Fast power
A modulus base number of higher powers, e.g. a32 is a conventional operation even by 32 times, the rapid power calculating a 2 , then calculates a . 4 , a . 8 , a 16 , a 32 , only the operation five times, the thief fast.

ll power(ll a,ll b,ll q) { ll res=1; while(b) { if(b%2) res=res*a%q; b=b/2; a=a*a%q; } return res%q; }
Fast power matrix
1. Matrix Multiplication
The former line * latter column . The ranks of the resulting matrix are the row number of the former, the latter number of columns. (Since it is a power of, bound to a matrix of n × n)
For example: A matrix is n × p matrix, the matrix B p × m matrix, so that A and B can be multiplied and the result is a matrix C, C dimension is n × m.
C of formula:
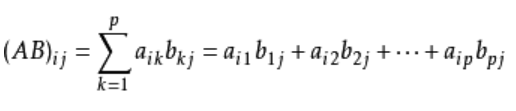
for example:

2. Matrix Quick fast digital power and power the same, but each time the matrix multiplication requires triple loop, looks pretty scary, patience to see a 5min is actually understandable.
P3390 : naked power of the n-order matrix fast, java only had 90 points? (I do not know there is no room for improvement, please enlighten me Gangster)

java.io.BufferedInputStream Import; Import java.util.Arrays; Import java.util.HashMap; Import java.util.LinkedList; Import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { // P3390 [template] matrix fast power static Long [] [] = A new new Long [ 105 ] [ 105 ]; static Long [] [] = E new new Long [ 105 ] [ 105 ]; // matrix static Long P = 1000000007 ; static int n-; static long k; public static void main(String []args) { //Scanner scan=new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in)); Scanner scan=new Scanner( System.in); n=scan.nextInt(); k=scan.nextLong(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) a[i][j]=scan.nextLong(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) e[i][i]=1; long [][] ans=pow(a, k); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) System.out.print(ans[i][j]+" "); System.out.println(); } } public static long[][] mul(long[][] x,long [][] y){// n-order matrix multiplication Long [] [] C = new new Long [ 105 ] [ 105 ]; for ( int I = . 1 ; I <= n-; I ++ ) for ( int J = . 1 ; J <= n-; J ++ ) c [I] [J] = 0 ; // the results c matrix is multiplied by x rows and y columns of results, as the number of columns of X k, Y necessarily correspond to the rows for ( int I = . 1 ; I <= n-; I ++ ) for ( int J = . 1 ; J <= n-; J ++ ) for(int k=1;k<=n;k++) c[i][j]=(c[i][j]+x[i][k]*y[k][j])%p; return c; } public static long[][] pow(long[][] x,long k ){ long [] [] res=e;//单位矩阵 while(k!=0) { if(k%2==1) res=mul(res,x); x=mul(x, x); k=k/2; } return res; } }

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<math.h> #include<string> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<set> #include<ctime> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f const double pi=3.1415926; using namespace std; struct matrix{ ll x[105][105]; }; matrix a,e; int n; ll p=1000000007; ll b; matrix mul(matrix a,matrix b){ matrix res; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) res.x[i][j]=0;//初始化清0操作 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) for(int k=1;k<=n;k++) res.x[i][j]=(res.x[i][j]+a.x[i][k]*b.x[k][j] )%p; return res; } matrix pow( matrix a,ll b) { matrix res=e; while(b){ if(b%2==1) res=mul(res,a); b=b/2; a=mul(a,a); } return res; } int main()//P3390 { scanf("%d %lld",&n,&b); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) scanf("%lld",&a.x[i][j]); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) e.x[i][i]=1; matrix ans=pow(a,b); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) printf("%lld ",ans.x[i][j]); printf("\n"); } return 0; }
Fibonacci matrix fast power
1. Fibonacci number recursive formula f (n) = f (n-1) + f (n-2)
The default is the first 0, f (0) = 0; f (1) = 1; f (2) = 1; f (3) = 2; f (4) = 3; f (5) = 5; f (6) = 8; ...
2. The integration into the matrix calculation formula
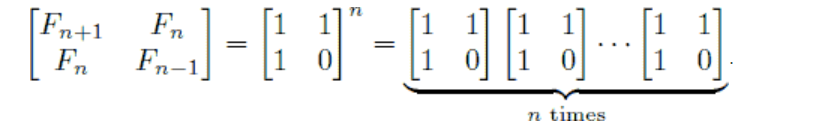
Base-matrix [f (2), f ( 1); f (1), f (0)]; take n power of the matrix A n the upper right corner is the number of f (n)
Manually verify [1,1; 1,0] * A n- = [1,1; 1,0] * [F (n-+. 1), F (n-); F (n-), F (n--. 1) ] = [f (n + 1 ) + f (n), f (n) + f (n-1); f (n + 1), f (n)] = [f (n + 2), f ( n + 1); f (n + 1), f (n)];
Fibonacci square and ask before n items
And permit formula as follows:
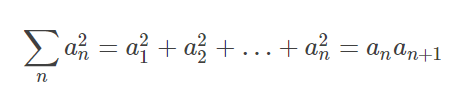
题目:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/3282/A,套用斐波那契矩阵快速幂的模板。

import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ static long[][] a=new long[3][3];//底数矩阵 static long[][] e=new long[3][3];//单位矩阵 static long p=1000000007; public static void main(String []args) { //Scanner scan=new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in)); Scanner scan=new Scanner( System.in); a[1][1]=1;a[1][2]=1;a[2][1]=1;a[2][2]=0; e[1][1]=e[2][2]=1; long k=scan.nextLong(); long[][] res=pow(a, k); long ans=res[1][1]*res[1][2]%p; System.out.println(ans); } public static long[][] mul(long[][] x,long [][] y){//n阶矩阵相乘 long [] [] c=new long [3][3]; for(int i=1;i<=2;i++) for(int j=1;j<=2;j++) for(int k=1;k<=2;k++) c[i][j]=(c[i][j]+x[i][k]*y[k][j])%p; return c; } public static long[][] pow(long[][] x,long k ){ long [] [] res=e;//单位矩阵 while(k!=0) { if(k%2==1) res=mul(res,x); x=mul(x, x); k=k/2; } return res; } }
斐波那契循环节
