Autor
You Yuxi, chino, creador de Vue.js, fundador de Vue Technology, está comprometido con la investigación y el desarrollo de Vue.
Una entrevista sobre el autor: https://www.jianshu.com/p/3092b382ee80
Adjunte una foto de ídolo:

Sobre Vue
Vue (pronunciación / vjuː /, similar a view) es un marco progresivo para construir interfaces de usuario. A diferencia de otros marcos grandes, Vue está diseñado para aplicarse capa por capa de abajo hacia arriba. La biblioteca principal de Vue solo se enfoca en la capa de vista, que no solo es fácil de comenzar, sino también fácil de integrar con bibliotecas de terceros o proyectos existentes. Por otro lado, cuando se combina con una cadena de herramientas moderna y varias bibliotecas de soporte, Vue también es totalmente capaz de impulsar aplicaciones complejas de una sola página.
Características (de todos modos es bueno, solo úsalo)
- Documentación completa, el soporte chino es súper amigable
- Potente sistema periférico
- Fácil de usar
- Fácil de integrar con otras bases de código.
- El archivo central es pequeño
- Desarrollo de componentes
- Modelo de objeto de documento virtual (DOM virtual), excelente rendimiento
- El concepto de un marco progresivo, es decir, "es a la vez un marco y no un marco"
- Proporcionar un marco de componentes de un solo archivo compilados como módulos ES que admiten preprocesadores híbridos
Instalar
<!-- 开发环境版本,包含了有帮助的命令行警告 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<!-- 生产环境版本,优化了尺寸和速度 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
Comprenda cómo template-Vue genera HTML
Ejemplo-1
Use {{}} para incrustar los datos en js en HTML
Archivos HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>vue-01-hello</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/start.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Archivo JS
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
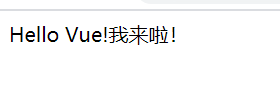
message: 'Hello Vue!我来啦!',
}
})
Resultado de ejecución
Ejemplo 2
// 将message内容拆分,倒序,再组合。
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}
// 将name字符串和指定字符串拼接
{{ name + '-slfsjflsfs'}}
// 打印todo中的数据
{{ todo }}
// 判断isBusy真假,如果为true执行"非常忙",为false则执行"不怎么忙"
{{ isBusy ? "非常忙" : '不怎么忙' }}
// 模板中显示的值始终为字符串
// 例如myHtml: '<p style="color:red">这里是纯html</p>'
// 显示内容为:用模板显示: <p style="color:red">这里是纯html</p>
用模板显示: {{ myHtml }}
// 如果要用html显示变量中值,则使用 v-html
// 格式 v-html="变量"
<span v-html="myHtml"></span>
Archivos HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>vue-02-模板</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}
<div>
{{ name + '-slfsjflsfs'}}
</div>
<div>
{{ todo }}
</div>
<h3>现在忙不忙?</h3>
<p>{{ isBusy ? "非常忙" : '不怎么忙' }}</p>
<div>
用模板显示: {{ myHtml }}
</div>
<div>
用v-html显示
<span v-html="myHtml"></span>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/start.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Archivo JS
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!我来啦!',
name: 'Riy' + 'aaabbb',
todo: '学习Vue',
isBusy: false,
myHtml: '<p style="color:red">这里是纯html</p>',
}
})
Resultado de ejecución

Vue renderizado y encuadernación de páginas
Renderizado
// v-show控制html是否显示,为true时显示,为false是隐藏
<div v-show="true">v-show ???</div>
// 迭代对象数组中 index为索引值,todo为数组的每一项
v-for="(todo, index) in todoList"
// 迭代对象时,key为键,item为值
v-for="(item, key) in user"
// 样式绑定,这里使用了3种方式,其中 v-bind: 可简写为 :
// class直接绑定样式,绑定属性或属性数值
class="error"
v-bind:class="test1"
:class="[activeClass, errorClass]"
// v-model双向绑定(重要!)
// 三种修饰符,lazy:控制输入数据同步、number:控制数据为int,trim:去掉前后空格
// placeholder="edit me" 输入框默认值为 edit me
// 使用v-model,输入框默认值变为属性值
<input v-model.lazy="message" placeholder="edit me">
Archivos HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
.active {
background-color: yellow;
}
.error {
color: red;
border: 1px solid red;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
<title>vue-03-渲染和绑定</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 这里是条件渲染,使用v-if -->
<div v-if="isShow">
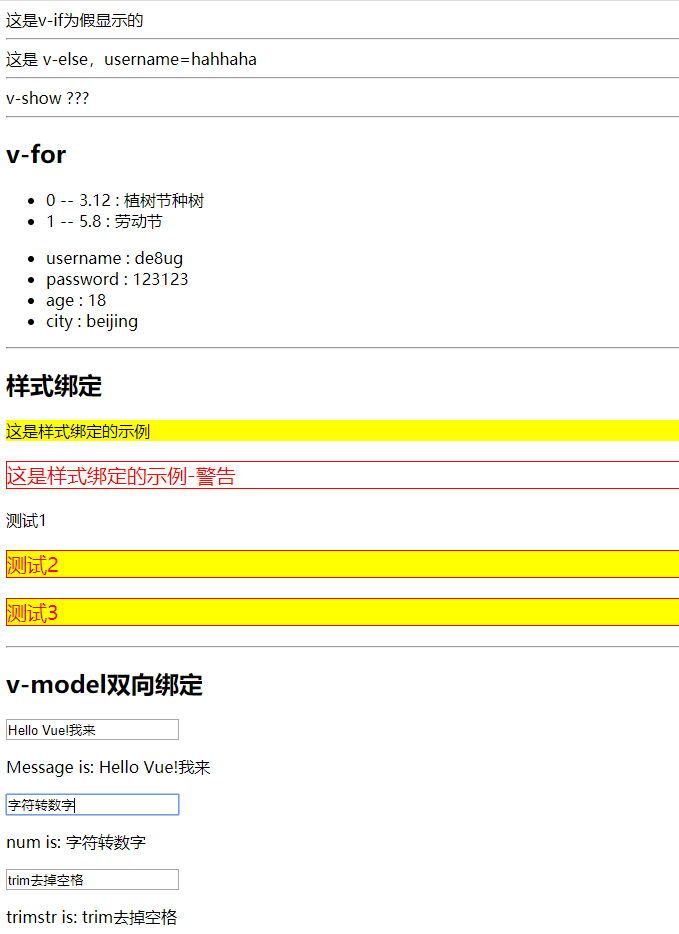
这是v-if为真显示的
</div>
<div v-else>
这是v-if为假显示的
</div>
<hr>
<div v-if="username=='Riy'">
这是:名字等于Riy
</div>
<div v-else-if="username=='lilei'">
这是:名字等于lilei
</div>
<div v-else>
这是 v-else,username={{ username }}
</div>
<hr>
<div v-show="true">
v-show ???
</div>
<hr>
<h2>v-for</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(todo, index) in todoList" :key="todo.id">
{{ index }} -- {{ todo.date }} : {{ todo.thing }}
</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, key) in user" :key="item.id">
{{ key }} : {{ item }}
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
<h2>样式绑定</h2>
<p class="active">这是样式绑定的示例</p>
<p class="error">这是样式绑定的示例-警告</p>
<p v-bind:class="test1">测试1</p>
<p :class="test2">测试2</p>
<p :class="[activeClass, errorClass]">测试3</p>
<hr>
<!-- v-model双向绑定,重要!!! -->
<h2>v-model双向绑定</h2>
<input v-model.lazy="message" placeholder="edit me">
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p>
<input v-model.number="num" placeholder="edit me">
<p>num is: {{ num }}</p>
<input v-model.trim="trimstr" placeholder="edit me">
<p>trimstr is: {{ trimstr }}</p>
<hr>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/start.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Archivo JS
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!我来啦!',
num: '字符转数字',
isShow: false,
trimstr: 'trim去掉空格',
username: 'hahhaha',
todoList: [
{date: '1.1', thing: '元旦快乐'},
{date: '3.12', thing: '植树节种树'},
{date: '5.8', thing: '劳动节'},
{date: '10.3', thing: '国庆节睡大觉'},
],
user: {
username: 'Riy',
password: '123123',
age: 23,
city: 'beijing'
},
test1: {
active: false
},
test2: {
active: true,
error: true
},
activeClass: 'active',
errorClass: 'error',
}
})
Resultado de ejecución
Vinculante
// v-on用于绑定事件,可简写为@
<button v-on:click="counter -= 1">减 1</button>
<button @click="counter -= 1">@@@减 1</button>
// 执行greet方法,逐层打印
<button @click="greet">Greet</button>
// 鼠标点击输入框,执行上层方法say,按按钮后再次执行say方法
// 两种事件修饰符,stop:停止事件冒泡传播,prevent:阻止默认行为
// 这里如果去掉.stop,则在执行button标签中的方法后会继续执行上层div的方法
<div class="error" @click="say('我是上层div')">
这里有个外层div
<input type="text" v-model="message">
<button @click.stop="say(message)">显示: {{message}}</button>
</div>
// @keyup.enter监听键盘回车事件
// 两种事件修饰符,stop:停止事件冒泡传播,prevent:阻止默认行为
// 这里如果去掉.prevent弹窗后会报错,因为submit默认会提交到action地址的后端,这里没有,所有会报错
<form action="">
<input type="text" @keyup.enter="submit('点击回车')">
<input type="submit" value="提交" @click.prevent="submit('提交数据')">
</form>
Archivos HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
.active {
background-color: yellow;
}
.error {
color: red;
border: 1px solid red;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
<title>vue-04-事件</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>事件</h2>
<button v-on:click="counter -= 1">减 1</button>
<button @click="counter -= 1">@@@减 1</button>
<p>点击按钮,counter= {{ counter }} .</p>
<hr>
<!-- `greet` 是在下面定义的方法名 -->
<button @click="greet">Greet</button>
<div class="error" @click="say('我是上层div')">
这里有个外层div
<input type="text" v-model="message">
<button @click.stop="say(message)">显示: {{message}}</button>
</div>
<hr>
<form action="">
<input type="text" @keyup.enter="submit('点击回车')">
<input type="submit" value="提交" @click.prevent="submit('提交数据')">
</form>
<hr>
<input type="text" @keyup.enter="submit('点击回车')">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/start.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Archivo JS
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
counter: 100,
message: 'Hello Vue!我来啦!',
methods: {
greet: function(event) {
alert('hahhaha!');
if (event) {
alert(event.target.tagName)
}
},
say: function(msg) {
alert(msg);
},
submit: function(data){
alert(data);
}
}
})