Definition:
Computer network: A collection of interconnected host computer interconnected using a single technique.
Independent single computer (not subject to other computers), that the connecting medium can be an optical fiber, copper wire may be microwave, infrared, satellite.
Internet (Internet): interconnected computer networks, is a network of networks, namely Internet.
World Wide Web (WWW): not a computer network. It is to build a distributed system online.
Topology: a channel (signal channel) in a distributed fashion. Common Topology bus, star, ring, tree, and mesh type. The most common is the bus and star.
- Bus Topology: master on the bus, direct access to each other.
- Star topology: hosts connected on a central node. This early a hub node, now the switch.
Protocol: a set of rules and conventions normative description of how to control the exchange of information between devices in the network.
Digital Bandwidth: The amount of information flowing through per unit of time. In bits per second (bps). Common M, K, G described
Throughput: real, measured bandwidth (the bandwidth of the user experience). Network equipment performance, the number of users of peer topology is a factor.
Transmission time (T), the relationship between the total amount of information (S) and throughput (P) is: T = S / P.
Point: directly connected between the machine. Point to Point
End: a connection point constructed (including switches, routers and the like). End to End
Partitioning the computer network: delineating an area are not, but by the technical features.
- PAN: Personnel Area NetWorks. Area network. Coverage of 1 m.
- LAN: Local Area NetWorks. local area network. Range is about 1 km
- MAN: Metropolitan Area NetWorks. MAN, the range is a city
- WAN:. Wide Area Networks WAN. 100 to 1000 km, a State or a State
- Internet: Internet, global coverage. About 10,000 km.
History:
In 1989, TIM has developed the world's first Web server and a Web client.
That WWW: World Wide Web. He founded the W3C.
China's first e-mail sent to Germany: Across the Great Wall we can reach every corner in the world.
RFC documents: Request For Comments. It contains almost all the important text information on the Internet.
What:
- Basic probability computer network such as the package, modulation, coding
- The basic theory of how the computer network such as the high-speed shared channel
- Basic computer network technologies and protocols (such as TCP / IP, CIDR)
- Using a router, switch
- Packet capture and analysis, basic socket programming
Hierarchical computer network & Reference Model
Stratified benefits:
- The layers work independently, through an interface layer between exercise and reduce the complexity of the work agreement
- Good flexibility, at any level of change does not affect the other layers
- Each different implementation techniques may reduce implementation complexity
- Facilitate standardization
Hierarchical principle:
Object sink layer from the n-th target machine to be sent to the n-th layer source machine exactly
Reference Model:
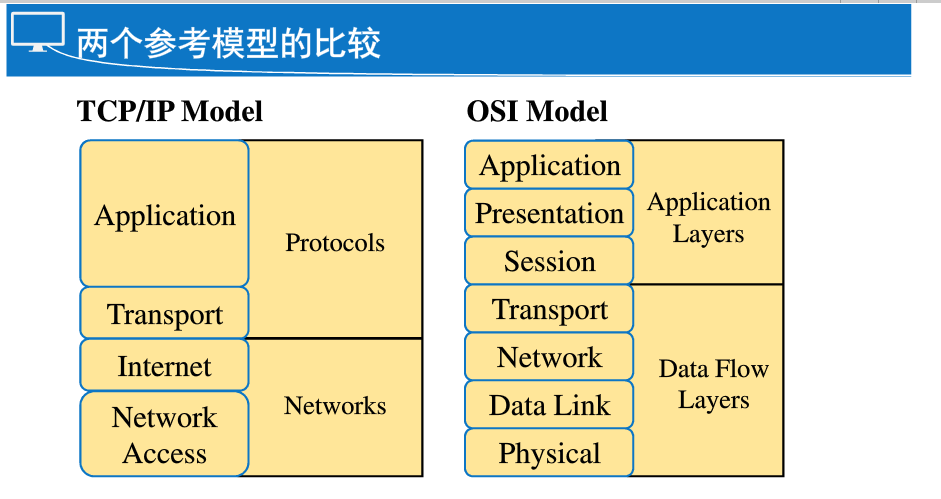
OSI reference model: Open System Inerconnection Open Systems Interconnection. Proposed by the International Organization for Standardization ISO 1983
- Application 7 application layer network applications provide a variety of network services. The micro-channel, EMAIL, FTP
- Presentation 6 represents the layer information indicates the formatted data stream. The computer 01 only recognize the bitstream. Compression, decompression, encryption, decryption, etc.
- Responsible for establishing a session between communicating hosts Session 5 Session Layer, management and removal. Coordinating communication session between the two sides.
- One of the core layer Transport 4 transport layer reference model. Responsible for communication between the host connection from end to end. TCP is responsible for reliable transmission, error recovery, and congestion control.
- NetWork 3 network layer is responsible for the way each packet delivered from the source machine object machine. Function: the address, the optimal route (the route, routing).
- Data Link 2 provides the data link layer medium access services. By identifying the communication host physical address, to provide a reliable frame delivery. Error control, flow control.
- Physical 1 Physical layer provides transparent transfer of the bit stream. It may be optical signals and the like.
Each layer perform specific functions for the service layer, and use the services provided by the next layer.
TCP / IP four-layer reference model:
- Application: 4 application layer
- Transport: 3 Transport Layer
- Internet: 2 Internet layer
- NetWork Access: 1 physical layer
the difference:
- TCP / IP session layer and the presentation layer to the application layer contains
- TCP / IP data link layer and the physical layer to the physical layer combined
- TCP / IP is more concise, easier to troubleshoot and OSI
- TCP / IP is generated in practice, and the OSI model is the ideal textbook (TCP / IP before OSI has come into fashion)
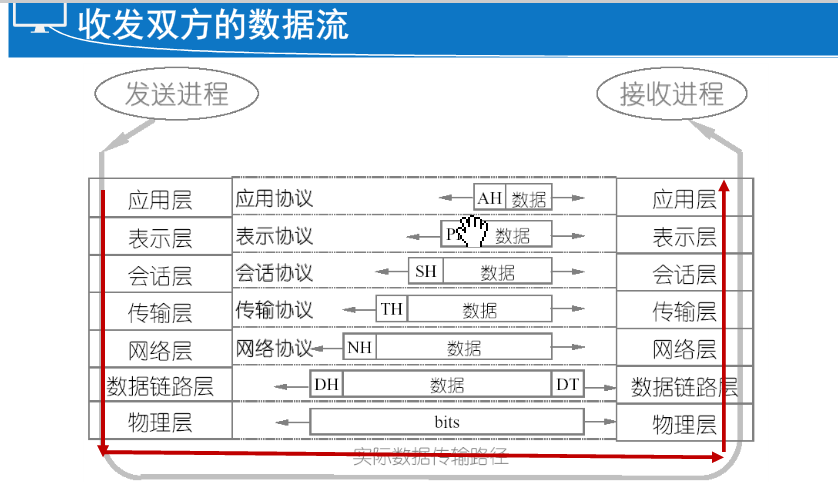
Communication process:
Any one communication is always started by the package sender, the receiver decapsulates get information until the end.
Protocol data unit PDU:
- Information (Information)
- Data stream (Data Stream)
- Data segment (Segment)
- Packet (Packet)
- Frame (Frame)
- Bitstream (Bit)