BFS wide search algorithm
Talk about traversing the graph, wide search.
Is a broad search of FIG traversed, it is possible to find a shortest path between two points in the drawing. But if you use only wide search, the number will scale with the point of the search and the number of edges related. When a large scale when wide search is not a good solution.
For example, it is in the form of FIG.
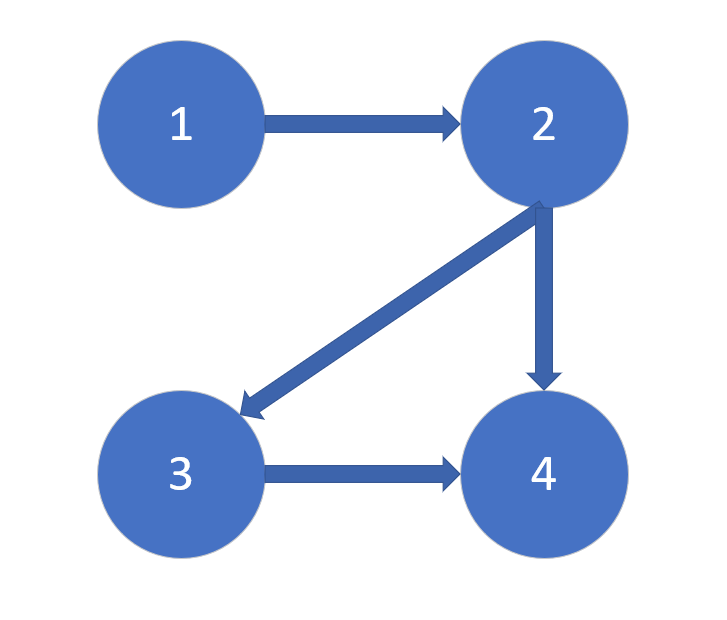
Then adjacency matrix is in the form of:
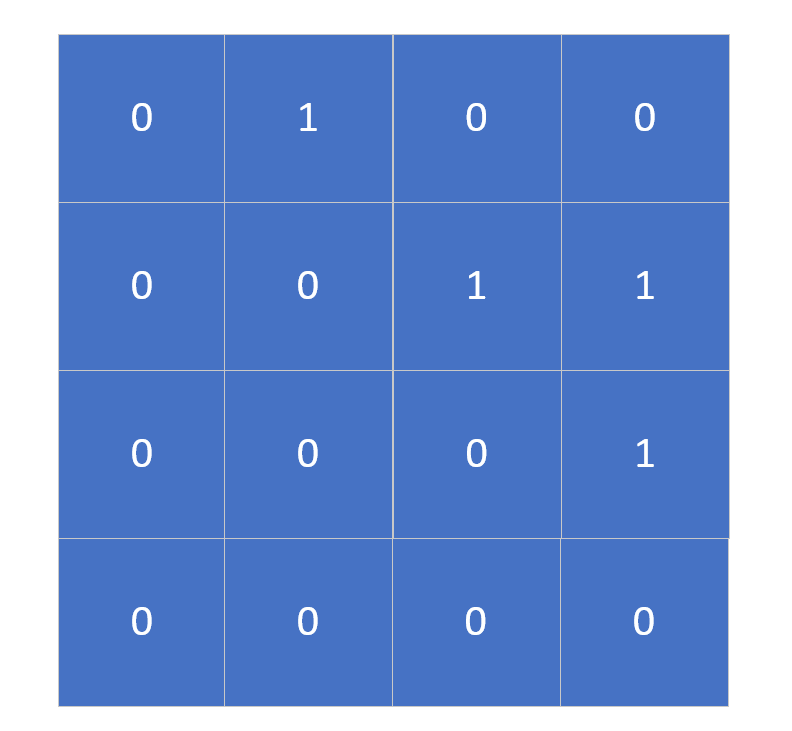
Furthermore it is in the form of the adjacency list:
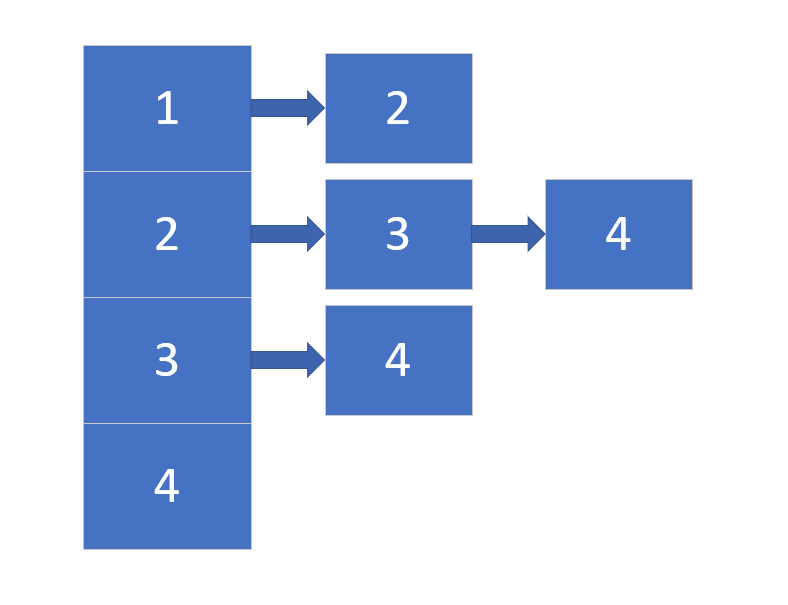
Should not understand the general idea of the algorithm, you can refer to another one of my articles
The following is the code, change the code using a chain structure, i.e. adjacency table implementation, the input format of the comment portion main.cpp
main.cpp
#include"GraphBFS.h"
int main()
{
GraphBFS g1;
g1.Init();
g1.Display();
return 0;
}
/*
5
5
1 5 2
1 2 4
2 3 5
3 4 1
4 5 6
*/
GraphBFS.h
#pragma once
#ifndef _GRAPHBFS_H_
#define _GRAPHBFS_H_
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 0xffffff;
struct nPoint
{
int arrive;
int d;
nPoint* next = nullptr;
};
class GraphBFS//使用邻接表访问
{
private:
int nodeNumber;
int begin, end;
vector<nPoint>Graph;//连续性,相当于头指针
vector<bool>visited;//判断是否经历过
vector<int>distance;//距离
vector<int>parent;//父母
queue<int>q1;//队列
void BFS(int s);//进行广搜
void PrintPath(int b, int e);//打印路线
void LinkNode(int locate,nPoint *p);//链接nPoint结点
public:
GraphBFS();//构造函数
void Init();//初始化
void Display();
~GraphBFS();
};
#endif // !_GRAPHBFS_H_
GraphBFS.cpp
#include "GraphBFS.h"
GraphBFS::GraphBFS()
{
nodeNumber = 0;
begin = end = 0;
Graph.clear();
visited.clear();
distance.clear();
while (!q1.empty())
q1.pop();
}
void GraphBFS::Init()
{
cout << "请输入点的个数" << endl;
cin >> nodeNumber;
Graph.resize(nodeNumber + 1);//链表申请
visited.resize(nodeNumber + 1, false);
distance.resize(nodeNumber + 1, MAX);
parent.resize(nodeNumber + 1, -1);
cout << "请输入有几个关系" << endl;
int a,b,c;
cin >> a;
cout << "请输入各边的关系以及距离" << endl;
while (a--)
{
nPoint* p = new nPoint;
cin >> b >> c >> p->d;
p->arrive = c;
LinkNode(b, p);//利用头插法插入链表中,b是定位到那个链表
}
cout << "请输入开始点和结束点" << endl;
cin >> begin >> end;
}
void GraphBFS::BFS(int s)
{
visited[s] = true;
distance[s] = 0;
q1.push(s);
while (!q1.empty())
{
int u = q1.front();
nPoint* op1 = Graph[u].next;
while (op1)
{
if (!visited[op1->arrive])
{
q1.push(op1->arrive);
parent[op1->arrive] = u;
distance[op1->arrive] = distance[u] + op1->d;
visited[op1->arrive] = true;
}
op1 = op1->next;
}
q1.pop();
}
}
void GraphBFS::LinkNode(int locate, nPoint *p)
{
nPoint* op1 = nullptr;
op1 = Graph[locate].next;
Graph[locate].next = p;
p->next = op1;
op1 = nullptr;
}
void GraphBFS::Display()
{
BFS(begin);
cout << "路径是: ";
PrintPath(begin, end);
cout << endl << "距离是: " << distance[end] << endl;
}
void GraphBFS::PrintPath(int b, int e)
{
if (b == e)
cout << b << " ";
else if (parent[e] == -1)
return;
else {
PrintPath(b, parent[e]);
cout << e << " ";
}
}
GraphBFS::~GraphBFS()
{
Graph.clear();
visited.clear();
while (!q1.empty())
q1.pop();
begin = end = 0;
nodeNumber = 0;
}