First, the system control service
In CentOS system, various system control script placed in the service of the default / usr / lib / systemd directory. Systemctl command tool can be achieved by control of the specified system services. 
Several common types of controls as described below.
1.start (start): run the specified system services to achieve service functions.
2.stop (Stop): terminates the specified system service program, turn off the corresponding function.
3.restart (restart): first exit and re-run the specified system services. [Usually not recommended]
4.reload (overloaded): Do not quit the service program, just refresh the configuration. For certain services and operation restart of
5 for the same.
6.status (Check status): Displays the operating status of system services and related information.
Second, the level switch operation
1, view operational level
(1) runlevel command: switching the operating level can only view the current operating level. 
(2) systemctl tool: Review the default run level.
2, temporary switch to run level
(1) init command: This command parameter is the number corresponding to run-level reduction.
Figure execute "init 3" command to enter the character interface. 
Enter your user name and password in the character interface, and then execute "init 5" command returns the graphical interface. 
(2) systemctl tool: the command argument is a specific target.
Figure execution "systemctl isolate multi-user.target" command may also be entered into the character interface. 
Enter your user name and password in the character interface, and then execute "systemctl isolate graphical.target" command returns the graphical interface. 
If you want to boot by default into the character interface, you can perform "ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target/etc/systemd/system/dafault.target" command to change the default graphical interface characters interface .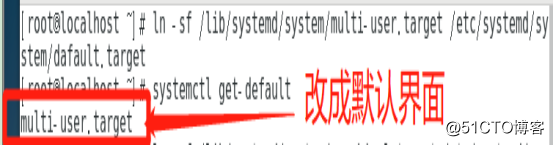
Third, optimize the boot process
1, ntsysv tool
ntsysv tool can be run in a character mode, to provide users with an interactive graphical user interface a copy, specifically for centralized configuration starting state of various systems and services. When the need to set multiple startup status of the service, use ntsysv tool will be very convenient. Figure execution "ntsysv" command is used to manage the current operation target service. 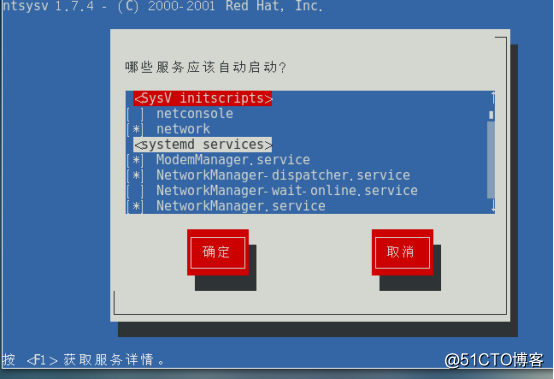
Operation by ↑, ↓ arrow keys to select a different system services, by default startup state Space (space) key and services provided ( "[*]" represents start, "[]" represents off). If you want to see a description of the selected information service, press the F1 key to get help.
2, using tools systemctl
Start state (1) view the system services 
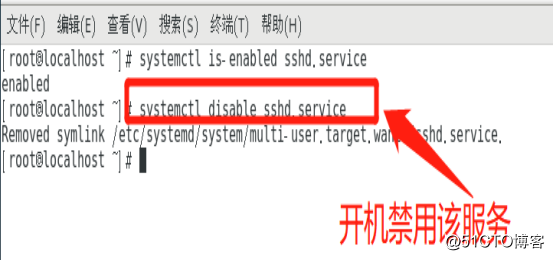
as shown in "systemctl is-enabled sshd.service" command is visible to the start-up of service. 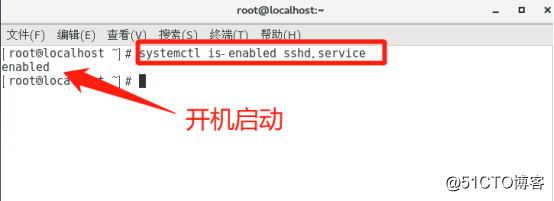
(2) set the system start-up state and services 
performed as "systemctl disable sshd.Service" start command to disable the service.