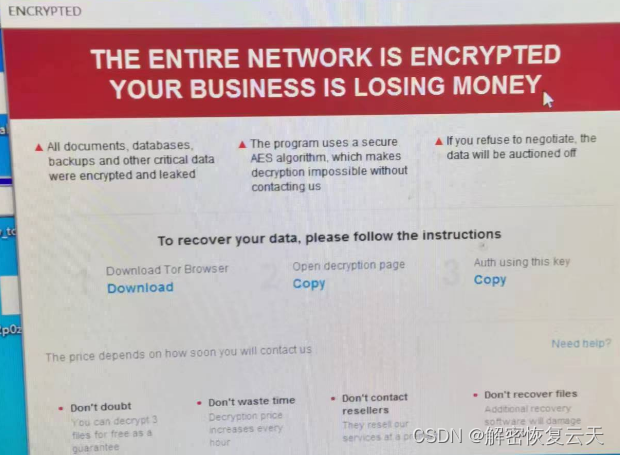
Ransomware is a serious cybersecurity threat that uses encryption technology to lock a victim's files and demands a ransom to restore access to the files. In a server environment, ransomware infection can come from many sources. The following are the causes of ransomware viruses in servers compiled by Yuntian Data Recovery Center:

- Weak passwords and permission management: Weak passwords and incorrect permission management are one of the main ways for ransomware to invade. If server administrators use simple or shared passwords, or grant users unnecessary permissions, hackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to gain access and plant ransomware.
- Insecure network connection: An insecure network connection can leave the server vulnerable to attack. For example, unencrypted wireless network connections could allow hackers to steal sensitive information, including usernames, passwords, and credentials. Additionally, using an unsecured VPN or remote access tool can also expose your server to external threats.
- Port exposure and Remote Desktop Protocol: Some servers may be exposed on unsecured ports, such as the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) default port 3389. If hackers discover these open ports, they could exploit these vulnerabilities to access servers and plant ransomware.
4. Unreasonable backup strategy: Backup is one of the important steps to deal with ransomware attacks. However, if the backup strategy is incomplete or unreasonable, it may be impossible to recover the data in the event of a ransomware attack. For example, backup data that is not encrypted or backup files stored in an unsecured location may result in backup data being exposed to hackers.
5. Insider Threats: Insider threats are another source of server infection with ransomware. Sometimes, internal users may inadvertently download and run malware, or use weak or shared passwords to gain access to servers. Additionally, internal users may expose sensitive information or misconfigure the server leaving it vulnerable to attack.
In summary, to prevent your server from being infected with ransomware, you need to take a series of security measures, including using strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, limiting user permissions, implementing secure network connections, choosing reliable antivirus software, and closing unnecessary open ports , protect sensitive files, formulate reasonable backup strategies, and strengthen security awareness education for internal users. These measures will help reduce the risk of server exposure to ransomware.