Introduction: Compared with Windowns operating system, the role of Linux system user account and group account is essentially the same, the same are based on user identity to control access to resources, but there is in the form of expression and individual details a little different.
user account
Supervisor: the root user, has the largest authority of the host.
Ordinary users: Ordinary account needs to be created by the root user or other administrator user has permission subject to certain restrictions, generally have complete authority in the user's own home directory.
User program: only system or a program for maintaining normal operation, generally not man-made log into the system.
The associated user account profiles have two, namely / etc / passwd / etc / shadow. The former package store for a user name, login shell and other home directory information, which the user saves the user's password, account number, expiration date. In these two configuration files, each row corresponds to a user account, different configuration items separated by a colon.
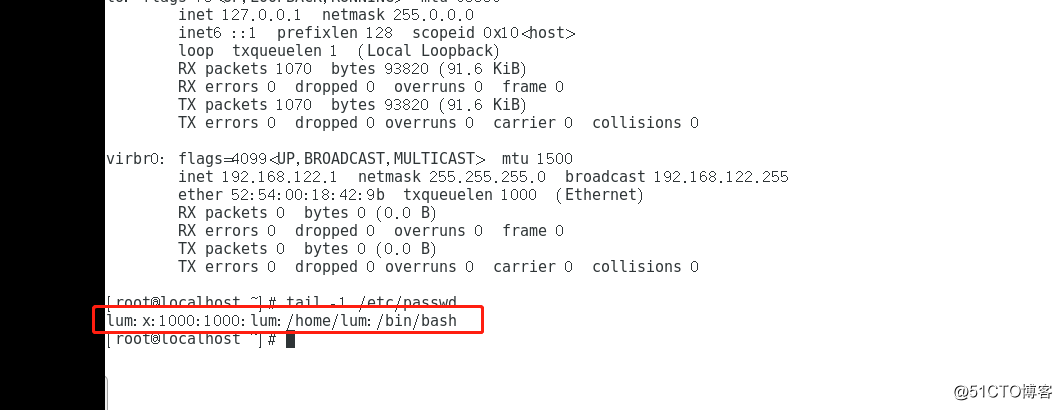
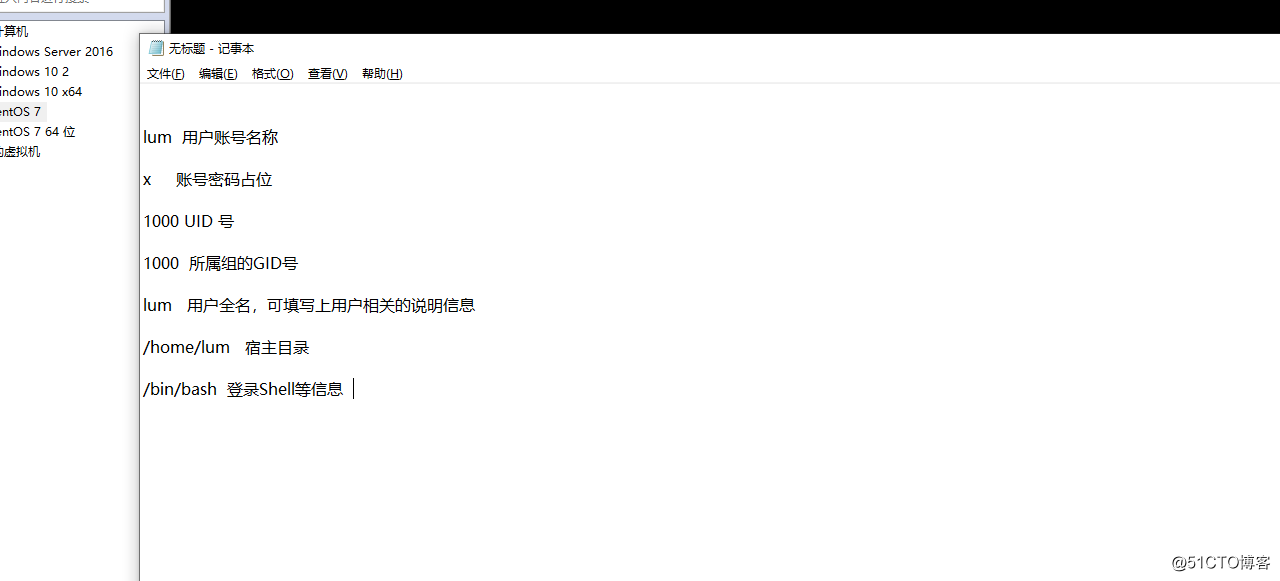
With the tail of the last line displayed instructions, i.e., red frame on the map is passwd file, his left to right as meaning a segment configuration.
See also be / etc / shadow by this head or tail command files, this is not the meaning of each segment annotation, self Baidu and clothing.
User Account Management
Each account has a digital form of identification tags, known as UID, user account management through the following command to complete the word
useradd command to add user accounts
passwd command to change the user password settings
usermod command to modify the account number property
userdel Delete user account