Blockchain technology is not a single technology, but a comprehensive technical system that integrates various research results. The industry generally recognizes that blockchain has three core technologies that are indispensable: distributed structure, consensus mechanism and asymmetric encryption .
(1) Distributed structure: not all equal to decentralization
In the first article we have briefly introduced the difference between centralization and decentralization. Today we will continue to go deeper and discuss the distributed structure of the blockchain.
Decentralized VS Distributed Structure
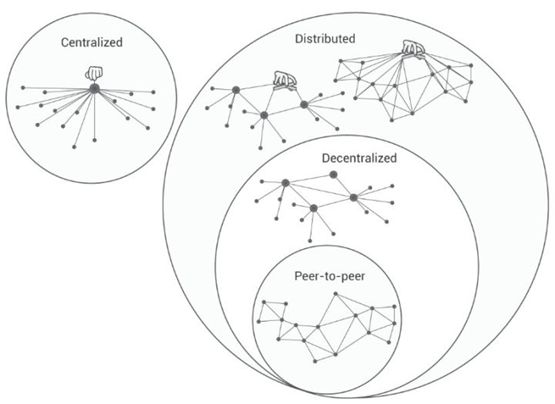
Centralization, distribution, decentralization, peer-to-peer (pictures from the Internet)
In traditional cognition, the opposite of centralization is decentralization. Here we must first correct a point of view: the antonym of centralization should be decentralized, that is, distributed. From the figure above, we can clearly see the relationship between Centralized, Distributed, Decentraliazed, and Peer-to-peer. Decentralization is only one type of distribution.
Why should we emphasize distributed rather than decentralized? Because the definition of distributed is not only decentralized, but also includes weak centralization. If we blindly emphasize decentralization, it will be difficult for blockchain technology to be accepted by the existing financial system and intellectual property system. If everything is decentralized, what roles will countries, banks, and institutions play in the future financial system? Does the future financial system not need banks with national coercive power? This is obviously unrealistic. Tencent Research Institute also emphasized in the "Blockchain Solution White Paper" that the new value interaction paradigm created by blockchain is based on "weak centralization".
But if we think of it as distributed, the problem is solved: the center has not disappeared, but a multi-center system will appear in large numbers. Private chains, alliance chains, and hybrid chains will serve as supplements to centralization to improve the operational efficiency of centralization.
Here we want to add a supplementary note, that is, the distributed storage of the blockchain is different from the traditional distributed storage:
- Traditional distributed storage divides data into multiple shares according to certain rules for storage, while each node of the blockchain stores complete data in a chain structure.
- Traditional distributed storage synchronizes data through the central node to the backup node, while the storage of each node in the blockchain is independent and low-level equal, relying on the consensus mechanism to ensure the consistency of storage.
(2) Consensus mechanism: achieve node consistency and ensure that the distributed ledger cannot be tampered with
Above we said that the distributed storage of the blockchain relies on the consensus mechanism to ensure the consistency of the storage. The so-called consensus mechanism is the core algorithm to realize the distributed structure of the blockchain. The process in which blockchain nodes reach consensus on certain data, behaviors, or processes through the interaction of multiple nodes under preset rules is called consensus. The core of the consensus mechanism is the construction and verification of blocks, with the purpose of solving the Byzantine general problem.
Byzantine failures is a fundamental problem in point-to-point communication proposed by Leslie Lambert.
The implication is that attempting to achieve consensus by means of message delivery over an unreliable channel with message loss is impossible. Therefore, research on consistency generally assumes that the channel is reliable, or this problem does not exist.
If we go back to our previous ledger metaphor, the consensus mechanism is to ensure that users in the entire system follow a recognized ledger record.
There are many consensus mechanisms in the blockchain, and each consensus mechanism has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here we will first explain the proof of work in detail, so that everyone can understand what a consensus mechanism is. We leave the analysis of other consensus mechanisms to the next one. Article.
- Proof of Work (POW)
Proof of Work (POW for short), as the name suggests, is the confirmation and proof of a certain amount of work you have done. We can understand that this is a result-oriented mechanism, because the monitoring of the work process is too cumbersome and inefficient.
Bitcoin adopts the consensus mechanism of proof of work. As we said in the previous article, the new block of Bitcoin needs to calculate the hash value of the previous block header to connect with the previous block to form a transaction chain. A qualified block hash value is usually composed of N leading zeros, and the number of zeros depends on the difficulty value of the network. To get a reasonable block hash value requires a lot of trial calculations, and the calculation time depends on the computing speed of the machine. Finding a reasonable hash value is a probabilistic event. When a node has n% of the computing power of the entire network, the node has an n% probability of finding the block hash value.
The workload proof mechanism relies on the mathematical operation of the machine to ensure that the ledger transaction records are not tampered with. Because to change the transaction records of a block, it is necessary to complete the proof of work of this block again, and also need to complete the proof of work of the blocks added after this block, and the income is not as good as the financial resources spent. POW can ensure reliable nodes in the network, and will use the longest blockchain in the network as a reliable chain, that is, a recognized ledger. As long as reliable nodes control most of the computing power, the reliable chain will grow the fastest, thus surpassing other blockchains. competition chain. Moreover, the possibility of chains controlled by unreliable nodes catching up with reliable chains will also decrease as the number of blocks increases.
Proof of work guarantees the distributed performance of the blockchain well. However, since Bitcoin has attracted most of the computing power in the world, it is difficult for other blockchain applications to obtain the same computing power to ensure their own security. And this kind of large-scale mining will cause huge waste of resources, and the cycle of reaching consensus is relatively long, so some blockchain applications after Bitcoin mostly use other consensus mechanisms.
(3) Asymmetric encryption: public key VS private key
In the distributed network of blockchain, the security of point-to-point information transmission is realized through mathematical encryption. To understand the encryption method of the blockchain, we first need to understand the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption.
Before 1976, there was only one encryption method: (1) Party A chooses a certain encryption rule to encrypt the information (2) Party B uses the same rule to decrypt the information. Since encryption and decryption use the same rules (keys), this is called a Symmetric-key algorithm. This encryption mode has one biggest weakness: Party A must tell Party B the encryption rules, otherwise it cannot be decrypted. Saving and transferring the key has become the most troublesome problem.
In 1977, three mathematicians Rivest, Shamir and Adleman designed an algorithm: (1) Party B generates two keys (public key and private key). The public key is public and can be obtained by anyone, while the private key is kept secret. (2) Party A obtains Party B's public key, and then uses it to encrypt information. (3) Party B obtains the encrypted information and decrypts it with the private key. The information encrypted by the public key can only be decrypted by the private key, so as long as the private key is not leaked, the communication is safe. This algorithm is named after the three of them, called the RSA algorithm. Encryption and decryption use different rules, thus achieving asymmetric encryption .
In the blockchain, the dissemination of information is based on asymmetric digital encryption technology such as public key and private key to achieve mutual trust between the two parties in the transaction. In the specific implementation process, after the information is encrypted by one key in the public-private key pair, it can only be decrypted by using the other key.
Taking Bitcoin as an example, the user's wallet does not actually contain Bitcoin, but only the key. A user's digital key is completely independent of the Bitcoin protocol, generated and managed by the user's wallet, and does not even require a zone. Block chain or network link. Each transaction needs a valid signature to be stored in the block, and a valid signature needs a valid digital key to generate, so having the key is equivalent to having control over Bitcoin.
The private key of Bitcoin is essentially an array of 32 bytes. The generation of the public key and address depends on the private key. With the private key, the public key and address can be generated, and the bitcoins corresponding to the address can be spent. The way the private key spends bitcoins is to sign the transaction corresponding to the private key.
For a better understanding, let's take an example of a transaction to illustrate the operation of the entire process. Suppose little A and little B want to conduct a transaction, and little A wants to prove to little B that he is the real little A, then little A only needs to use the private key to sign the file and send it to little B, and little B uses little A’s The public key performs signature verification on the file. If the verification is successful, it proves that the file was encrypted by the real little A with the private key.

In this way, the ownership of the blockchain is determined through digital keys, blockchain addresses, and digital signatures. Mastering the private key is equivalent to mastering the ownership of digital assets