I especially remember that during the Chinese New Year, everyone in the north was celebrating the Spring Festival, while some cities in the south were already looking for opportunities for migrant workers to go overseas next year.
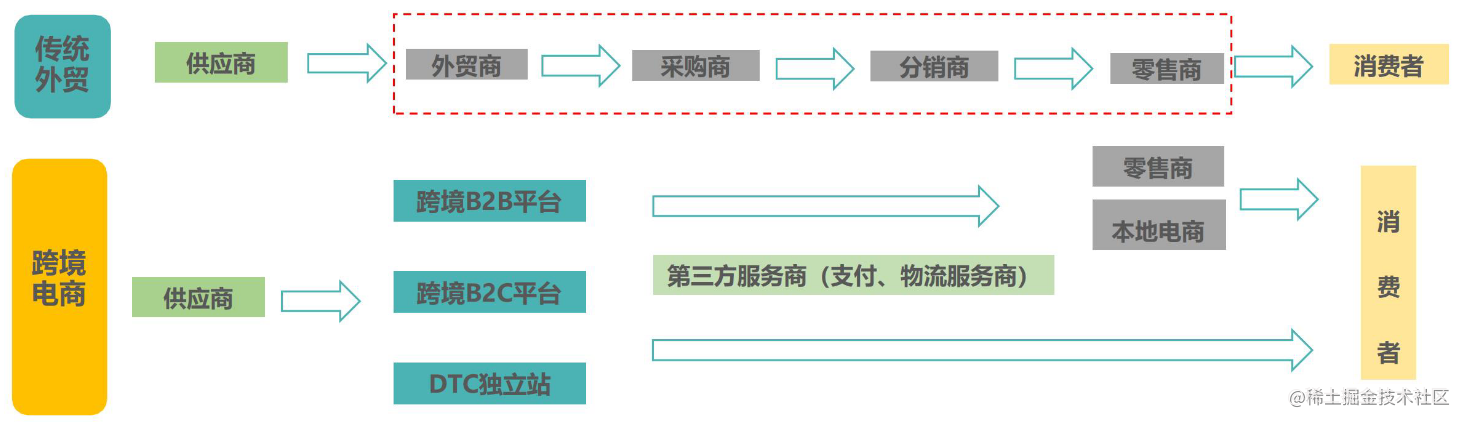
Since 2020, the COVID-19 epidemic has swept the world, global retail links have been impacted, and consumers have moved online on a large scale. Online retail in major countries and regions around the world has entered a period of rapid growth, which has also provided sufficient growth for the development of cross-border e-commerce. space. In addition, driven by independent websites, live short videos, and social media, the cross-border e-commerce DTC model has experienced explosive growth, creating new links for overseas companies. Cross-border e-commerce has entered a multi-mode parallel stage, and at the same time, a new Cross-border e-commerce industry ecology.
The big difference between cross-border e-commerce and domestic payment methods is that domestic payment methods prefer online Alipay or WeChat payment, while foreign ones mainly use credit cards. This is because on the one hand, in some developed countries, the penetration rate of credit cards is quite high, and people are accustomed to using credit cards for payment. Credit cards are globally applicable, making it easier for people to make purchases in different countries and regions. On the other hand, foreign banking systems are relatively sound, and credit card payments have complete online payment systems and relevant regulations, making credit card payments one of the main payment methods. .

This leads to the risk of fraud: chargebacks, stolen cards
Payment Fraud: Chargebacks & Stolen Cards
There are many reasons for chargebacks:
- False Transactions : A consumer may claim to have never made a particular transaction, or claim that the transaction was not authorized, in the hope of receiving a full refund.
- Goods or Services Not Received: Consumers may claim that they did not receive goods or services and thus request a refund. In some cases, this may be real, but sometimes it may be fraudulent and they intend to achieve "zero dollar purchases" this way.
- The goods or services are not as described: They may also claim that the goods they received are not as described by the seller or have quality problems, and demand a refund on this basis.
- Malicious refunds: In addition, after receiving goods or services, you may deliberately initiate a refund request to obtain additional refunds or free goods.
Card theft occurs when fraudsters use stolen card information to pay after purchasing goods. When the owner discovers that his or her card has been stolen, he or she will call the bank to reverse the transaction and charge back the transaction. At this time, the merchant has sent the goods to the buyer, thus facing the situation of losing both money and goods.
These two situations are actually problems that are often faced in the field of cross-border e-commerce. If these two problems are serious, the third-party payment account used by the merchant will be frozen or even blocked, which means that the merchant can no longer use this channel to conduct any cross-border transactions. Overseas sales will directly hinder the brand’s overseas sales and even threaten the survival of the entire company.
Therefore, cross-border e-commerce merchants are currently committed to finding suitable solutions.
In this article, we just want to briefly talk about the solution.
Payment fraud solutions
On the one hand, from the perspective of the business itself, it is natural to do what it can, for example:
- Provide detailed product descriptions and service policies: including product specifications, functional characteristics, quality assurance and other information to reduce disputes about products that do not match the description. At the same time, clarify and publicize the refund policy and after-sales service terms to let buyers understand the relevant regulations.
- Cooperation and information sharing: Join relevant industry associations or organizations, participate in information sharing and cooperation mechanisms, understand the latest developments and preventive measures for payment fraud, and work with other merchants to resist fraud.
However, this is just a very routine operation and does not ensure the security of payment, so you can consider starting from a technical perspective.
-
Strengthened identity verification: During the transaction process, merchants can use multiple identity verification measures, such as requiring buyers to provide identification, verify payment account information, use payment passwords or verification codes, etc., to ensure the authenticity of the buyer's identity.
-
Monitor abnormal transaction behavior: Merchants should establish an effective risk monitoring system to detect abnormal transaction behavior by monitoring transaction patterns, order quantities, transaction amounts and other indicators. For example, consecutive large orders, frequent changes to shipping addresses, and unusual purchasing patterns may be signs of fraud.
-
Deploy professional anti-fraud products
Simply relying on merchants to manually determine fraud risks is very inefficient, so it is important to deploy a professional business security service. The Dingxiang risk control system conducts in-depth analysis of consumer portraits, conducts multi-dimensional, in-depth analysis and big data matching to accurately identify abnormal transactions, helps risk review rules and systems, and helps cross-border sellers create a healthy and safe trading environment.
Based on the above characteristics of cross-border e-commerce payment fraud, we recommend:
- Timely detect malicious and fraudulent accounts through external mobile phone number risk scoring, IP risk database, agent email detection, etc.
- Detect whether the device fingerprint of the client (or browser) is legal, whether there are injections, hooks, and simulators, and promptly discover batch cheating software risks.
- Detect and intercept abnormal behaviors such as frequent orders placed by the same device (or the same user), a large number of accounts associated with the same device, and a large number of orders associated with the same delivery location. Accounts with abnormal behavior are marked and stored in the corresponding list database. Follow-up focused investigations will be carried out.
- Based on risk control data and business precipitation data, the scenario of user placing an order is modeled. The output of the model can be directly used in risk control strategies to explore potential risks and further improve security.
Today we mainly analyze the risks brought by payment fraud from the perspective of merchant owners. In the next article, we will try to show the code to see if we can solve this problem from the code level.