
Pregunta del DO de lista única enlazada
Prefacio
¡Esta vez hay dos preguntas de práctica!
Es un poco difícil, ¡pero creo que no será difícil para todos!
También daré enlaces a las dos preguntas sobre el DO, para que todos deberían probarlo rápidamente.
1. Devuelva el primer nodo donde la lista vinculada comienza a ingresar al bucle.
Enlace de pregunta: enlace del DO


pista:
El número de nodos en la lista vinculada oscila entre [0, 104]
-105 <= Node.val <= 105.
El valor de pos es -1 o un índice válido en la lista vinculada.
Hay dos ideas analíticas para esta pregunta ~


Idea 1

Demostración de código:
//解题方法一
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode *move1=head;
struct ListNode *move2=head;
while(move1&&move2&&move2->next){
//快慢指针移动
move1=move1->next;
move2=move2->next->next;
if(move1==move2){
{
//找到相遇点
struct ListNode *meet=move1;//meet从相遇点开始移动
struct ListNode *move3=head;//move3从head开始移动
while(meet!=move3){
//两个指针同时移动找到起始点
meet=meet->next;
move3=move3->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}
idea 2

Consejo: Si no sabes cómo encontrar puntos en común, ¡el blog anterior te ayudará!
Enlace del blog: Pregunta del DO de lista única enlazada
Demostración de código:
//解题方法二
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode *move1=head;
struct ListNode *move2=head;
while(move1&&move2&&move2->next){
//快慢指针移动
move1=move1->next;
move2=move2->next->next;
if(move1==move2){
//找到相遇点
struct ListNode *temp=move1;//保存相遇点位置
move1=move1->next;//将move1变为第二链表起始点
temp->next=NULL;//将相遇点的next置空
struct ListNode *head1=head;
struct ListNode *head2=move1;
int len1=0,len2=0;
while(head1!=NULL){
//计算链表长度
len1++;
head1=head1->next;
}
while(head2!=NULL){
head2=head2->next;
len2++;
}
int k=abs(len1-len2);//得到两链表长度相减的绝对值
//将longs指向较长的链表,shorts指向较短的链表
struct ListNode *shorts=head;
struct ListNode *longs=move1;
if(len1>len2){
shorts=move1;
longs=head;
}
while(k--&&longs!=NULL){
//较长的链表移动k位
longs=longs->next;
}
if(k>0&&longs==NULL){
return NULL;
}
while(shorts!=longs){
//两链表同时遍历,找到第一个公共点
shorts=shorts->next;
longs=longs->next;
}
return longs;
}
}
return NULL;
}
2. Devolver una copia profunda de la lista vinculada
Enlace de pregunta: enlace del DO



pista:
0 <= n <= 1000
-104 <= Node.val <= 104
Node.random es nulo o apunta a un nodo en la lista vinculada.
Ideas para resolver problemas:

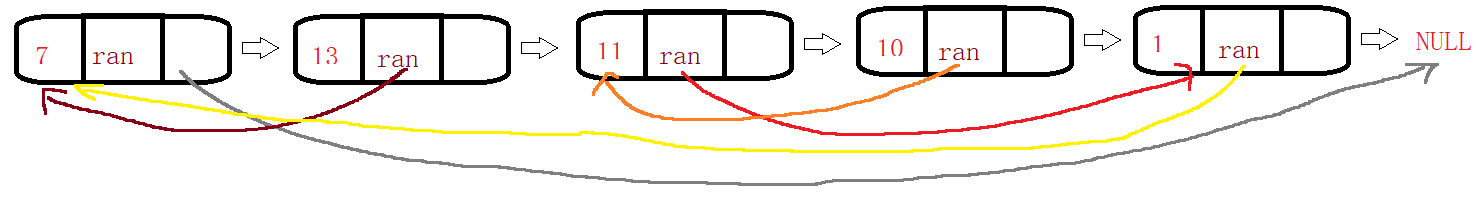
demostración de código
struct Node* BuyNewnode(int x){
//创建结点函数
struct Node*newnode=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newnode->val=x;
newnode->next=NULL;
newnode->random=NULL;
return newnode;
}
//查找random所在位置的函数
struct Node* findrandom(struct Node* head,struct Node* newhead,struct Node* random){
struct Node*move1=head;
struct Node*move2=newhead;
while(move1!=random){
move1=move1->next;
move2=move2->next;
}
return move2;
}
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
struct Node*move=head;
struct Node*newhead=NULL;
struct Node*tail=NULL;
while(move!=NULL){
//将新建结点依次尾插到新链表中
if(tail==NULL){
struct Node*newnode= BuyNewnode(move->val);
newhead=tail=newnode;
move=move->next;
}
else{
struct Node*newnode= BuyNewnode(move->val);
tail->next=newnode;
tail=tail->next;
move=move->next;
}
}
struct Node*setran=newhead;
struct Node*findran=head;
while(setran&&findran){
struct Node*temp=findrandom(head,newhead,findran->random);
setran->random=temp;
setran=setran->next;
findran=findran->next;
}
return newhead;
}
Resumir
¡Esta vez las preguntas son un poco más difíciles!
¡Pero definitivamente no será un problema para todos!
¡vamos! ¡vamos!