*** Introduction
With the development of network economy, expanding distribution companies, partners increasing mobility of employees is increasing. This enables enterprises urgently need the help of a service provider network connecting corporate headquarters and branch offices, form their own corporate network, while mobile workers can easily access the internal network outside the enterprise
Initially, telecom operators are leasing Line ( Leased Line) way for businesses to provide Layer 2 link, the main disadvantage of this approach are: the construction of a long, expensive, difficult to manage
Since then, with ATM (Asynchronous Transfer mode) and Frame Relay FR (Frame Relay) technology rise, carriers turned to ways to provide virtual circuit Layer 2 connections point, their customers constructed of three layer network to carry IP data stream on the other thereof. VC manner compared with lease line, operator network construction time is short, low price, can share the network structure between the different operators of private networks. The disadvantage of this is that the traditional private network: dependent on special media (such as ATM or FR): *** to provide ATM-based services, operators need to establish the scope of services covers the entire ATM network; to provide a basis FR ** * service, but also need to establish cover the full range of services FR network. High cost of network construction
slower rate: can not meet the current requirements for Internet application rate of
deployment of complex : When adding a new site to an existing private network, you need to modify the configuration of all access to the site of the edge node
traditional private network difficult to meet the business requirements on network flexibility, security, economy, scalability, etc.. This prompted the production of a new alternative, emulating a traditional private network over the existing IP network, this new solution is a virtual private network *** (Virtual Private Network)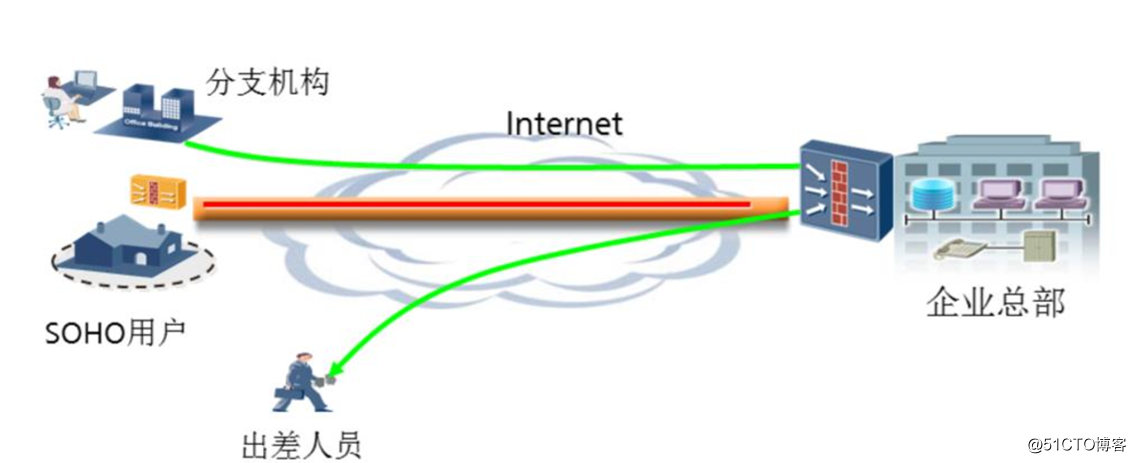
***Characteristics
virtual private network *** (Virtual Private Network) is a public network established by a shared private data channel, each terminal need access to this network or virtual network connected through the passage, constituting a dedicated, having certain security and guaranteed quality of service network
dedicated (private): *** for users, the use of traditional private network *** with the use of no difference. Maintaining resource independent, i.e. *** network resources are not used by a user between Africa *** *** the underlying bearer network; *** and to provide sufficient security guarantees, to ensure that information is not inside *** by external intrusion
virtual (virtual): *** internal communications users is through the public network, while the public network and can also be used by other users of non-*** *** on just a logical sense obtained by the user the private network. The public network is called the backbone network *** (*** Backbone)
***The advantages
Security: establish a reliable connection between remote users, overseas offices, partners, suppliers, and company headquarters, to ensure data transmission security
cheap: the use of public information and communication networks, companies can use lower cost connect remote offices, remote users and business partners
support mobile business: *** diplomatic support users at any time, anywhere mobile access, to meet the growing demand for mobile services
service quality assurance: building with quality of service guaranteed *** (such as MPLS ***), can provide different levels of service quality assurance for users ***
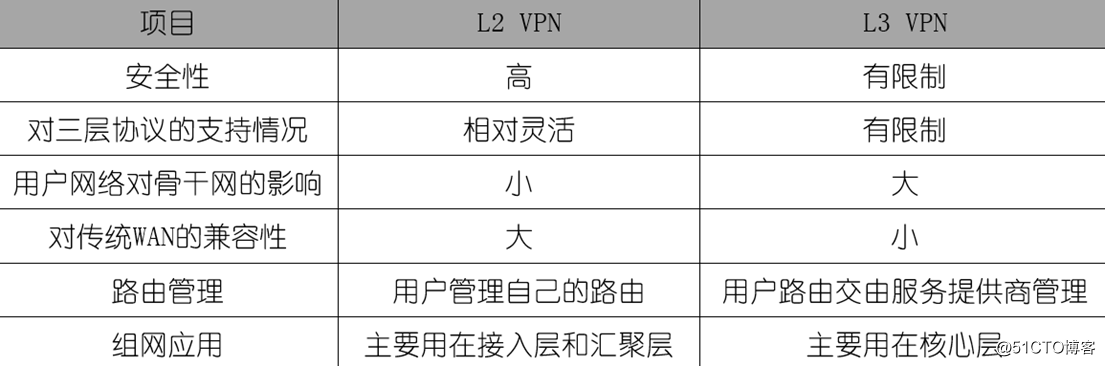
*** contrast common
***classification
Depending on the classification of construction unit
hire carriers *** *** Line to build enterprise networks
such as: MPLS ***, E1, SDH
user-created enterprise network ***
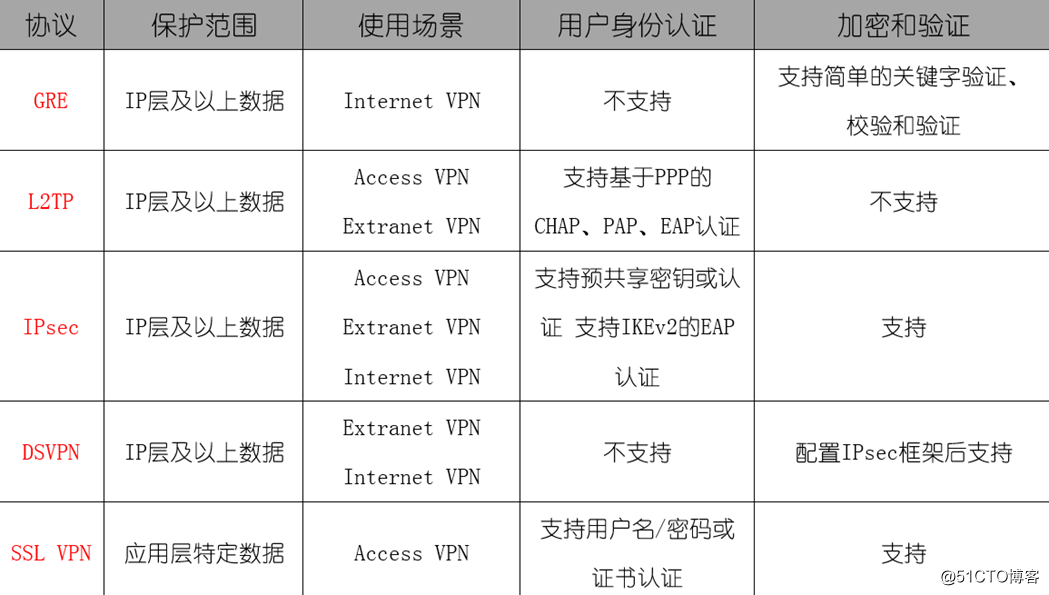
such as: GRE, L2TP, IPsec, SSL , DS ***
By network type classification
*** link between the gateway and the gateway
*** flow between the nodes of the public network forwarding data, the data packet is forwarded in the forwarding network layer, each node of the public network *** needs to establish a dedicated route for each ***, comprising network layer reachability information. Interworking between a local network is implemented to generate a plurality of types including, for example ATM, Frame Relay, GRE, MPLS ***, IPSec ***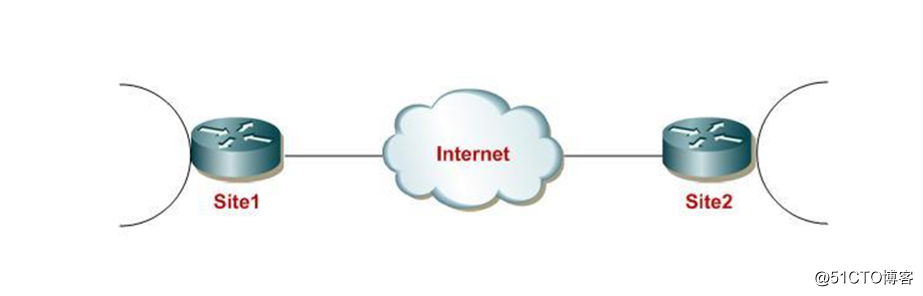
*** link between the host and the gateway
Access *** the staff on business, home office workers and small remote offices can be an inexpensive dial-up access to the internal media server, and corporate Intranet and Extranet establish private network connections include a variety of types, IPsec, PPTP, L2TP over IPsec, SSL ***
*** link between the host and the host
slightly
Achieved by hierarchical classification
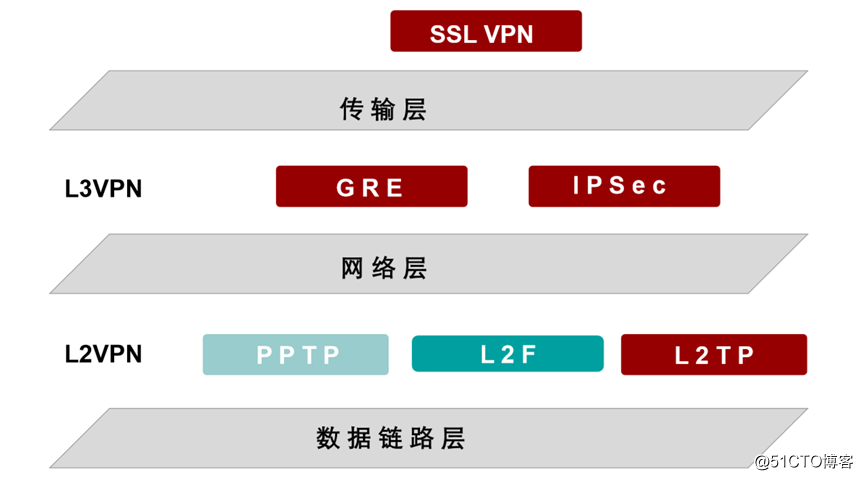
Floor ***
Add a Layer 2 "delivery header " ( Layer increase a transport header)
Layer 2 *** Example
A) the L2TP
B) the ATM (eliminated)
C) Frame Relay (out)
Layer 2 *** advantage of
- It can encapsulate three kinds of traffic, such as IP, IPX, AppleTalk, IP Multicast, etc.
- Good QOS guarantees
Layer 3 ***
Add a Layer 3 "delivery header " ( increase in a three-layer transport header)
Layer. 3 *** Example
a) GRE (advantage: *** full functionality disadvantages: lack of security)
B) the MPLS *** (advantage: any-to-any, disadvantages: SP access point, the lack of security)
c) IPSec *** (advantages: money, security, Cons: bandwidth can not guarantee)L2 *** contrast and L3 ***