1.ssh no secret log on principle
See online are not clear on their own to draw a.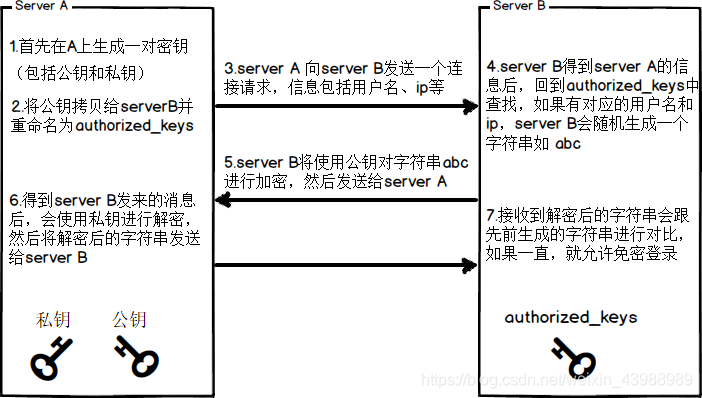
2.ssh Configuration
1. Configure ssh
(1) The basic syntax
ssh另一台电脑的ip地址
(2) Host key verification failed solutions while connecting ssh
[ch@hadoop102 opt] $ ssh 192.168.1.103
The authenticity of host '192.168.1.103 (192.168.1.103)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is cf:1e:de:d7:d0:4c:2d:98:60:b4:fd:ae:b1:2d:ad:06.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
Host key verification failed.
(3) the following solutions: direct input yes
2. No key configuration
(1) to generate public and private keys:
[ch @ hadoop102 .ssh] $ ssh -keygen -t rsa
then hit (three carriage return), it generates two files id_rsa (private key), id_rsa.pub (public)
(2) the public key to be copied to the target machine Free density log
[CH @ hadoop102 .ssh] $ SSH-Copy-ID hadoop102
[CH @ hadoop102 .ssh] $ SSH-Copy-ID hadoop103
[CH @ hadoop102 .ssh] $ SSH-Copy-ID hadoop104
Note:
further need in hadoop102 root account, configure it no secret log on to hadoop102, hadoop103, hadoop104;
also need an account configured on hadoop103 ch no secret about log on to hadoop102, hadoop103, on hadoop104 server.
3. .ssh folder (~ / .ssh) file interpretation function
| authorized_keys | Store authorization nice no secret login server's public key |
|---|---|
| known_hosts | Ssh public records accessed the computer (public key) |
| id_rsa | Generated private key |
| id_rsa.pub | Generated public key |
