1.引言
在前面的章节中,我们已经使用过@SentinelResource注解,本篇文章我们将如何使用@SentinelResource注解灵活的定义控制资源以及如何配置控制策略。在定义了资源点之后,我们就可以通过Dashboard来设置限流和降级策略来对资源点进行保护了。同时,也可以通过@SentinelResource来指定出现限流和降级时候的异常处理策略。下面,就来一起看看限流和降级都是如何实现的。
2.@SentinelResource案例解析
下面我们分为两种情况介绍@SentinelResource注解的使用方法:
按资源名称进行限流;
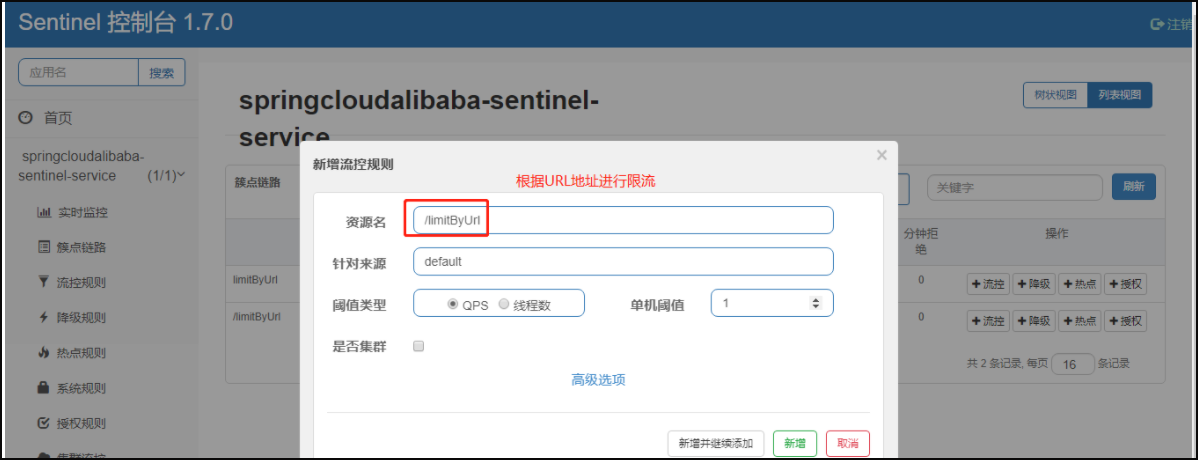
按URL请求路径进行限流;
2.1.按资源名称进行限流
所以我们需要对模块【springcloudalibaba-sentinel-service8401】进行改造:
【a】新建RateLimitController.java
@SentinelResource主要用来定义一个资源。blockHandler 用来指定降级兜底方法。
package com.bruce.controller;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException;
import com.bruce.pojo.JsonResult;
import com.bruce.pojo.Payment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.UUID;
@RestController
public class RateLimitController {
/**
* 根据资源名称进行限流
*/
@GetMapping("/limitByResource")
@SentinelResource(value = "limitByResource", blockHandler = "blockHandlerLimitByResource")
public JsonResult limitByResource() {
return new JsonResult(200, "根据资源名称进行限流", new Payment(20200906L, UUID.randomUUID().toString()));
}
/**
* 服务兜底降级方法
*/
public JsonResult blockHandlerLimitByResource(BlockException exception) {
return new JsonResult(500, exception.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "\t 服务不可用");
}
/**
* 根据URL进行限流
*/
@GetMapping("/limitByUrl")
@SentinelResource(value = "limitByUrl")
public JsonResult limitByUrl() {
return new JsonResult(200, "根据URL进行限流", new Payment(20200906L, UUID.randomUUID().toString()));
}
}
【b】配置流控规则,具体见下图
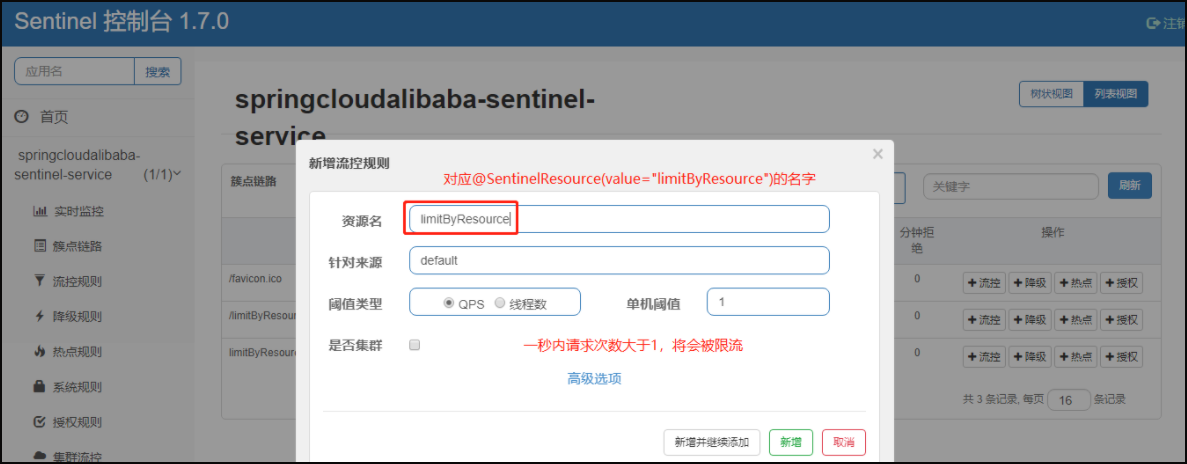
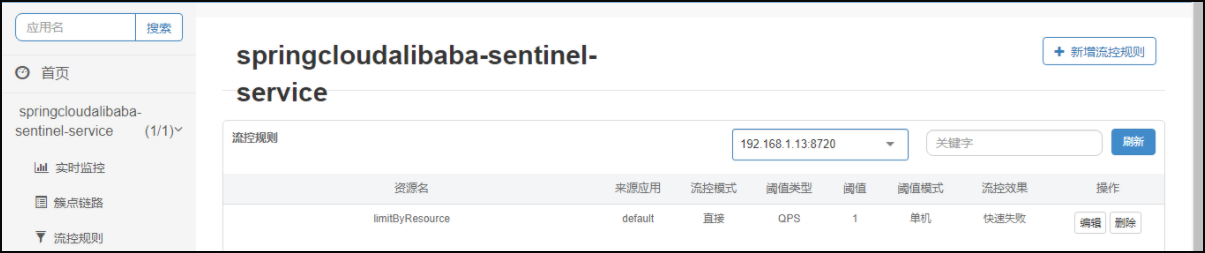
【c】按资源名称限流 - 测试
浏览器正常访问:http://localhost:8401/limitByResource
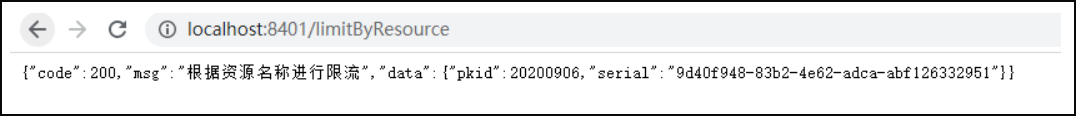
以上是正常访问,也就是一秒内只发了一次请求,下面我们一秒内疯狂请求该接口:http://localhost:8401/limitByResource
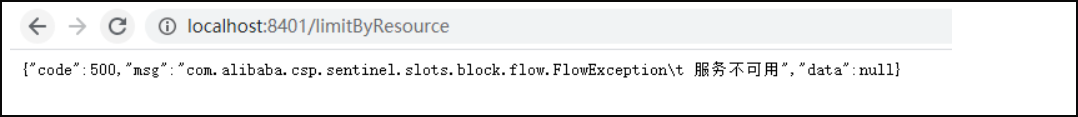
我们发现,当一秒内请求次数大于1次时,接口被限流,微服务不可用。 这些在前面的章节中都已经介绍过,相信小伙伴们都不陌生,接下来我们来看看一个额外的问题,我们将8401服务停止掉,重新回到Sentinel控制台:

我们发现,当我们停止微服务后,之前配置的所有流控规则都消失了,很明显,Sentinel的流控规则时临时性的,目前并不是持久化的,此处先引出问题,后面我们再说说如何解决。
2.2.按URL限流
【a】按URL限流 - 测试
浏览器正常访问:http://localhost:8401/limitByUrl
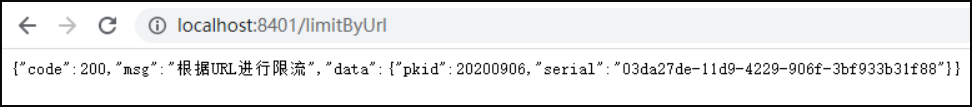
一秒一下,一秒一下,都是正常访问,也就是一秒内只发了一次请求,下面我们一秒内疯狂请求该接口:http://localhost:8401/limitByUrl

我们发现,由于/limitByUrl方法我们并没有指定blockHandler兜底降级方法,所以限流的提示信心也是自带的默认的报错【Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)】,如上图所示。
总结一下以上兜底处理方法目前存在的问题:
1.系统默认的,没有体现我们自己的业务要求;
2.依照现有条件,我们自定义的处理方法又和业务代码耦合在一块,不直观;
3.每个业务方法都需要添加一个降级方法,代码膨胀加剧;
4.没有体现全局统一的处理方法;
3.客户自定义限流处理逻辑
默认情况下,Sentinel对控制资源的限流处理是直接抛出异常。在没有合理的业务承接或者前端对接情况下可以这样,但是正常情况为了更好的用户业务,都会实现一些被限流之后的特殊处理,我们不希望展示一个生硬的报错,这就需要我们自定义限流处理逻辑。
【a】创建CustomBlockHandler类用于自定义限流处理逻辑
package com.bruce.controller;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException;
import com.bruce.pojo.JsonResult;
/**
* @Description 自定义BlockHandler限流处理类
* 说明: 必须是static静态方法
*/
public class CustomBlockHandler {
public static JsonResult customBlockHandlerMethodA(BlockException exception) {
return new JsonResult(500, "[客户自定义限流处理逻辑]--->customBlockHandlerMethodA");
}
public static JsonResult customBlockHandlerMethodB(BlockException exception) {
return new JsonResult(500, "[客户自定义限流处理逻辑]--->customBlockHandlerMethodB");
}
}
【b】RateLimitController.java
blockHandlerClass: 指定限流逻辑处理类;
blockHandler: 指定限流处理方法, 对应blockHandlerClass处理类中的方法名称;
/**
* 客户自定义限流处理逻辑
* blockHandlerClass: 指定限流逻辑处理类
* blockHandler: 指定限流处理方法, 对应blockHandlerClass处理类中的方法名称
*/
@GetMapping("/customBlockHandler")
@SentinelResource(value = "customBlockHandler",
blockHandlerClass = CustomBlockHandler.class,
blockHandler = "customBlockHandlerMethodA")
public JsonResult customerBlockHandler() {
return new JsonResult(200, "客户自定义限流处理逻辑", new Payment(20200906L, UUID.randomUUID().toString()));
}
主要做了两件事:
通过@SentinelResource注解的blockHandler属性制定具体的处理函数
实现处理函数,该函数的传参必须与资源点的传参一样,并且最后加上BlockException异常参数;同时,返回类型也必须一样。
如果熟悉Hystrix的读者应该会发现,这样的设计与HystrixCommand中定义fallback很相似,还是很容易理解的
【c】Sentinel配置
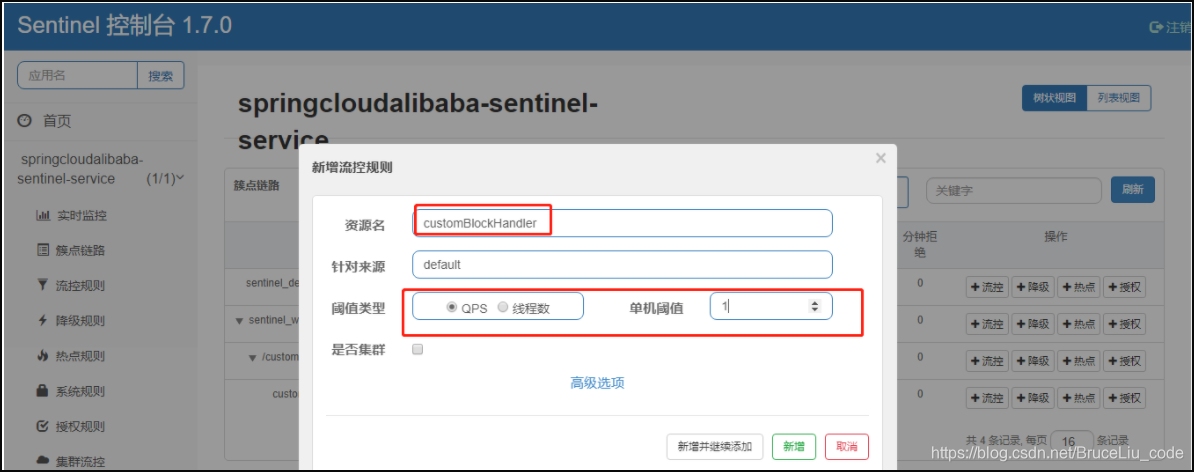
【d】测试
浏览器正常访问:http://localhost:8401/customBlockHandler
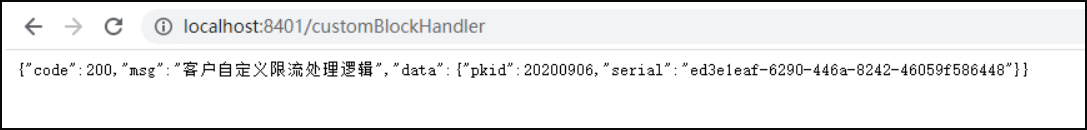
一秒一下,一秒一下,都是正常访问,也就是一秒内只发了一次请求,下面我们一秒内疯狂请求该接口:http://localhost:8401/customBlockHandler
可以看到,由于我们指定的降级方法是customBlockHandlerMethodA,所以当流量超过阈值时,降级处理的也是customBlockHandlerMethodA方法的逻辑。 通过以上方式,将所有的降级处理抽离出来,这样有利于与业务逻辑之间的解耦,推荐使用。
4.更多注解属性说明
查看 Sentinel的源码,可以看到 SentinelResource 定义了value,entryType,resourceType,blockHandler,fallback,defaultFallback等属性,源码如下:
/*
* Copyright 1999-2018 Alibaba Group Holding Ltd.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.EntryType;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* The annotation indicates a definition of Sentinel resource.
*
* @author Eric Zhao
* @since 0.1.1
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface SentinelResource {
/**
* @return name of the Sentinel resource
*/
String value() default "";
/**
* @return the entry type (inbound or outbound), outbound by default
*/
EntryType entryType() default EntryType.OUT;
/**
* @return the classification (type) of the resource
* @since 1.7.0
*/
int resourceType() default 0;
/**
* @return name of the block exception function, empty by default
*/
String blockHandler() default "";
/**
* The {@code blockHandler} is located in the same class with the original method by default.
* However, if some methods share the same signature and intend to set the same block handler,
* then users can set the class where the block handler exists. Note that the block handler method
* must be static.
*
* @return the class where the block handler exists, should not provide more than one classes
*/
Class<?>[] blockHandlerClass() default {
};
/**
* @return name of the fallback function, empty by default
*/
String fallback() default "";
/**
* The {@code defaultFallback} is used as the default universal fallback method.
* It should not accept any parameters, and the return type should be compatible
* with the original method.
*
* @return name of the default fallback method, empty by default
* @since 1.6.0
*/
String defaultFallback() default "";
/**
* The {@code fallback} is located in the same class with the original method by default.
* However, if some methods share the same signature and intend to set the same fallback,
* then users can set the class where the fallback function exists. Note that the shared fallback method
* must be static.
*
* @return the class where the fallback method is located (only single class)
* @since 1.6.0
*/
Class<?>[] fallbackClass() default {
};
/**
* @return the list of exception classes to trace, {@link Throwable} by default
* @since 1.5.1
*/
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToTrace() default {
Throwable.class};
/**
* Indicates the exceptions to be ignored. Note that {@code exceptionsToTrace} should
* not appear with {@code exceptionsToIgnore} at the same time, or {@code exceptionsToIgnore}
* will be of higher precedence.
*
* @return the list of exception classes to ignore, empty by default
* @since 1.6.0
*/
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore() default {
};
}
下面解释下这几个属性的作用:
value:资源名称,必需项,因为需要通过resource name找到对应的规则,这个是必须配置的。entryType:entry 类型,可选项,有IN和OUT两个选项,默认为 EntryType.OUT。
public enum EntryType {
IN("IN"),
OUT("OUT");
}
blockHandler:blockHandler 对应处理 BlockException 的函数名称,可选项。blockHandler 函数访问范围需要是 public,返回类型需要与原方法相匹配,参数类型需要和原方法相匹配并且最后加一个额外的参数,类型为 BlockException。blockHandlerClass:blockHandler 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中,如果希望使用其他类的函数,则需要指定 blockHandlerClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。fallback:fallback 函数名称,可选项,用于在抛出异常的时候提供 fallback 处理逻辑。fallback 函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了 exceptionsToIgnore 里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。fallbackClass:fallbackClass的应用和blockHandlerClass类似,fallback 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 fallbackClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。defaultFallback(since 1.6.0):如果没有配置defaultFallback方法,默认都会走到这里来。默认的 fallback 函数名称,可选项,通常用于通用的 fallback 逻辑。默认 fallback 函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了 exceptionsToIgnore 里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。若同时配置了 fallback 和 defaultFallback,则只有 fallback 会生效。exceptionsToIgnore(since 1.6.0):用于指定哪些异常被排除掉,不会计入异常统计中,也不会进入 fallback 逻辑中,而是会原样抛出。
注:1.6.0 之前的版本 fallback 函数只针对降级异常(DegradeException)进行处理,不能针对业务异常进行处理。
5.总结
本篇文章主要总结了如何使用@SentinelResource注解灵活的定义控制资源以及如何配置控制策略,实现了对于某个方法的调用限流或者某个外部资源的调用限流等控制。