Program Counter
程序计数器(Program Counter)Is used to store the address of the next instruction unit is located.
During program execution, the initial value of the PC of the first instruction address during program execution order, 控制器first by the program counter address of an instruction indicated an instruction taken from the memory, then analyzed and the instruction is executed while the PC 1 point value plus the next instruction to be executed.

Address 0100is the starting position of the run. After the Windows operating system and other programs to be copied from the hard disk into memory, the program counter is set as the start position 0100, and then executes the program, after each execution of an instruction, the program counter value will be incremented by one (or directly to the next instruction address), and then, the CPU will be based on the value of the program counter is read from the memory and execute the command, i.e., the program counter control the flow of a program .
Conditional branching and looping mechanism
High-level language is divided into three main conditions for the flow of control: 顺序执行、条件分支、循环判断three kinds of instruction execution order is executed in accordance with the contents of the order of addresses. Conditional branch instruction is executed according to the conditions at any address. Loop is repeated the same address instruction execution.
- The relatively simple implementation of the order, the program counter value of each instruction is executed + 1.
- Conditions and cycle values will branch the program counter address of an arbitrary point, this way, the program can return an address to the same instruction is repeatedly executed, or jump to any instruction.

The program is started and the process sequence is the same, the CPU 0100 starts from the execution command, are executed in the order of 0100 and 0101, value of the order +1 PC, when executed instruction addresses 0102, 0106 determines the value of the register is greater than 0 jump (Jump) instruction address 0104, the value output to the display, and the program ends, the instruction 0103 is skipped, and this program and our if()judgment are the same, the case where the condition is not satisfied , skip instruction. So there will be no execution of PC + 1 directly, but the address of the next instruction.
Flag register
条件和循环分支会使用到 jump(跳转指令),会根据当前的指令来判断是否跳转,上面我们提到了标志寄存器,无论当前累加寄存器的运算结果是正数、负数还是零,标志寄存器都会将其保存
CPU 在进行运算时,标志寄存器的数值会根据当前运算的结果自动设定,运算结果的正、负和零三种状态由标志寄存器的三个位表示。标志寄存器的第一个字节位、第二个字节位、第三个字节位各自的结果都为1时,分别代表着正数、零和负数。
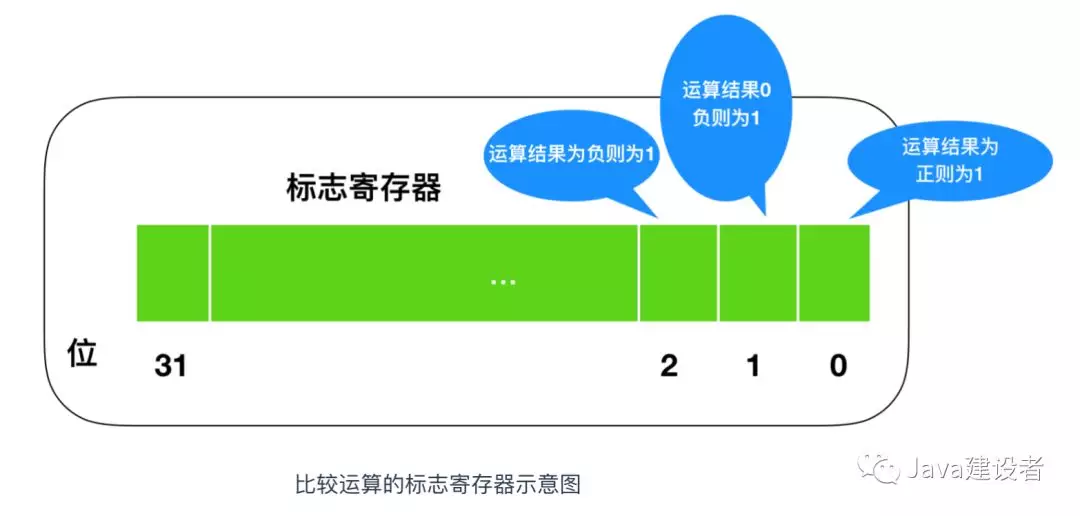
CPU 的执行机制比较有意思,假设累加寄存器中存储的 XXX 和通用寄存器中存储的 YYY 做比较,执行比较的背后,CPU 的运算机制就会做减法运算。而无论减法运算的结果是正数、零还是负数,都会保存到标志寄存器中。结果为正表示 XXX 比 YYY 大,结果为零表示 XXX 和 YYY 相等,结果为负表示 XXX 比 YYY 小。程序比较的指令,实际上是在 CPU 内部做减法运算。
函数调用机制
接下来,我们继续介绍函数调用机制,哪怕是高级语言编写的程序,函数调用处理也是通过把程序计数器的值设定成函数的存储地址来实现的。函数执行跳转指令后,必须进行返回处理,单纯的指令跳转没有意义,下面是一个实现函数跳转的例子

图中将变量 a 和 b 分别赋值为 123 和 456 ,调用 MyFun(a,b) 方法,进行指令跳转。图中的地址是将 C 语言编译成机器语言后运行时的地址,由于1行 C 程序在编译后通常会变为多行机器语言,所以图中的地址是分散的。在执行完 MyFun(a,b)指令后,程序会返回到 MyFun(a,b) 的下一条指令,CPU 继续执行下面的指令。
函数的调用和返回很重要的两个指令是 call 和 return 指令,再将函数的入口地址设定到程序计数器之前,call 指令会把调用函数后要执行的指令地址存储在名为栈的主存内。函数处理完毕后,再通过函数的出口来执行 return 指令。return 指令的功能是把保存在栈中的地址设定到程序计数器。MyFun 函数在被调用之前,0154 地址保存在栈中,MyFun 函数处理完成后,会把 0154 的地址保存在程序计数器中。这个调用过程如下
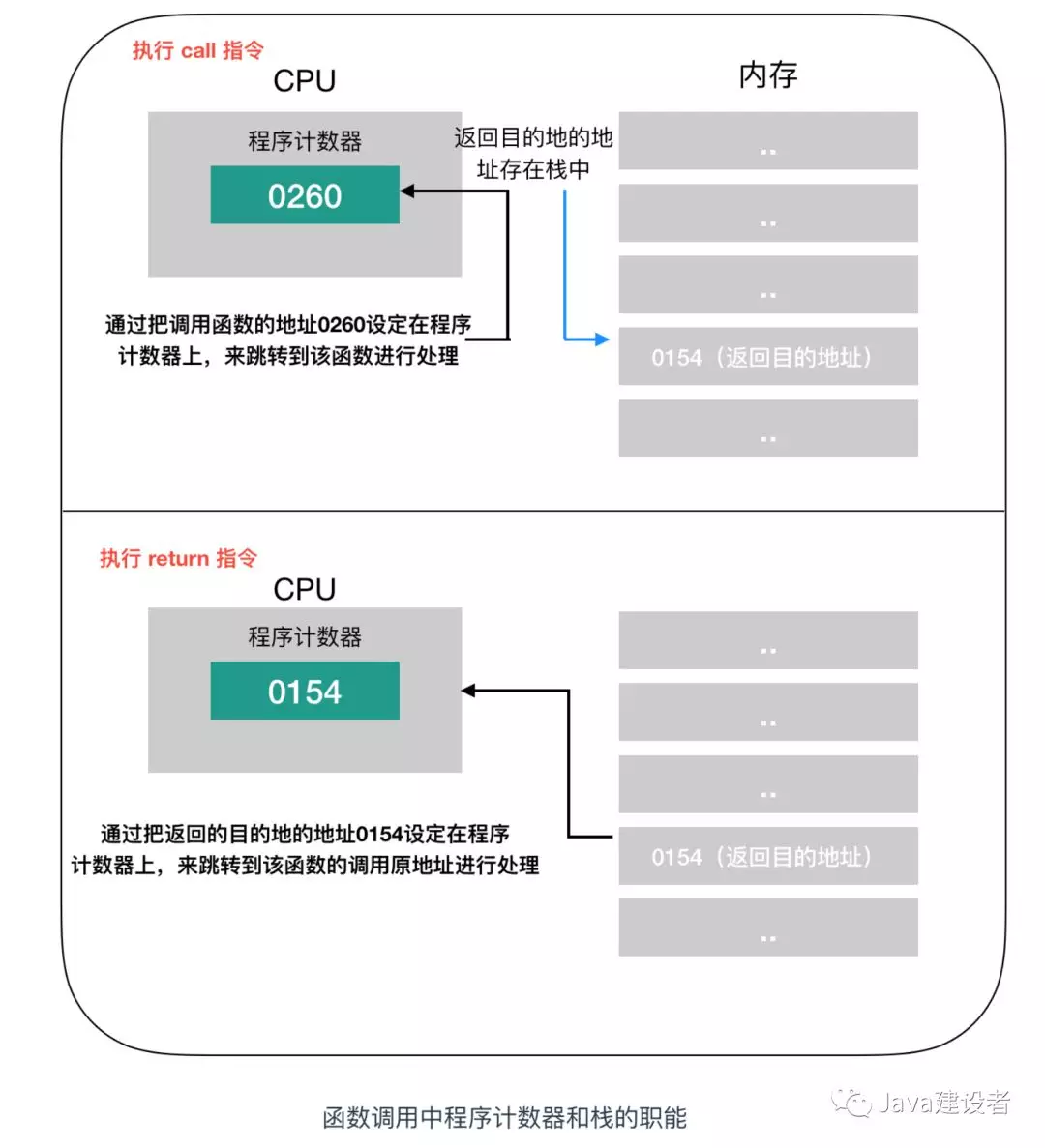
在一些高级语言的条件或者循环语句中,函数调用的处理会转换成 call 指令,函数结束后的处理则会转换成 return 指令。
通过地址和索引实现数组
接下来我们看一下基址寄存器和变址寄存器,通过这两个寄存器,我们可以对主存上的特定区域进行划分,来实现类似数组的操作,首先,我们用十六进制数将计算机内存上的 00000000 - FFFFFFFF 的地址划分出来。那么,凡是该范围的内存地址,只要有一个 32 位的寄存器,便可查看全部地址。但如果想要想数组那样分割特定的内存区域以达到连续查看的目的的话,使用两个寄存器会更加方便。
例如,我们用两个寄存器(基址寄存器和变址寄存器)来表示内存的值

这种表示方式很类似数组的构造,数组是指同样长度的数据在内存中进行连续排列的数据构造。用数组名表示数组全部的值,通过索引来区分数组的各个数据元素,例如: a[0] - a[4],[]内的 0 - 4 就是数组的下标。
CPU 指令执行过程
几乎所有的冯·诺伊曼型计算机的CPU,其工作都可以分为5个阶段:取指令、指令译码、执行指令、访存取数、结果写回。
取指令阶段是将内存中的指令读取到 CPU 中寄存器的过程,程序寄存器用于存储下一条指令所在的地址指令译码阶段,在取指令完成后,立马进入指令译码阶段,在指令译码阶段,指令译码器按照预定的指令格式,对取回的指令进行拆分和解释,识别区分出不同的指令类别以及各种获取操作数的方法。执行指令阶段,译码完成后,就需要执行这一条指令了,此阶段的任务是完成指令所规定的各种操作,具体实现指令的功能。访问取数阶段,根据指令的需要,有可能需要从内存中提取数据,此阶段的任务是:根据指令地址码,得到操作数在主存中的地址,并从主存中读取该操作数用于运算。结果写回阶段,作为最后一个阶段,结果写回(Write Back,WB)阶段把执行指令阶段的运行结果数据“写回”到某种存储形式:结果数据经常被写到CPU的内部寄存器中,以便被后续的指令快速地存取;