中序遍历的序列,每个字符后面都有一个空格。 每个输出结果占一行。
示例:

思路:
当str为#时,返回NULL,i++,当str不为#时,创建节点,并且设置值,left和right指向下一个str值递归下去。
代码实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
char data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
BTNode*TreecCreate(char* str,int* i)
{
if(str[*i]=='#')
{
(*i)++;
return NULL;
}
BTNode*root=(BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
root->data=str[(*i)++];
root->left=TreecCreate(str,i);
root->right=TreecCreate(str,i);
return root;
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
int main() {
int a, b;
char str[100];
scanf("%s",str);
int i=0;
BTNode*root=TreecCreate(str,&i);
InOrder(root);
return 0;
}144. 二叉树的前序遍历
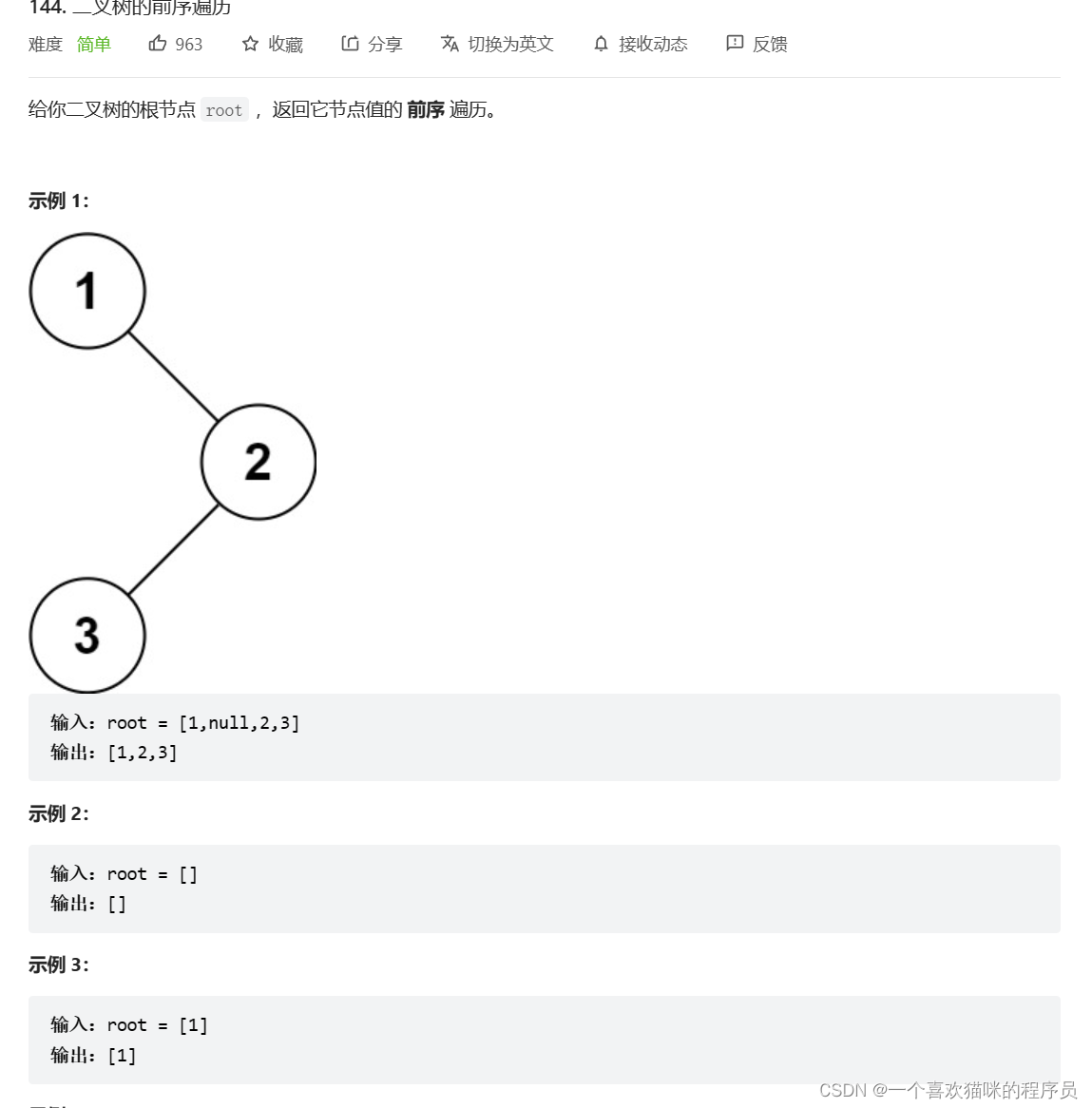
int Treesize(struct TreeNode*root)
{
return root==NULL?0:Treesize(root->left)+Treesize(root->right)+1;
}
void PreOrder(int*a,struct TreeNode*root,int*i)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
a[(*i)++]=root->val;
PreOrder(a,root->left,i);
PreOrder(a,root->right,i);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
*returnSize=Treesize(root);
int*a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize*sizeof(int));
int i=0;
PreOrder(a,root,&i);
return a;
}94. 二叉树的中序遍历

int Treesize(struct TreeNode*root)
{
return root==NULL?0:Treesize(root->left)+Treesize(root->right)+1;
}
void InOrder(int*a,struct TreeNode*root,int*i)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
InOrder(a,root->left,i);
a[(*i)++]=root->val;
InOrder(a,root->right,i);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
*returnSize=Treesize(root);
int*a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize*sizeof(int));
int i=0;
InOrder(a,root,&i);
return a;
}145. 二叉树的后序遍历
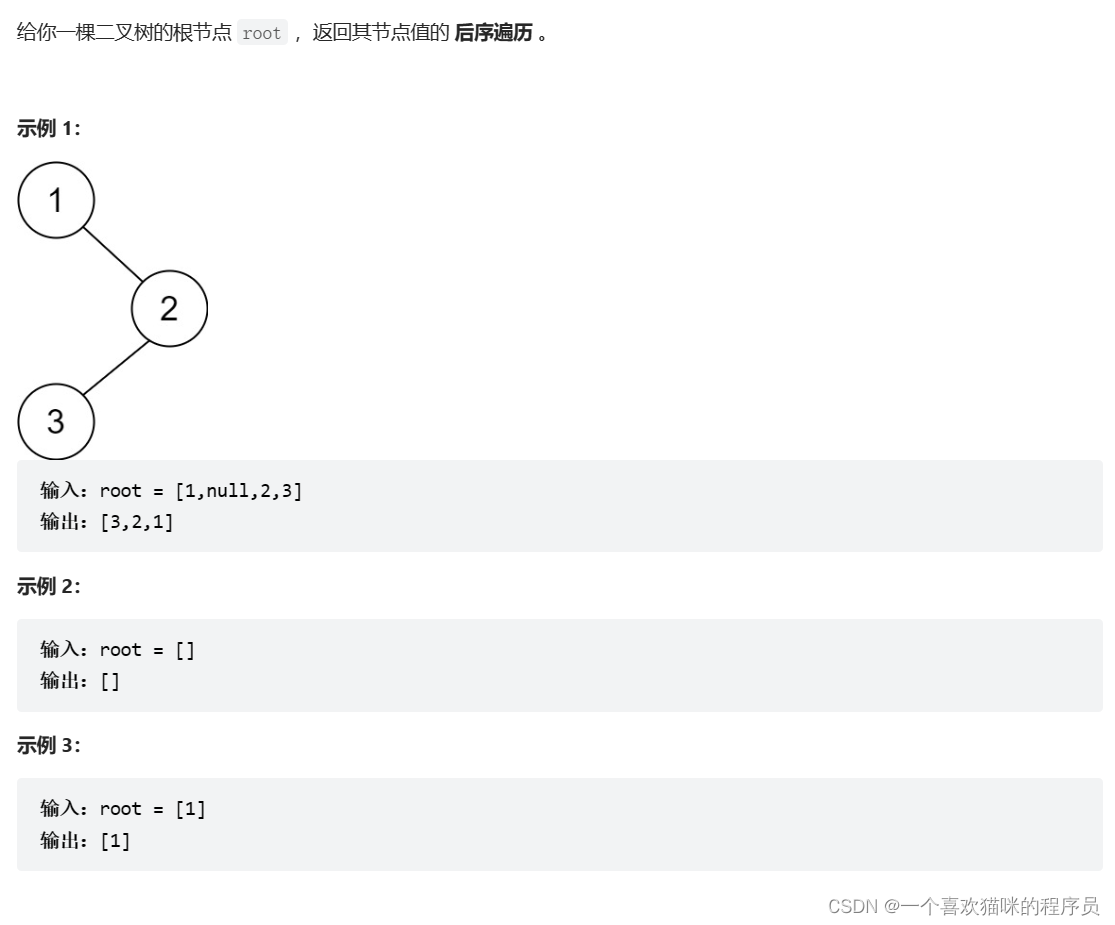
int Treesize(struct TreeNode*root)
{
return root==NULL?0:Treesize(root->left)+Treesize(root->right)+1;
}
void PostOrder(int*a,struct TreeNode*root,int*i)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
PostOrder(a,root->left,i);
PostOrder(a,root->right,i);
a[(*i)++]=root->val;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
*returnSize=Treesize(root);
int*a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize*sizeof(int));
int i=0;
PostOrder(a,root,&i);
return a;
}