2019-10-06
Computer network top-down approach 7th edition answer: https://www.cise.ufl.edu/~sahni/dsaac/?tdsourcetag=s_pctim_aiomsg
- Duration of HTTP links and non-persistent HTTP link for transferring files
Thanks a million of these blog owners! ! ! Let me after the class teacher's kick the tires to understand computer network.
Learning Link: https://blog.csdn.net/wbwang1998/article/details/80813391

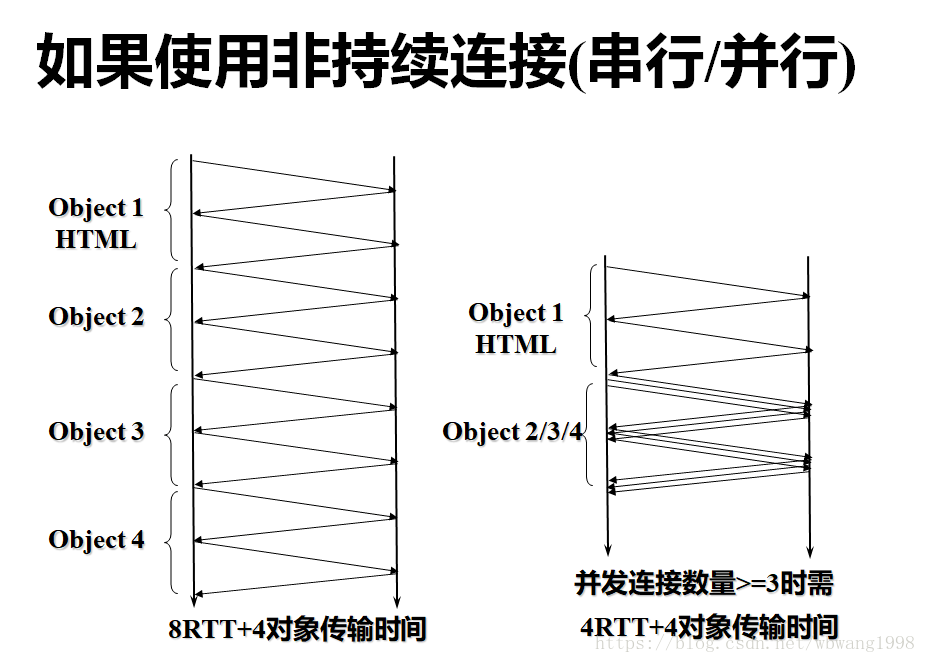
1. (4 points) Suppose a client browser to access another Web page by clicking a hyperlink. If the client only know the name of the server where the Web page, but do not know the IP address of the server. Therefore, the client must use the IP address of the DNS server queries. Assume that clients use DNS to obtain the IP address of the Web server took a total tdns. It is further assumed that the Web page a total of 10 very small objects. So RTT0 represents the RTT value between client and Web server data transmission, transmission time (transmission time) HTML document and embedded objects are negligible. In the following cases, click the hyperlink from the beginning, to receive the complete page how much time was needed? (Note that the reason to explain the results obtained shall ratio)
1, (4 points)
(1) non-parallel non-persistent HTTP connections
Answer: (1) DNS resolve required TDNS; serial non-persistent connection, an object is obtained need 2RTT0. Therefore, totaling 20RTT0 + tdns.
(2) pipeline has continued HTTP 3RTTo + Tdns
A: (2) a continued pipeline of HTTP, DNS resolution requires tdns. Establish a TCP connection time-consuming RTT0; then, access to the page html document takes RTT0; get a page other objects consumption when RTT0. To sum up, it took a total of: 3RTT0 + tdns. (Tips: To download the page once alone, once with other parallel downloads)
2.nslookup use
Learning Link: http: //www.webkaka.com/blog/archives/nslookup-dns-ip-cname.html
nslookup domain name
This is the most common and easiest usage, can be directly obtained IP addresses and domain names CNAME target.
A case where the following is returned records
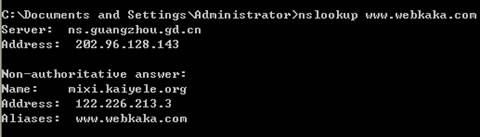
nslookup command using the first reverse explain Obtain DNS server to use the name, image above ns.guangzhou.gd.cn DNS server that I use. Three rows behind, Name is CNAME target domain name, Address is the IP address of the destination domain, Aliases target domain.
nslookup -qt = type of the target domain
Note qt must be lowercase.
What type of character can be case-insensitive:
A record address (Ipv4)
AAAA address records (Ipv6)
AFSDB Andrew file system database server records (do not know)
ATMA ATM address records (not ATM)
CNAME alias record
HINFO hardware configuration records, including CPU, operating system information
ISDN domain corresponding ISDN number
MB to store the specified mailbox server
MG mail group recorded
information recorded MINFO mailing lists and mailboxes
MR renamed mailbox record
MX records for the mail server
NS name server records
PTR reverse records (domain name explanation from the IP address)
RP responsible for record
RT routing penetrate records (do not know)
SRV TCP server information records (there will be much use)
TXT text information corresponding to the domain name
X.25 address corresponding to the domain name record X25