1 physical address
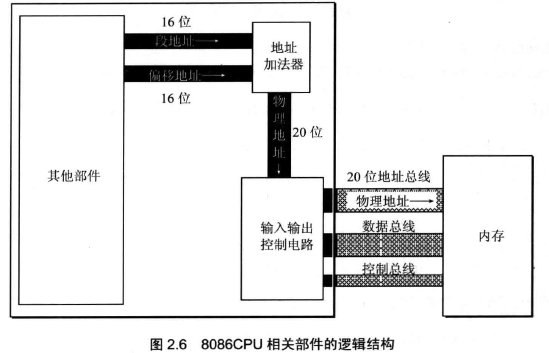
- Address = address adder using physical segment address (SA) * 16 + offset address (EA) is synthesized.
- Address segment base address * 16 == == == segment address left behind a segment address 0 plus one;
- Base address must be a multiple of 16, offset address addressing range is 0 ~ FFFFH, the addressing capacity of 64KB (16 bit CPU, 2 ^ 16 = 64), so the maximum length of one segment is 64KB.
- CPU physical address may be formed with a different segment address and offset address.
2 assembly instructions
2.1 General Data transfer instructions
- Assembler instruction and the register names are case insensitive.
- An 8-bit bit can only store two hexadecimal bits, 1111 1111 = FF
- Operation target number of bits inconsistent with each other between the two can not be operated. As add ax, bh; (err)
1、数据传输指令
MOV ;传送字或字节
MOVSX ;先符号扩展,再传送
MOVZX ;先零扩展,再传送
PUSH ;把字压入堆栈
POP ;把字弹出堆栈
PUSHA ;把AX,CX,DX,BX,SP,BP,SI,DI依次压入堆栈
POPA ;把DI,SI,BP,SP,BX,DX,CX,AX依次弹出堆栈
PUSHAD ;把EAX,ECX,EDX,EBX,ESP,EBP,ESI,EDI依次压入堆栈
POPAD ;把EDI,ESI,EBP,ESP,EBX,EDX,ECX,EAX依次弹出堆栈
BSWAP ;交换32位寄存器里字节的顺序
XCHG ;交换字或字节.( 至少有一个操作数为寄存器,段寄存器不可作为操作数)
CMPXCHG ;比较并交换操作数.( 第二个操作数必须为累加器AL/AX/EAX )
XADD ;先交换再累加.( 结果在第一个操作数里 )
XLAT ;字节查表转换
;── BX 指向一张 256 字节的表的起点, AL 为表的索引值 (0-255,即
;0-FFH); 返回 AL 为查表结果. ( [BX+AL]->AL )
2、输入输出端口传送指令
IN ;I/O端口输入( 语法: IN 累加器, {端口号│DX} )
OUT ;I/O端口输出( 语法: OUT {端口号│DX},累加器 )
;输入输出端口由立即方式指定时, 其范围是 0-255; 由寄存器 DX 指定时, 其范围是 0-65535
3、目的地址传送指令
LEA ;装入有效地址. 例: LEA DX,string ;把偏移地址存到DX.
LDS ;传送目标指针,把指针内容装入DS. 例: LDS SI,string ;把段地址:偏移地址存到DS:SI.
LES ;传送目标指针,把指针内容装入ES. 例: LES DI,string ;把段地址:偏移地址存到ES:DI.
LFS ;传送目标指针,把指针内容装入FS. 例: LFS DI,string ;把段地址:偏移地址存到FS:DI.
LGS ;传送目标指针,把指针内容装入GS. 例: LGS DI,string ;把段地址:偏移地址存到GS:DI.
LSS ;传送目标指针,把指针内容装入SS. 例: LSS DI,string ;把段地址:偏移地址存到SS:DI.
4、标志传送指令.
LAHF ;标志寄存器传送,把标志装入AH.
SAHF ;标志寄存器传送,把AH内容装入标志寄存器.
PUSHF ;标志入栈.
POPF ;标志出栈.
PUSHD ;32位标志入栈.
POPD ;32位标志出栈. 2.2 arithmetic instructions
ADD ;加法,等价于ax += bx
ADC ;带进位加法
INC ;加 1
AAA ;加法的ASCII码调整
DAA ;加法的十进制调整
SUB ;减法
SBB ;带借位减法
DEC ;减 1
NEC ;求反(以 0 减之)
CMP ;比较.(两操作数作减法,仅修改标志位,不回送结果)
AAS ;减法的ASCII码调整
DAS ;减法的十进制调整
MUL ;无符号乘法
IMUL ;整数乘法
;以上两条,结果回送AH和AL(字节运算),或DX和AX(字运算)
AAM ;乘法的ASCII码调整
DIV ;无符号除法
IDIV ;整数除法
;以上两条,结果回送:
;商回送AL,余数回送AH, (字节运算);
;或 商回送AX,余数回送DX, (字运算).
AAD ;除法的ASCII码调整
CBW ;字节转换为字(把AL中字节的符号扩展到AH中去)
CWD ;字转换为双字(把AX中的字的符号扩展到DX中去)
CWDE ;字转换为双字(把AX中的字符号扩展到EAX中去)
CDQ ;双字扩展(把EAX中的字的符号扩展到EDX中去) 2.3 program branch instruction
- Can change the CS, IP content instruction is collectively referred to as program branch instructions.
1、无条件转移指令 (长转移)
JMP ;无条件转移指令
;jmp 2AE3:3; 等价于 mov CS, 2AE3 mov IP, 3;
;jmp ax; 等价于 mov IP, ax;
CALL ;过程调用
RET/RETF ;过程返回
2、条件转移指令 (短转移,-128到+127的距离内)
( 当且仅当(SF XOR OF)=1时,OP1<OP2 )
JA/JNBE ;不小于或不等于时转移
JAE/JNB ;大于或等于转移
JB/JNAE ;小于转移
JBE/JNA ;小于或等于转移
;以上四条,测试无符号整数运算的结果(标志C和Z)
JG/JNLE ;大于转移
JGE/JNL ;大于或等于转移
JL/JNGE ;小于转移
JLE/JNG ;小于或等于转移
;以上四条,测试带符号整数运算的结果(标志S,O和Z)
JE/JZ ;等于转移
JNE/JNZ ;不等于时转移
JC ;有进位时转移
JNC ;无进位时转移
JNO ;不溢出时转移
JNP/JPO ;奇偶性为奇数时转移
JNS ;符号位为 "0" 时转移
JO ;溢出转移
JP/JPE ;奇偶性为偶数时转移
JS ;符号位为 "1" 时转移
3、循环控制指令(短转移)
LOOP ;CX不为零时循环
LOOPE/LOOPZ ;CX不为零且标志Z=1时循环
LOOPNE/LOOPNZ ;CX不为零且标志Z=0时循环
JCXZ ;CX为零时转移
JECXZ ;ECX为零时转移
4、中断指令
INT ;中断指令
INTO ;溢出中断
IRET ;中断返回
5、处理器控制指令
HLT ;处理器暂停, 直到出现中断或复位信号才继续
WAIT ;当芯片引线TEST为高电平时使CPU进入等待状态
ESC ;转换到外处理器
LOCK ;封锁总线
NOP ;空操作
STC ;置进位标志位
CLC ;清进位标志位
CMC ;进位标志取反
STD ;置方向标志位
CLD ;清方向标志位
STI ;置中断允许位
CLI ;清中断允许位2.4 Logical operation instructions
AND ;与运算.
OR ;或运算.
XOR ;异或运算.
NOT ;取反.
TEST ;测试.(两操作数作与运算,仅修改标志位,不回送结果).
SHL ;逻辑左移.
SAL ;算术左移.(=SHL)
SHR ;逻辑右移.
SAR ;算术右移.(=SHR)
ROL ;循环左移.
ROR ;循环右移.
RCL ;通过进位的循环左移.
RCR ;通过进位的循环右移.
;以上八种移位指令,其移位次数可达255次.
;移位一次时, 可直接用操作码. 如 SHL AX,1.
;移位>1次时, 则由寄存器CL给出移位次数.
;如 MOV CL,04
;SHL AX,CL 2.5 instruction string
DS:SI ;源串段寄存器 :源串变址.
ES:DI ;目标串段寄存器:目标串变址.
CX ;重复次数计数器.
AL/AX ;扫描值
D标志 ;0表示重复操作中SI和DI应自动增量; 1表示应自动减量
Z标志 ;用来控制扫描或比较操作的结束
MOVS ;串传送
;(MOVSB 传送字符, MOVSW 传送字, MOVSD 传送双字)
CMPS ;串比较.
;(CMPSB 比较字符, CMPSW 比较字)
SCAS ;串扫描,把AL或AX的内容与目标串作比较,比较结果反映在标志位.
LODS ;装入串,把源串中的元素(字或字节)逐一装入AL或AX中
;(LODSB 传送字符, LODSW 传送字, LODSD 传送双字)
STOS ;保存串,是LODS的逆过程
REP ;当CX/ECX<>0时重复
REPE/REPZ ;当ZF=1或比较结果相等,且CX/ECX<>0时重复
REPNE/REPNZ ;当ZF=0或比较结果不相等,且CX/ECX<>0时重复
REPC ;当CF=1且CX/ECX<>0时重复
REPNC ;当CF=0且CX/ECX<>0时重复2.6 directive
DW ;定义字(2字节)
PROC ;定义过程
ENDP ;过程结束
SEGMENT ;定义段
ASSUME ;建立段寄存器寻址
ENDS ;段结束
END ;程序结束3 ordinary data registers
- Register 16 -> AX; 32-bit registers -> EAX; 64-bit registers -> RAX;
- General Registers: used to store general data generally have AX, BX, CX, DX other four.
- 8086CPU in
- AX can be divided into AH and AL; (accumulation register Accumulator: can be used for multiplication, division, inputs, and outputs the intermediate result cache operation.)
- BH, and BL can be divided into BX; (Base Address Register Base: may be used as a memory pointer.)
- CH, and CX can be divided CL; (Count Register Count: When cycle and string operations, it is used to control the number of cycles; bit operation, when the shift number, use the number of bits to indicate the shift CL .)
- DX can be divided into the DL and DH; (Data Register Data: during multiplication and division, it can be used as the default operand involved in computing, it may also be used to store port addresses of I / O.)
- The AX: AX low 8 bits (0 ~ 7) constitutes the AL register upper 8 bits (8 ~ 15) constitutes the AH register. AH and AL are two registers can be used independently of the 8-bit registers.
- In addition to the data register can be divided into two separate 8-bit registers, the rest are not separable.
- A word consists of two bytes, i.e., there may be a word in a 16-bit register.
Segment register 4
Data can not be fed directly into a segment register, general register transfer need;
2 words stored in memory, to use two consecutive memory means to store;
3 high storage address high byte, the lower byte of the lower address.
CS (Code Segment): the code segment register, indicating the start address of the code;
- The use of CS: IP to obtain the next instruction to be executed.
DS (Data Segment): the data segment register to indicate the start address of the data;
Using DS: EA accessing data in the data section.
EA is an offset address, i.e., the effective address.
; 如果没有指定前缀,一般的数据访问在DS(数据)段 mov ax,[1000]; = mov ax,ds:[1000h] mov ax,cs:[1000]; 从指定的CS段取出数据。 [1000] ;代表内存中的数据,1000表示内存单元的偏移地址。
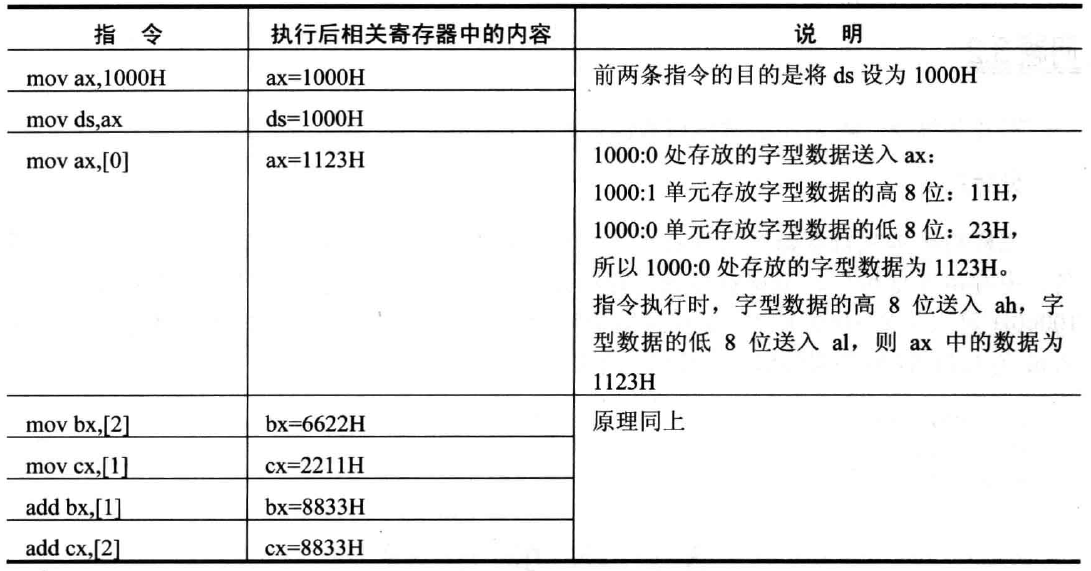
SS (Stack Segment): the stack segment register, the start address specified in the stack (segment address);
- Using a SS: SP stack operation data.
ES (Extra Segment): start address register additional segments, the additional segments specified;
- Using ES: EA access the additional data section.
FS: additional segment register.
GS: additional segment register.
CPU is identified only CS: IP contents of the memory cell pointed to by the instruction.

Instruction pointer register 5
- IP: instruction pointer register;
6 flag register
- Flags: flag register;
7 addressing register
SI (Source Index): a source index register used to store the segment relative to the source DS index pointer, the processing instruction string, as implied by the SI source address of the string, the default in DS.
DI (Destination Index): index register object can be used to store the index pointer object with respect to the ES segment, the string of processing instruction, the DI string object is used as an implicit address, default ES.
; 将字符串"welcome to masm!" 复制到后面的数据区中 assume cs:codesg, ds:datasg datasg segment db 'welcome to masm!' db '…………………………………………' datasg ends codesg segment start: mov ax, datasg mov ds, ax mov si, 0 ;源变址 mov di, 16 ;目的变址,"welcome to masm!"占16个字节 mov cx, 8 ;si,di为16位寄存器,每次2个字节,共需8次 s: mov ax, [si] mov [di], ax add si, 2 add di, 2 loop s mov ax, 4c00h int 21h codesg ends end start
8 Pointer Register
- SP (Stack Pointer): storing offset address stack register;
- BP (Base Pointer): base pointer register, to determine the operand address in the stack;
9 Debug use
R: See, change the contents of CPU registers;
r # 查看 r ax # 把ax修改为1100 :1100D: View the contents of memory;
d 段地址/寄存器:偏移地址 # d 500:100 d 段地址/寄存器:偏移地址 结束偏移地址 # d 500:100 109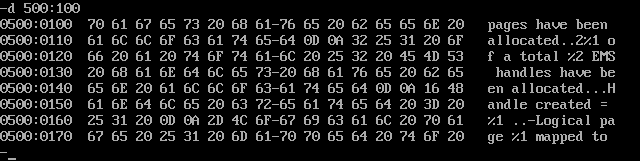
- On the left is the starting address of each line.
- Right side of each memory cell in the data corresponding to the character codes displayable ASCⅡ.
- Intermediate content from the specified address of the memory unit 128, a hexadecimal format of the output, the output of each line from the start address of an integer multiple of 16, up to 16 units of the content output.
E: overwrite the contents of memory;
e 段地址/寄存器:偏移地址 数据/字符/字符串/机器码 …… e 段地址/寄存器:偏移地址
U: The translated into machine instructions in memory assembly instructions;
# 查看指定的内存单元中的机器指令和它们所对应的汇编指令。 u 段地址/寄存器:偏移地址T: execute a machine instruction;
- Execute CS: IP instructions at.
A: format of the assembler instruction writes a machine instruction in memory.
Assembly instructions written in the form of machine instructions in memory.
a 段地址/寄存器:偏移地址
P: automatic instructions in the loop repeatedly performed until the loop condition is not met;
G: g 0016, to automatically execute CS: 16 place;
Description: assembler instruction section taken from: https://www.kanxue.com/chm.htm?id=10101&pid=node1001139