Distributed environment ID of how to ensure it is not repeated? Generally, we might think of using UUID thing to achieve. But UUID generally can get the number of milliseconds plus the current time point random numbers, but still may be repeated at high concurrency. The most important thing is, if I use this UUID Unique ID afterlife ingredient list, repeat aside, this random string to insert our innodb storage engine efficiency is very low. So if we generate ID as the primary key, there are two best features: unique distributed and orderly.
Uniqueness would not have said, to ensure the efficient and orderly inserted in the index field. We specifically look at ShardingJDBChow distributed generation strategy is to ensure that ID.
snowflake algorithm

sharding-jdbcDistributed ID using twitterthe open source snowflakemethod does not depend on any third-party assembly, so that its extensibility and maintainability maximum simplified; however, snowflakedefects algorithm ( strongly time dependent, if the clock callback, will generate duplicate ID ) .
Snow algorithm was developed by Twittergeneration algorithm published a distributed master key, it can not guarantee the repeatability of different processes of the primary key, and the orderly process of the same primary key .
In the same process , it is the first time bit by guarantee of non-repetition, if the time is the same as the sequence bit by guarantee. At the same time due to the time position is monotonically increasing, and each server is generally done if time synchronization, it generates a primary key in a distributed environment it can be considered general ordered, which ensures efficient insertion of index fields. For example the primary key Innodb MySQL storage engine.
Snow algorithm used to generate the primary key, portion 4 comprises a binary representation, from high to low sub-table is: 1bit sign bit, 41bit bit time stamp, and the bit 12bit 10bit worker process sequence number bits.
Big Box distributed ID generation strategy · fossiDetailed structure shown below snow primary key algorithm.
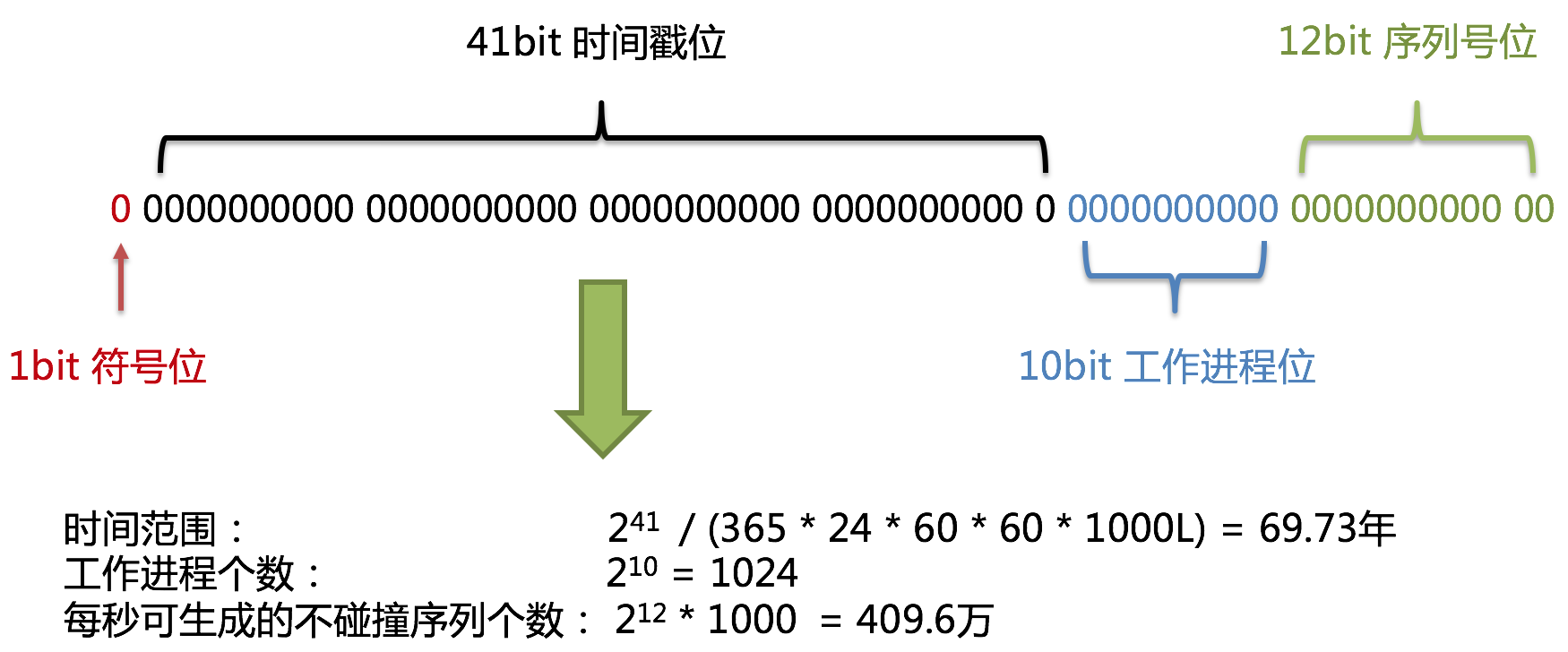
- Sign bit (1bit)
Reserved sign bit, a zero constant.
- Bit timestamp (41bit)
41 milliseconds timestamp 41 may be accommodated a power of 2, the number of milliseconds year was used: 365 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000. By calculation shows:
1 |
Math.pow(2, 41) / (365 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000L); |
The results approximately equal to 69.73 years. ShardingSphereTime algorithm era of snow from at 0:01 on November 2016 onwards, you can use to 2086, the vast majority believe that we can meet the requirements of the system.
- Worker Process bits (10bit)
The logo is unique within the Java process, if it is a distributed application deployment should ensure that each worker process id is different. The default value is 0, it can be obtained by calling the static method DefaultKeyGenerator.setWorkerId()set.
- SEQ ID bits (12bit)
This sequence is used to generate the same ID within a different milliseconds. If the number generated within the millisecond than 4096 (12 th power of 2), then the generator will continue to wait until the next generation milliseconds.
Clock Callback
Callback server clock can result in repeated sequences, the default primary key generator distributed callback number of milliseconds provides a maximum tolerable clock. If the clock number of milliseconds callback time exceeds a threshold maximum tolerable, given the program; falls within a tolerable range, the default primary key generator distributed clock synchronization wait time after the last time the generated key to continue the work. The default maximum number of tolerated clock callback milliseconds is 0, it can be obtained by calling the static method DefaultKeyGenerator.setMaxTolerateTimeDifferenceMilliseconds()is provided.