1. Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (RAID) means “an array of independent disks with redundant capabilities”.
A disk array is a disk group with a huge capacity that is composed of many cheaper disks, either in hardware (RAID card) or software (MDADM). Multiple disks are combined together to improve the performance of the entire disk system. Using this technology, data is cut into many segments and stored on each hard drive. The disk array can also use the concept of parity check. When any hard disk in the array fails, the data can still be read out.
Note: RAID can prevent data loss, but it does not completely guarantee that your data will not be lost, so when using RAID, you should also pay attention to backing up important data.
2. RAID creation method
There are two ways to create RAID: soft RAID (implemented through operating system software) and hard RAID (using hardware array cards); understand raid1, raid5 and raid10. However, with the rapid development of the cloud, suppliers can generally solve hardware problems.
3. RAID disk array characteristics
| 1 2 3 |
|
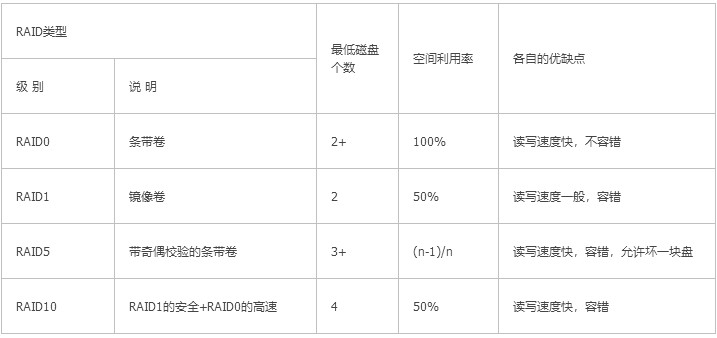
4. RAID type
Raid level: raid 0 raid 1 raid5 raid 10 raid 01
RAID 0
0: (stripe) stripe mode, which requires at least two hard disks. Each piece of data is evenly divided into multiple parts and stored in multiple disks, and they are all on a horizontal stripe.
Advantages: The reading and writing speed is increased, which is doubled as many disks are used. Disadvantages: No redundancy (also called fault tolerance). Space utilization: the sum of multiple disks, 100%.

RAID 1
1: (mirror) mirror mode, the number of disks needs to be a multiple of 2. The data stored in the two disks are exactly the same. When one disk is damaged, the data can still be read and written.
Advantages: Redundant capability
Disadvantages: disk utilization is only 50%, writing speed decreases

RAID 5
5: Check code verification code mode requires at least three hard disks. Each time data is stored, the stripe mode is used to store the data in n-1 number of disks. The other disk stores the data in several other disks in a certain format. The encrypted data obtained after an encryption method, and every time it is stored, the disk storing the encrypted data is constantly changing. When the data on any one of the disks is damaged, it can be known through the encryption method and the data on the other two disks. Data on another disk has high redundancy capability
Advantages: fast reading and writing speed, redundancy capability
Disadvantages: Disk utilization is n-1/n. When two disks are damaged, data will be lost.

Combined with RAID10
10: Mirror+stripe mode requires at least 4 fast hard drives. First, combine two hard drives into Raid1, and then combine two sets of Raid1 into Raid0. When storing one point of data, the data stored in each Raid1 combination is equally divided. Then the Raid1 combination is stored in mirror mode.
Advantages: fast reading and writing speed, strong redundancy capability
Disadvantages: Disk utilization is 50%

Combined with RAID01
RAID01 is striping first and then mirroring. The essence is to mirror the physical disk.
Advantages: fast reading and writing speed, strong redundancy capability
Disadvantages: disk utilization is 50%, security performance is worse than 10

Compare:
Comparison of RAID10 and RAID01
The most important difference between the two is that the bottom layer of RAID10 is mirrored RAID1, and mirroring ensures that when a hard disk such as A1 is damaged, its writing function will not be affected, and the reading performance may be slightly reduced (about 1/8). ). But the bottom layer of RAID01 is striped RAID0, and striping means that as long as one hard disk, such as A1 in Disk0 on the left, is damaged, the entire left RAID0 cannot be used, so the entire RAID01 becomes only the right RAID0. It can be used, that is, from RAID01 to RAID0, the read performance will immediately decrease, the write performance will not be affected, and the reliability will become the worst. For this reason alone, we should never use RAID01 but choose RAID10