Supermarket
Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K
Total Submissions: 23513 Accepted: 10318
Description
A supermarket has a set Prod of products on sale. It earns a profit px for each product x∈Prod sold by a deadline dx that is measured as an integral number of time units starting from the moment the sale begins. Each product takes precisely one unit of time for being sold. A selling schedule is an ordered subset of products Sell ≤ Prod such that the selling of each product x∈Sell, according to the ordering of Sell, completes before the deadline dx or just when dx expires. The profit of the selling schedule is Profit(Sell)=Σx∈Sellpx. An optimal selling schedule is a schedule with a maximum profit.
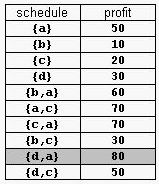
For example, consider the products Prod={a,b,c,d} with (pa,da)=(50,2), (pb,db)=(10,1), (pc,dc)=(20,2), and (pd,dd)=(30,1). The possible selling schedules are listed in table 1. For instance, the schedule Sell={d,a} shows that the selling of product d starts at time 0 and ends at time 1, while the selling of product a starts at time 1 and ends at time 2. Each of these products is sold by its deadline. Sell is the optimal schedule and its profit is 80.
Write a program that reads sets of products from an input text file and computes the profit of an optimal selling schedule for each set of products.
Input
A set of products starts with an integer 0 <= n <= 10000, which is the number of products in the set, and continues with n pairs pi di of integers, 1 <= pi <= 10000 and 1 <= di <= 10000, that designate the profit and the selling deadline of the i-th product. White spaces can occur freely in input. Input data terminate with an end of file and are guaranteed correct.
Output
For each set of products, the program prints on the standard output the profit of an optimal selling schedule for the set. Each result is printed from the beginning of a separate line.
Sample Input
4 50 2 10 1 20 2 30 1
7 20 1 2 1 10 3 100 2 8 2
5 20 50 10
Sample Output
80
185
Supermarkets have N products. I-th commodity must sell before the warranty period (day di), allowing supermarkets to sell if a profit of pi.
Can only sell a product every day.
Now you want to maximize profits supermarket .
Input
plurality of sets of data.
Each test an integer N (0 <= N <= 10000), i.e. the number of supermarket goods
after two lines have integer N, the behavior of the i pi, di (1 <= pi , di <= 10000)
Output
For each set of data, maximum output current profit under the condition supermarket
Sample Input
4
50 2
10 1
20 2
30 1
7
20 1
2 1
10 3
100 2
8 2
5 20
50 10
Sample Output
80
185
Subject to the effect: given n commodities, each with the value and shelf life of one day only to sell a commodity, seeking maximum profits before all goods have expired can get.
Problem-solving ideas: This question can be greedy and disjoint-set of ideas to think about, set value and shelf life of a structure node is stored for each commodity, because I wanted to maximize profits, have the highest value of the goods are sold every day, because each product has a shelf life, so the maximum profit obtained every day is not necessarily the same: For chestnut shelf life of goods worth 1 203 050, the shelf life of goods 2 50 60 70, 60 and 70 because the second genius expired, if not the first day to sell 203,050 of the one, then the next day will be expired, so we chose the first day of the 50 commodities, 70 commodities selected next day we can get the maximum profit, first of all product information stored in an array of structures, the value of descending to sort the array, and then check the set of ideas, because the value is descending, assuming the highest value of goods was 70, his shelf life of 2, then according to him the next day is the maximum value of the next day can not be used if there is commodity shelf life of 2 (602), it is certainly not, I can only go 2-1 on the first day sold. AC Code:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int _max=1e5+50;
struct node {int p,d;};
int f[_max];
node a[_max];
bool cmp(node a,node b) {return a.p>b.p;}
int find(int x)
{
if(f[x]==-1)
return x;
return f[x]=find(f[x]);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
while(cin>>n)
{
memset(f,-1,sizeof f);//初始化为-1表示一开始都没被占用
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>a[i].p>>a[i].d;
sort(a,a+n,cmp);//按照价值降序
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int x=find(a[i].d);//检查该商品的保质期之内是否能销售
if(x>0)
{
f[x]=x-1;//表示这天已经被占用了 自己减一
sum+=a[i].p;
}
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
