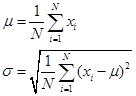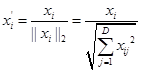data preprocessing
Data preprocessing generally includes:
(1) Data standardization
This is the most commonly used data preprocessing, converting all samples of a certain feature into a mean of 0 and a variance of 1.
Methods for transforming data into a standard normal distribution:
Treat each dimension feature separately:
in,
StandardScaler() in sklearn.preprocessing can be called to standardize the data.
(2) Data normalization
Limit all sample values of a feature within the specified range (usually [-1,1] or [0,1]).
The normalized method is:
You can call MinMaxScaler() in sklearn.preprocessing to limit the data to the [0,1] range, and call MaxAbsScaler() to limit the data to the [-1,1] range.
(3) Data normalization
Convert the modulus length of all samples of a feature to 1. The method is:
You can call the Normalizer() implementation in sklearn.preprocessing
(4) Data binarization
Convert the feature value of the data to 0 or 1 according to the threshold.
(5) Data missing value processing
For the missing feature data, data filling is carried out, and the general filling methods are: mean, median, mode filling, etc.
(6) Data outlier processing
Remove outlier data.
(7) Data type conversion
If the features of the data are not numeric features, they need to be converted to numeric.
1. Import the necessary toolkit
The data processing toolkits are: Numpy, SciPy, pandas, among which SciPy, pandas are further packaged based on Numpy The
data visualization toolkits are: Matplotlib, Seaborn, where Seaborn is a further package based on Matplotlib
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
%matplotlib inline2. Read data
dpath = './data/'
data = pd.read_csv(dpath +"boston_housing.csv")
data.head()
data.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 506 entries, 0 to 505
Data columns (total 14 columns):
CRIM 506 non-null float64
ZN 506 non-null int64
INDUS 506 non-null float64
CHAS 506 non-null int64
NOX 506 non-null float64
RM 506 non-null float64
AGE 506 non-null float64
DIS 506 non-null float64
RAD 506 non-null int64
TAX 506 non-null int64
PTRATIO 506 non-null int64
B 506 non-null float64
LSTAT 506 non-null float64
MEDV 506 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(9), int64(5)
memory usage: 55.4 KB
3. Split the data into training data and test data
Delete a row or column:
DataFrame.drop(labels, axis=0, level=None, inplace=False, errors=’raise’)
labels : single label or list-like
axis : int or axis name
level : int or level name, default None For MultiIndex
inplace : bool, default False. If True, do operation inplace and return None.
errors : {‘ignore’, ‘raise’}, default ‘raise’,If‘ignore, suppress error and existing labels are dropped.
Returns: dropped : type of caller
y = data['MEDV'] # 获取列名为'MEDV'的列的数据
#print y
X = data.drop('MEDV', axis=1) # 从axis=1轴(列)中删去列名为'MEDV'的列
X.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 506 entries, 0 to 505
Data columns (total 13 columns):
CRIM 506 non-null float64
ZN 506 non-null int64
INDUS 506 non-null float64
CHAS 506 non-null int64
NOX 506 non-null float64
RM 506 non-null float64
AGE 506 non-null float64
DIS 506 non-null float64
RAD 506 non-null int64
TAX 506 non-null int64
PTRATIO 506 non-null int64
B 506 non-null float64
LSTAT 506 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(8), int64(5)
memory usage: 51.5 KB
4.采样训练样本和测试样本
sklearn.cross_validation.train_test_split(*arrays, **options)
*arrays : sequence of indexables with same length / shape[0]
Allowed inputs are lists, numpy arrays, scipy-sparse matrices or pandas dataframes.
test_size : float, int, or None (default is None)
If float, should be between 0.0 and 1.0 and represent the proportion of the dataset to include in the
test split. If int, represents the absolute number of test samples. If None, the value is automatically
set to the complement of the train size. If train size is also None, test size is set to 0.25.
train_size : float, int, or None (default is None)。
If float, should be between 0.0 and 1.0 and represent the proportion of the dataset to include
in the train split. If int, represents the absolute number of train samples. If None, the value is
automatically set to the complement of the test size.
random_state : int or RandomState。Pseudo-random number generator state used for random sampling.
stratify : array-like or None (default is None)
X_train,X_test,y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0, test_size=0.25)
X:输入特征,
y:输入标签,
random_state:随机种子,
test_size:测试样本数占比,为默认为0.25
[X_train, y_train] 和 [X_test, y_test]是一对,分别对应分割之后的训练数据和训练标签,测试数据和训练标签
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
# 随机采样25%的数据构建测试样本,其余作为训练样本
# X:输入特征,y:输入标签,random_state随机种子为27, test_size:测试样本数占比,如果train_size=NULL,则为默认的0.25
# 输出为训练样本和测试样本的DataFrame数据
X_train,X_test,y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=27, test_size=0.25)
print X_train.shape
print y_train.shape
print X_test.shape
print y_test.shape(379, 13)
(379L,)
(127, 13)
(127L,)
5.数据预处理
数据标准化:
初始化:
sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler(copy=True, with_mean=True, with_std=True)
with_mean : boolean, True by default.If True, center the data before scaling.
with_std : boolean, True by default.If True, scale the data to unit variance (or equivalently, unit
standard deviation).
copy : boolean, optional, default True.If False, try to avoid a copy and do inplace scaling instead.
方法:
X_new = fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params) 进行mean和std计算,并进行数据的标准化
X : numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features].Training set.
y : numpy array of shape [n_samples].Target values.
X_new : numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features_new].Transformed array.
X_new = transform(X, y=None, copy=None) 使用已经计算的mean和std进行数据的标准化
X : array-like, shape [n_samples, n_features].The data used to scale along the features axis.
X_new : numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features_new].Transformed array.
# 数据标准化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# 分别初始化对特征和目标值的标准化器
ss_X = StandardScaler()
ss_y = StandardScaler()
# 分别对训练和测试数据的特征以及目标值进行标准化处理
X_train = ss_X.fit_transform(X_train) # 先计算均值和方差,再进行变换
X_test = ss_X.transform(X_test) # 利用上面计算好的均值和方差,直接进行转换
y_train = ss_y.fit_transform(y_train)
y_test = ss_y.transform(y_test)
print X_train[[-0.37683627 -0.50304409 2.48277286 ..., 0.86555269 -0.13431739
1.60921499]
[ 5.13573477 -0.50304409 1.0607873 ..., 0.86555269 -2.93693892
3.44576006]
[-0.37346431 0.01751212 -0.44822848 ..., -1.31269744 0.33223834
2.45055308]
...,
[-0.39101613 -0.50304409 -1.13119458 ..., -0.87704742 0.28632785
-0.36708256]
[-0.38897021 -0.50304409 -1.2462515 ..., -0.44139739 0.38012111
0.19898553]
[-0.31120842 -0.50304409 -0.40840109 ..., 1.30120272 0.37957325
-0.18215757]]转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/tan-v