1. Definition of power consumption of digital chips
2. How to reduce power consumption?
2.1 Reduce dynamic power consumption
2.2 Reduce static power consumption
foreword
Beginner to learn digital IC with zero foundation, learn what to write, and make progress together with everyone.
During the recent interview process, I was often asked questions about power consumption, and the answers were not very good, so this article mainly summarizes the questions related to power consumption for subsequent review.
1. Definition of power consumption of digital chips
The power consumption of digital chips can be divided into two parts: dynamic power consumption and static power consumption. Dynamic power consumption is the power consumption generated by signal inversion when the chip is working normally, and static power consumption is the power consumption generated when the circuit is powered on but not working.
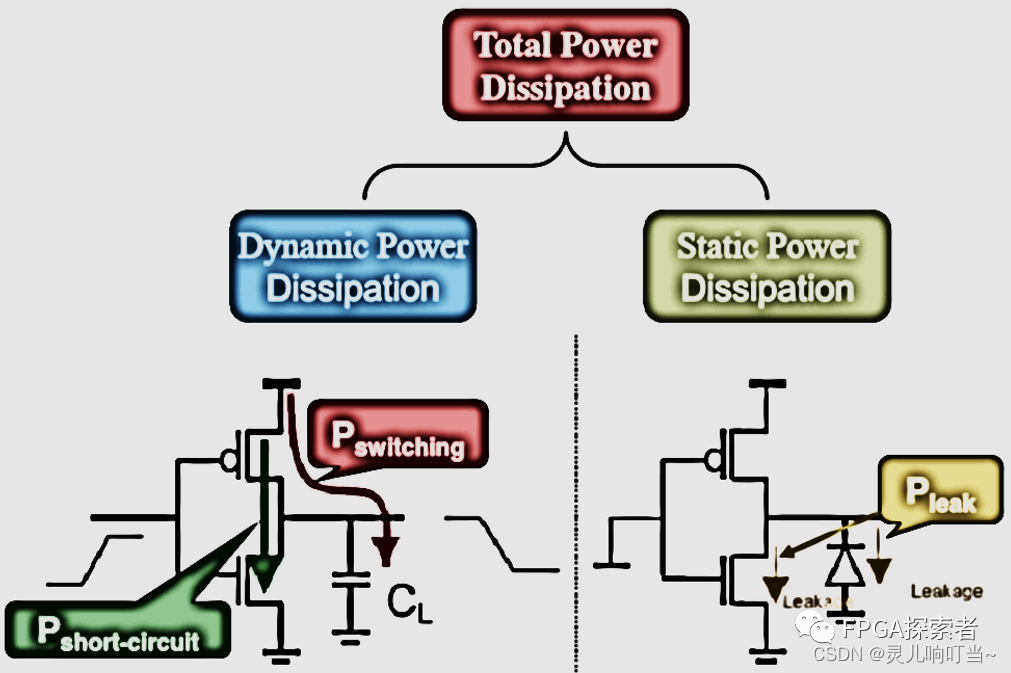
dynamic power consumption
Dynamic Power = Switch Power + Internal Power
Flip power consumption: the power consumption caused by the charge and discharge of the load capacitor during the working process of the chip;
Short-circuit power consumption (Internal Power): The inversion of the signal is not completed instantaneously, so there will always be a period of time during the inversion process that will cause the NMOS and PMOS to be turned on at the same time, which is equivalent to forming a short circuit between VDD and GND, by The resulting power consumption is the short-circuit power consumption;
Static power
Static power consumption (Leakage Power) is mainly the power consumption caused by leakage current. In CMOS gates, leakage current mainly comes from four sources:
- Sub-threshold Leakage (ISUB): Sub-threshold leakage current is the current that flows when the transistor should be turned off;
- Gate Leakage, Igate: Due to gate oxide tunneling and hot carrier injection, the current flows from the gate directly through the oxide to the substrate;
- Gate Induced Drain Leakage (IGIDL): Junction leakage occurs when the source or drain diffusion is at a different potential than the substrate. Junction leakage currents are usually small when compared to other leakage currents.
- Reverse Bias Junction Leakage (Reverse Bias Junction Leakage, IREV): caused by minority carrier drift and electron/hole pair generation in the depletion region.
Static power consumption can be viewed as a function of voltage, threshold voltage, and transistor size.
2. How to reduce power consumption?
2.1 Reduce dynamic power consumption
Voltage angle:
- Reduce the working voltage ;
- Use multiple voltage domains : provide different voltages for blocks and modules of different functions; for example, use high power supply voltage for memory to ensure the stability of memory cells, use medium-sized voltage for processors, and use low-speed IO peripherals The circuit uses low voltage; the method to determine the signal transmission across the voltage domain is to use a level shifter;
- Dynamic voltage scaling technology DVS (Dynamic voltage scaling) : The chip dynamically adjusts the voltage of some parts during operation; for example: the processor can use different voltages in different operating modes;
- Dynamic voltage frequency scaling technology DVFS (Dynamic voltage frequency scaling) : the chip dynamically adjusts the voltage and frequency of certain parts during operation; this technology requires software and hardware co-processing;
- Power off Power-gating ;
Load capacitance angle:
- Reasonable layout and wiring ;
- Reduce the size of transistors in proportion ;
- In multi-chip systems, multi-chip packaging technology can be considered to reduce interface capacitance;
- Reduce logic depth ;
Data flip angle:
- Reduce unnecessary data flipping ;
- When no operation is required, the data remains unchanged, and it is not mandatory to set 0 or 1 ;
- Use codes with less state flips such as Gray codes;
Frequency Angle:
- Reduce working frequency ;
- multiple clock domains ;
- DVFS dynamic voltage frequency scaling technology ;
- Use gated clock , clock gating;
2.2 Reduce static power consumption
Voltage angle:
- Reduce the working voltage ;
- Using multiple voltage domains ;
- Dynamic voltage scaling technology DVS (Dynamic voltage scaling) ;
- Dynamic voltage frequency scaling technology DVFS (Dynamic voltage frequency scaling) ;
- Power off Power-gating ;
Leakage current angle:
- Increase the proportion of transistors HVT using high threshold voltage ;
- Transistors with multiple threshold voltages : For different blocks, modules arrange transistors with different threshold voltages to achieve a balance of performance and power;
- Use multiple gate oxide thickness transistors ;
- Adjust the substrate voltage so that the transistor is in reverse body bias ;
Summarize
The above is the content related to power consumption in digital chips learned today. Welcome everyone to discuss and exchange~
References:
Methods of saving static power consumption and dynamic power consumption in IC design_Methods of reducing dynamic power consumption_Little by little progress blog-CSDN blog digital IC written test questions (7) - low power design [static power consumption] 【Dynamic Power Consumption】
Basics of Low Power Design: In-depth Understanding of Internal Power - zhihu.com