最近在复习数据结构 二叉树。
现在用的是Java 语言, 代码实现了测量深度和大小的 方法。
最主要的 是二叉树的 遍历 。
用了非递归和 递归的方法 来实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历。
代码和注释如下:
import java.util.Stack;
/*
* 此类 构造了二叉树 以及二叉树的递归遍历与非递归遍历
*/
public class BinaryTree {
//根节点
private TreeNode root = null;
/*
* Bingtree的构造函数
*/
public BinaryTree() {
root = new TreeNode(1, "A");
}
/*
* 下面构造节点和关系
* A
* B C
* D E F
*/
public void createBinaryTree() {
//构造节点
TreeNode nodeB = new TreeNode(2, "B");
TreeNode nodeC = new TreeNode(3, "C");
TreeNode nodeD = new TreeNode(4, "D");
TreeNode nodeE = new TreeNode(5, "E");
TreeNode nodeF = new TreeNode(6, "F");
//构造关系
root.leftChild = nodeB;
root.rightChild = nodeC;
nodeB.leftChild = nodeD;
nodeB.rightChild = nodeE;
nodeC.rightChild = nodeF;
}
/*
* 迭代法 求出树的高度
*/
public int getHeight() {
return getHeight(root);
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode node) {
//节点为空 那么高度就为0;
if(node == null)
return 0;
else {
// i 和j的作用就是记录数有多高,不断迭代一个节点的左子树和右子数,直到子数出现空的情况
int i = getHeight(node.leftChild);
int j = getHeight(node.rightChild);
//i 和 j的比较是为了求出高度的最大值
return (i<j)?j+1:i+1 ;
}
}
/*
* 迭代法求树的大小
*/
public int getSize() {
return getSize(root);
}
public int getSize(TreeNode node) {
//空节点大小为0
if(node == null)
return 0;
else {
return 1+getSize(node.leftChild)+getSize(node.rightChild);
}
}
/*
* 迭代法实现 先顺遍历
*/
public void preOrder(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null)
return;
else {
System.out.println("preOrder data:"+node.data);
preOrder(node.leftChild);
preOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
/*
* 迭代法实现 中序遍历
*/
public void midOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null)
return;
else {
midOrder(node.leftChild);
System.out.println("midOrder data"+node.data);
midOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
/*
* 迭代法实现 后序遍历
*/
public void lastOrder(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null)
return;
else {
lastOrder(node.leftChild);
lastOrder(node.rightChild);
System.out.println("lastOrder data"+node.data);
}
}
/*
* 非迭代法实现 先序遍历
*
* 此方法主要使用栈这种数据结构
* 首先将 根节点压入一个栈中 , 再将根节点弹出栈
* 压入根节点的左右子节点(注意的时 右节点要在左节点下面,因为栈是从上面弹出的)
* 接着类似的操作 弹出根节点 加入子节点(没有子节点不进行操作)
* 弹出栈的顺序就是 先序遍历的顺序
*
*
*/
public void nonRecOrder(TreeNode node) {
//空节点直接返回
if(node == null)
return;
//创建一个栈 来存节点
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//传入根节点
stack.push(node);
//栈不为空接着操作
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
//弹出根节点
TreeNode n = stack.pop();
//打印弹出节点
System.out.println("nonPreOrder data:"+n.data);
//压入根节点的子节点
if(n.rightChild != null) //必须要用if判断 因为若果一个节点没有左或者右子节点 就会报空指针异常
stack.push(n.rightChild);
if(n.leftChild != null)
stack.push(n.leftChild);
}
}
/*
* 非迭代法实现 中序遍历
* 思想:
* 传入 A 节点
* A节点不为空 则将操作单位移到A的左孩子上 (B)
* 看B为不为空 不为空就一直移动到左孩子身上
*
* 最终某个节点的左孩子为空
* 那么弹出栈顶节点(就是这个节点)
* 操作单位移动到这个节点的右孩子上
*
*
*/
public void nonmidOrder(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null)
return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode temp = node;
//栈为空 且 节点空的时候退出
while(!stack.isEmpty() || temp!=null){
//当一个节点的左孩子不为空
if(temp != null) {
//不断向左孩子遍历的过程
stack.push(temp);
temp = temp.leftChild;
}else {
//当一个节点的左孩子为空
//返回此节点根节点
TreeNode bT = stack.pop();
//打印此节点的根节点
System.out.println("nonmidOrder data:"+bT.data);
//遍历此节点根节点的后孩子
temp = bT.rightChild;
}
}
}
/*
* 非迭代法实现 后序遍历
* 要用到两个栈,根节点首先入栈1,然后栈1依次出栈,
* 每次出栈时该元素入栈2并将左右孩子压入栈1。最后得到的栈2依次出栈就是后序遍历结果
*
*/
public void nonlastOrder(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null)
return ;
//需要使用两个栈
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<TreeNode>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//
stack1.push(node);
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode tr = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(tr);
if(tr.leftChild != null)
stack1.push(tr.leftChild);
if(tr.rightChild != null)
stack1.push(tr.rightChild);
}
while(!stack2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("nonlastOrder data:"+stack2.pop().data);
}
}
/*
* 构造节点类
*/
public class TreeNode{
private int index ; //节点的下标
private String data; //节点的数据
private TreeNode leftChild; //节点的左子数
private TreeNode rightChild; //节点的右子数
public int getIndex() {
return index;
}
public void setIndex(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
public String getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
//节点的构造函数
public TreeNode(int index,String data) {
this.index = index;
this.data = data;
this.leftChild = null;
this.rightChild = null;
}
}
public static void main(String []args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
binaryTree.createBinaryTree();
System.out.println("树的高度为:"+binaryTree.getHeight());
System.out.println("树的大小为:"+binaryTree.getSize());
// 迭代 前 中 后 遍历
binaryTree.preOrder(binaryTree.root);
binaryTree.midOrder(binaryTree.root);
binaryTree.lastOrder(binaryTree.root);
//非迭代 实现 前 中 后 遍历
binaryTree.nonRecOrder(binaryTree.root);
binaryTree.nonmidOrder(binaryTree.root);
binaryTree.nonlastOrder(binaryTree.root);
}
}
结果如图所示:
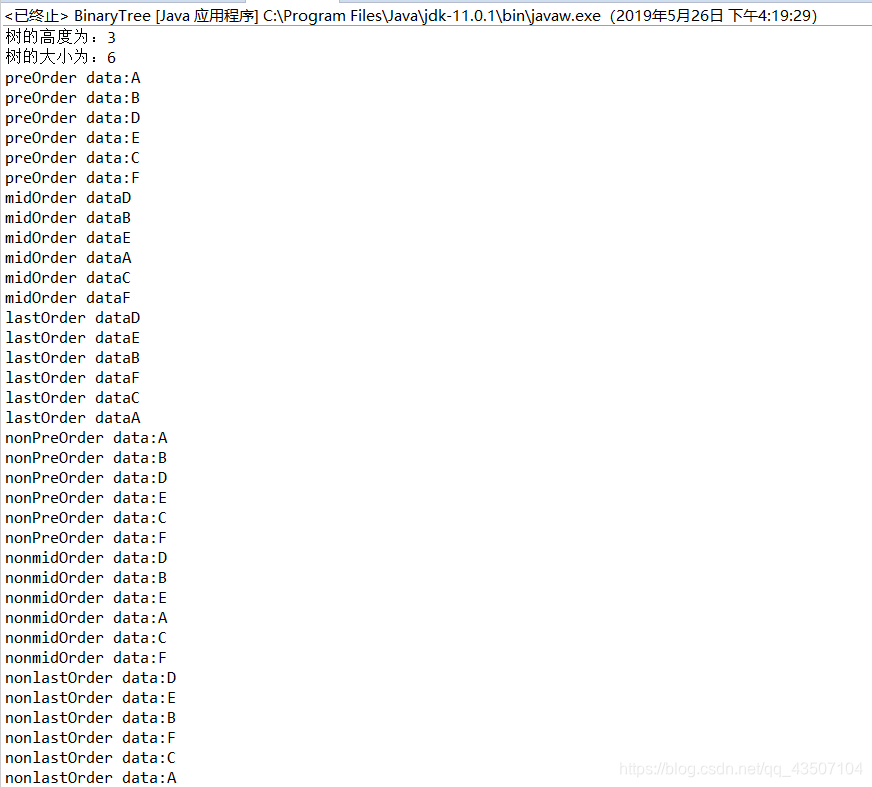
有的方法我解释的不是很容易懂,想要理解的透彻些可以举例子带入,自己用笔算一算更容易理解一些