Four binary tree traversal
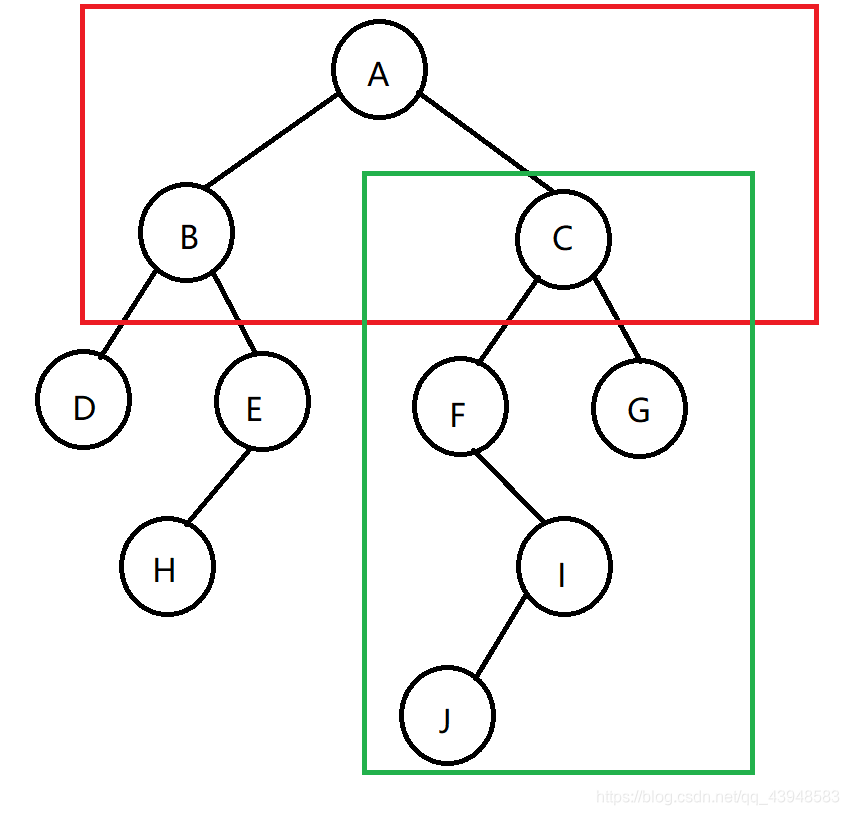
Now there is such a binary tree:
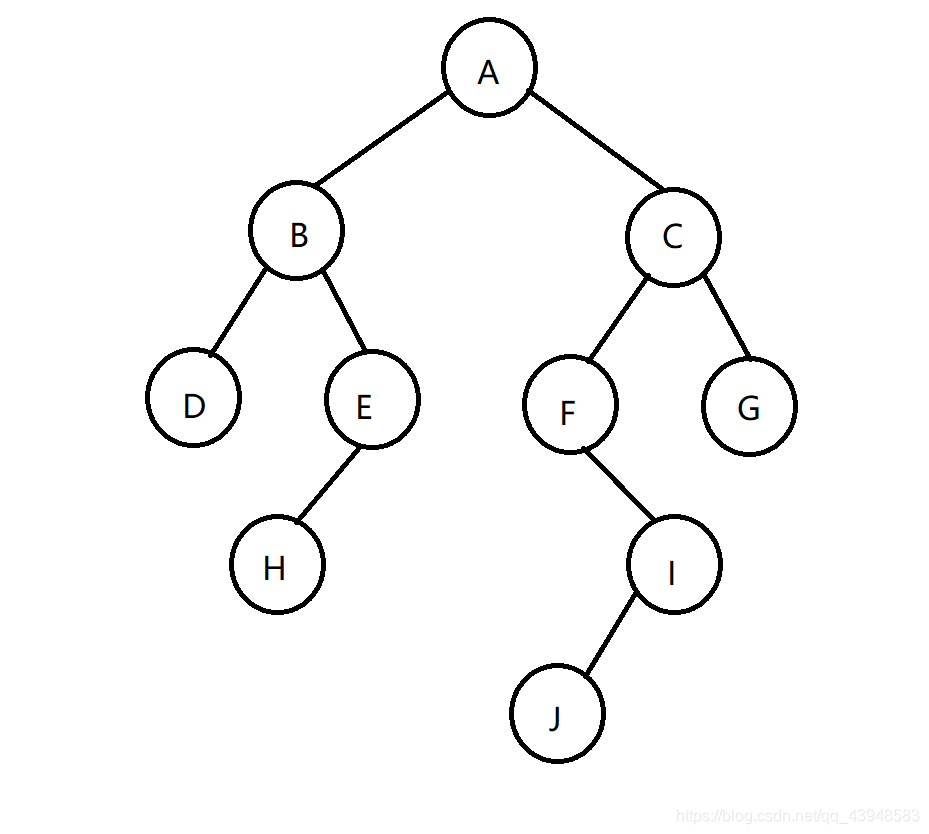
Preorder
Ideas and Code
According to: node, the left sub-tree, the order of traversal right subtree
void PriorOrder(BTNode* b)
{
if(b)
{
printf("%c", b->data);
PriorOrder(b->lchild);
PriorOrder(b->rchild);
}
}
Process Analysis
At first, we will first traverse the topmost tree (the red box)
in three parts this number: the root, left subtree, right subtree, respectively, circled by a blue box
we first access node A and then visit the left subtree, which is on the left in the blue box as a whole
a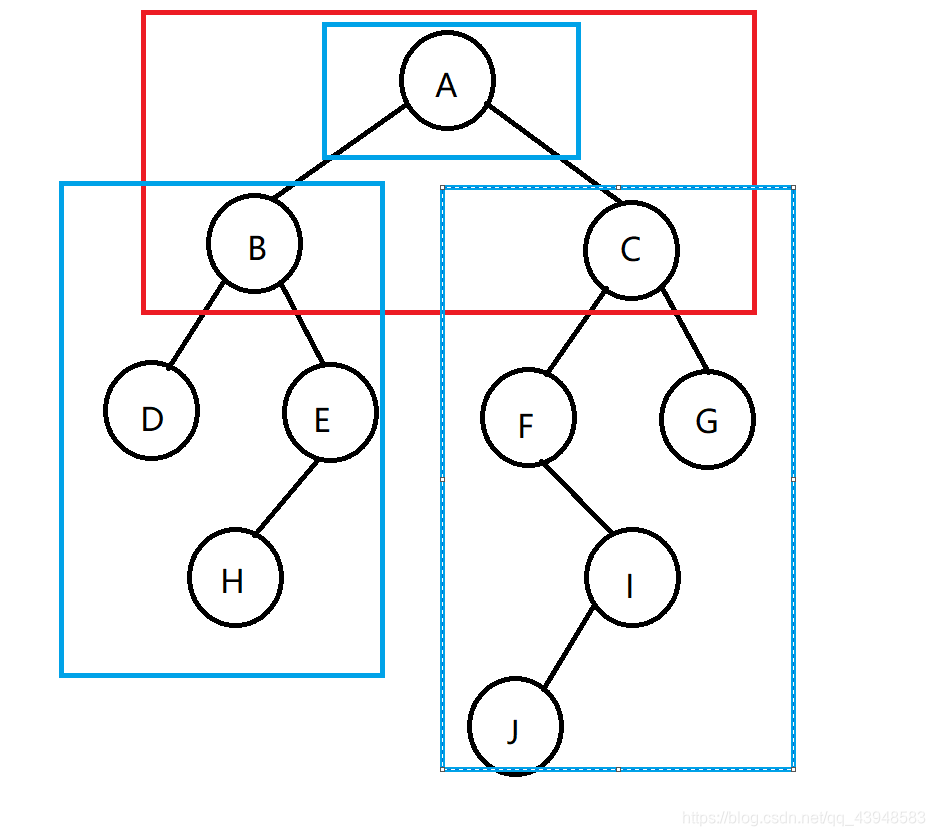
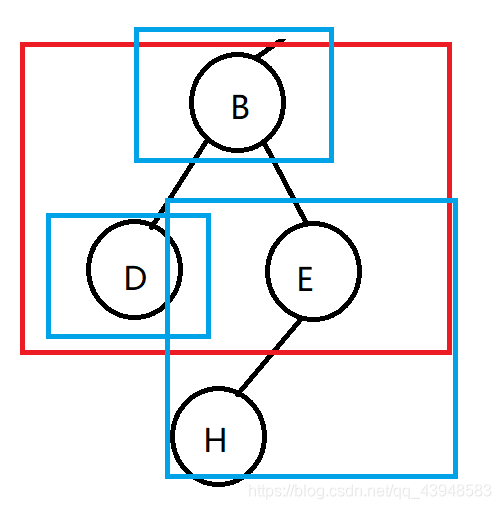
Now separate the left sub-tree made of view, is the same: first visit B, then visit the left node, D, and then visit the right subtree.
We then raised the right subtree: still the same, then access to access E H, then and now, the beginning and the left sub-tree root node consisting of a number of ABC have visited over, so now begin to access the right node number of the ABC
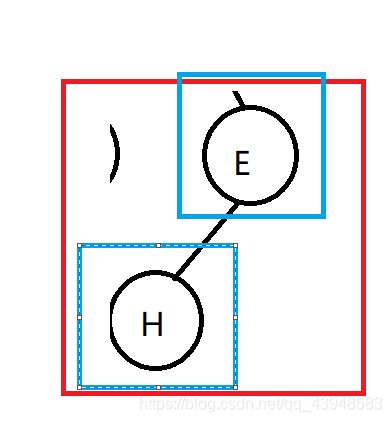
ABC right node of the tree:
the same as above, can be accessed.
The final access order: ABDEHCFIJG
Preorder
Ideas and Code
According to: order left node, this node, right node traversal
void InOrder(BTNode* b)
{
if(b)
{
InOrder(b->lchild);
printf("%c", b->data);
InOrder(b->rchild);
}
}
The process is still the same as above, except that the left subtree first visit complete.
Output order: DBHEAFJICG
Subsequent traversal
Ideas and Code
According to: order the left node, right node, this node traversal
void PostOrder(BTNode* b)
{
if(b)
{
PostOrder(b->lchild);
PostOrder(b->rchild);
printf("%c", b->data);
}
}
Output order: DHEBJIFGCA
Traverse the level
Ideas and Code
According to: root, the order of the first layer, the second layer traversal ...
void LevelTraversal(BTNode* b)
{
if(b)
{
//定义队列
BTNode* queue[MaxSize];
int top=0;
queue[top] = b;
int i = 0;
//只要队列里有元素
while(i<=top)
{
//将左右子树加入队列
if(queue[i]->lchild)
{
top++;
queue[top] = queue[i]->lchild;
}
if(queue[i]->rchild)
{
top++;
queue[top] = queue[i]->rchild;
}
i++;
}
//现在这个队列按层次顺序容纳了二叉树的每个节点
for(i=0;i<=top;i++)
{
//挨个打出来即可
printf("%c", queue[i]->data);
}
//我比较懒所以就没写出队,这其实当成个栈也可以
}
}
It is clear that is one level of access, the order is ABCDEFGHIJ
