在图像中寻找轮廓
例程
教程的代码在下面给出. 你也可以从 这里 下载
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat src; Mat src_gray;
int thresh = 100;
int max_thresh = 255;
RNG rng(12345);
/// Function header
void thresh_callback(int, void* );
/** @function main */
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/// 加载源图像
src = imread( argv[1], 1 );
/// 转成灰度并模糊化降噪
cvtColor( src, src_gray, CV_BGR2GRAY );
blur( src_gray, src_gray, Size(3,3) );
/// 创建窗体
char* source_window = "Source";
namedWindow( source_window, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( source_window, src );
createTrackbar( " Canny thresh:", "Source", &thresh, max_thresh, thresh_callback );
thresh_callback( 0, 0 );
waitKey(0);
return(0);
}
/** @function thresh_callback */
void thresh_callback(int, void* )
{
Mat canny_output;
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
/// 用Canny算子检测边缘
Canny( src_gray, canny_output, thresh, thresh*2, 3 );
/// 寻找轮廓
findContours( canny_output, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_TREE, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0) );
/// 绘出轮廓
Mat drawing = Mat::zeros( canny_output.size(), CV_8UC3 );
for( int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++ )
{
Scalar color = Scalar( rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0,255), rng.uniform(0,255) );
drawContours( drawing, contours, i, color, 2, 8, hierarchy, 0, Point() );
}
/// 在窗体中显示结果
namedWindow( "Contours", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( "Contours", drawing );
}
例程说明¶
结果
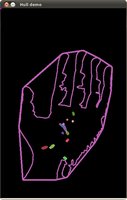
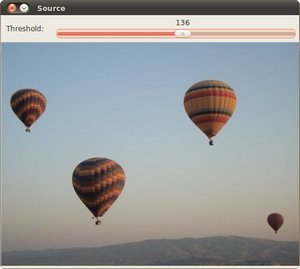
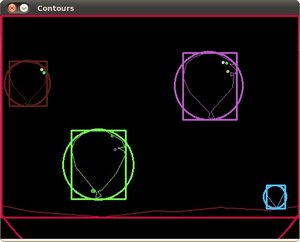
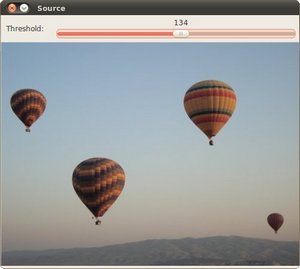
原图和检测到的轮廓如下:


计算物体的凸包
例程
教程的代码在下面给出. 你也可以从 这里 下载
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat src; Mat src_gray;
int thresh = 100;
int max_thresh = 255;
RNG rng(12345);
/// Function header
void thresh_callback(int, void* );
/** @function main */
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/// 加载源图像
src = imread( argv[1], 1 );
/// 转成灰度图并进行模糊降噪
cvtColor( src, src_gray, CV_BGR2GRAY );
blur( src_gray, src_gray, Size(3,3) );
/// 创建窗体
char* source_window = "Source";
namedWindow( source_window, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( source_window, src );
createTrackbar( " Threshold:", "Source", &thresh, max_thresh, thresh_callback );
thresh_callback( 0, 0 );
waitKey(0);
return(0);
}
/** @function thresh_callback */
void thresh_callback(int, void* )
{
Mat src_copy = src.clone();
Mat threshold_output;
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
/// 对图像进行二值化
threshold( src_gray, threshold_output, thresh, 255, THRESH_BINARY );
/// 寻找轮廓
findContours( threshold_output, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_TREE, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0) );
/// 对每个轮廓计算其凸包
vector<vector<Point> >hull( contours.size() );
for( int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++ )
{ convexHull( Mat(contours[i]), hull[i], false ); }
/// 绘出轮廓及其凸包
Mat drawing = Mat::zeros( threshold_output.size(), CV_8UC3 );
for( int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++ )
{
Scalar color = Scalar( rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0,255), rng.uniform(0,255) );
drawContours( drawing, contours, i, color, 1, 8, vector<Vec4i>(), 0, Point() );
drawContours( drawing, hull, i, color, 1, 8, vector<Vec4i>(), 0, Point() );
}
/// 把结果显示在窗体
namedWindow( "Hull demo", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( "Hull demo", drawing );
}
创建包围轮廓的矩形和圆形边界框
代码
下面是本节教程源码. 你也可以从 这里 下载.
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat src; Mat src_gray;
int thresh = 100;
int max_thresh = 255;
RNG rng(12345);
/// 函数声明
void thresh_callback(int, void* );
/** @主函数 */
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/// 载入原图像, 返回3通道图像
src = imread( argv[1], 1 );
/// 转化成灰度图像并进行平滑
cvtColor( src, src_gray, CV_BGR2GRAY );
blur( src_gray, src_gray, Size(3,3) );
/// 创建窗口
char* source_window = "Source";
namedWindow( source_window, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( source_window, src );
createTrackbar( " Threshold:", "Source", &thresh, max_thresh, thresh_callback );
thresh_callback( 0, 0 );
waitKey(0);
return(0);
}
/** @thresh_callback 函数 */
void thresh_callback(int, void* )
{
Mat threshold_output;
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
/// 使用Threshold检测边缘
threshold( src_gray, threshold_output, thresh, 255, THRESH_BINARY );
/// 找到轮廓
findContours( threshold_output, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_TREE, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0) );
/// 多边形逼近轮廓 + 获取矩形和圆形边界框
vector<vector<Point> > contours_poly( contours.size() );
vector<Rect> boundRect( contours.size() );
vector<Point2f>center( contours.size() );
vector<float>radius( contours.size() );
for( int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++ )
{ approxPolyDP( Mat(contours[i]), contours_poly[i], 3, true );
boundRect[i] = boundingRect( Mat(contours_poly[i]) );
minEnclosingCircle( contours_poly[i], center[i], radius[i] );
}
/// 画多边形轮廓 + 包围的矩形框 + 圆形框
Mat drawing = Mat::zeros( threshold_output.size(), CV_8UC3 );
for( int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++ )
{
Scalar color = Scalar( rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0,255), rng.uniform(0,255) );
drawContours( drawing, contours_poly, i, color, 1, 8, vector<Vec4i>(), 0, Point() );
rectangle( drawing, boundRect[i].tl(), boundRect[i].br(), color, 2, 8, 0 );
circle( drawing, center[i], (int)radius[i], color, 2, 8, 0 );
}
/// 显示在一个窗口
namedWindow( "Contours", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( "Contours", drawing );
}
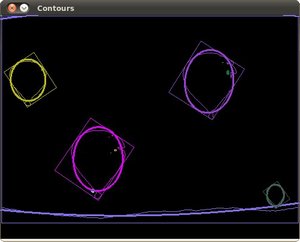
为轮廓创建可倾斜的边界框和椭圆
例程
例程的代码在下面显示. 你也可以从 这里 下载
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat src; Mat src_gray;
int thresh = 100;
int max_thresh = 255;
RNG rng(12345);
/// Function header
void thresh_callback(int, void* );
/** @function main */
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/// 加载源图像
src = imread( argv[1], 1 );
/// 转为灰度图并模糊化
cvtColor( src, src_gray, CV_BGR2GRAY );
blur( src_gray, src_gray, Size(3,3) );
/// 创建窗体
char* source_window = "Source";
namedWindow( source_window, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( source_window, src );
createTrackbar( " Threshold:", "Source", &thresh, max_thresh, thresh_callback );
thresh_callback( 0, 0 );
waitKey(0);
return(0);
}
/** @function thresh_callback */
void thresh_callback(int, void* )
{
Mat threshold_output;
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
/// 阈值化检测边界
threshold( src_gray, threshold_output, thresh, 255, THRESH_BINARY );
/// 寻找轮廓
findContours( threshold_output, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_TREE, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0) );
/// 对每个找到的轮廓创建可倾斜的边界框和椭圆
vector<RotatedRect> minRect( contours.size() );
vector<RotatedRect> minEllipse( contours.size() );
for( int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++ )
{ minRect[i] = minAreaRect( Mat(contours[i]) );
if( contours[i].size() > 5 )
{ minEllipse[i] = fitEllipse( Mat(contours[i]) ); }
}
/// 绘出轮廓及其可倾斜的边界框和边界椭圆
Mat drawing = Mat::zeros( threshold_output.size(), CV_8UC3 );
for( int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++ )
{
Scalar color = Scalar( rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0,255), rng.uniform(0,255) );
// contour
drawContours( drawing, contours, i, color, 1, 8, vector<Vec4i>(), 0, Point() );
// ellipse
ellipse( drawing, minEllipse[i], color, 2, 8 );
// rotated rectangle
Point2f rect_points[4]; minRect[i].points( rect_points );
for( int j = 0; j < 4; j++ )
line( drawing, rect_points[j], rect_points[(j+1)%4], color, 1, 8 );
}
/// 结果在窗体中显示
namedWindow( "Contours", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( "Contours", drawing );
}
轮廓矩
目标
在这节教程中您将学到:
- 使用OpenCV函数 moments 计算图像所有的矩(最高到3阶)
- 使用OpenCV函数 contourArea 来计算轮廓面积
- 使用OpenCV函数 arcLength 来计算轮廓或曲线长度
代码
下面是本节教程源码. 你也可以从 这里 下载.
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat src; Mat src_gray;
int thresh = 100;
int max_thresh = 255;
RNG rng(12345);
/// 函数声明
void thresh_callback(int, void* );
/** @主函数 */
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/// 读入原图像, 返回3通道图像数据
src = imread( argv[1], 1 );
/// 把原图像转化成灰度图像并进行平滑
cvtColor( src, src_gray, CV_BGR2GRAY );
blur( src_gray, src_gray, Size(3,3) );
/// 创建新窗口
char* source_window = "Source";
namedWindow( source_window, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( source_window, src );
createTrackbar( " Canny thresh:", "Source", &thresh, max_thresh, thresh_callback );
thresh_callback( 0, 0 );
waitKey(0);
return(0);
}
/** @thresh_callback 函数 */
void thresh_callback(int, void* )
{
Mat canny_output;
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
/// 使用Canndy检测边缘
Canny( src_gray, canny_output, thresh, thresh*2, 3 );
/// 找到轮廓
findContours( canny_output, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_TREE, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0) );
/// 计算矩
vector<Moments> mu(contours.size() );
for( int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++ )
{ mu[i] = moments( contours[i], false ); }
/// 计算中心矩:
vector<Point2f> mc( contours.size() );
for( int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++ )
{ mc[i] = Point2f( mu[i].m10/mu[i].m00 , mu[i].m01/mu[i].m00 ); }
/// 绘制轮廓
Mat drawing = Mat::zeros( canny_output.size(), CV_8UC3 );
for( int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++ )
{
Scalar color = Scalar( rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0,255), rng.uniform(0,255) );
drawContours( drawing, contours, i, color, 2, 8, hierarchy, 0, Point() );
circle( drawing, mc[i], 4, color, -1, 8, 0 );
}
/// 显示到窗口中
namedWindow( "Contours", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( "Contours", drawing );
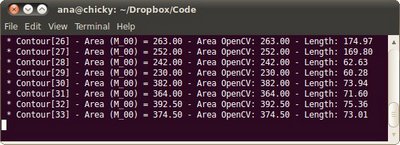
/// 通过m00计算轮廓面积并且和OpenCV函数比较
printf("\t Info: Area and Contour Length \n");
for( int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++ )
{
printf(" * Contour[%d] - Area (M_00) = %.2f - Area OpenCV: %.2f - Length: %.2f \n", i, mu[i].m00, contourArea(contours[i]), arcLength( contours[i], true ) );
Scalar color = Scalar( rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0,255), rng.uniform(0,255) );
drawContours( drawing, contours, i, color, 2, 8, hierarchy, 0, Point() );
circle( drawing, mc[i], 4, color, -1, 8, 0 );
}
}
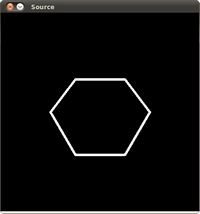
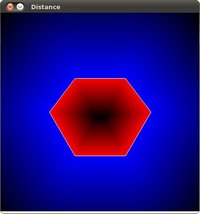
多边形测试
代码
本教程代码如下所示. 用户也可以点击 这里下载
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
/** @function main */
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/// 创建一个图形 const int r = 100;
Mat src = Mat::zeros( Size( 4*r, 4*r ), CV_8UC1 );
/// 绘制一系列点创建一个轮廓:
vector<Point2f> vert(6);
vert[0] = Point( 1.5*r, 1.34*r );
vert[1] = Point( 1*r, 2*r );
vert[2] = Point( 1.5*r, 2.866*r );
vert[3] = Point( 2.5*r, 2.866*r );
vert[4] = Point( 3*r, 2*r );
vert[5] = Point( 2.5*r, 1.34*r );
/// 在src内部绘制
for( int j = 0; j < 6; j++ )
{ line( src, vert[j], vert[(j+1)%6], Scalar( 255 ), 3, 8 ); }
/// 得到轮廓
vector<vector<Point> > contours; vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
Mat src_copy = src.clone();
findContours( src_copy, contours, hierarchy, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
/// 计算到轮廓的距离
Mat raw_dist( src.size(), CV_32FC1 );
for( int j = 0; j < src.rows; j++ )
{ for( int i = 0; i < src.cols; i++ )
{ raw_dist.at<float>(j,i) = pointPolygonTest( contours[0], Point2f(i,j), true ); }
}
double minVal; double maxVal;
minMaxLoc( raw_dist, &minVal, &maxVal, 0, 0, Mat() );
minVal = abs(minVal); maxVal = abs(maxVal);
/// 图形化的显示距离
Mat drawing = Mat::zeros( src.size(), CV_8UC3 );
for( int j = 0; j < src.rows; j++ )
{ for( int i = 0; i < src.cols; i++ )
{
if( raw_dist.at<float>(j,i) < 0 )
{ drawing.at<Vec3b>(j,i)[0] = 255 - (int) abs(raw_dist.at<float>(j,i))*255/minVal; }
else if( raw_dist.at<float>(j,i) > 0 )
{ drawing.at<Vec3b>(j,i)[2] = 255 - (int) raw_dist.at<float>(j,i)*255/maxVal; }
else
{ drawing.at<Vec3b>(j,i)[0] = 255; drawing.at<Vec3b>(j,i)[1] = 255; drawing.at<Vec3b>(j,i)[2] = 255; }
}
}
/// 创建窗口显示结果
char* source_window = "Source";
namedWindow( source_window, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( source_window, src );
namedWindow( "Distance", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( "Distance", drawing );
waitKey(0);
return(0);
}
解释¶
from: http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/doc/tutorials/imgproc/table_of_content_imgproc/table_of_content_imgproc.html#table-of-content-imgproc