1 Introduction to asset loss prevention and control
Dewu provides a large number of commodity trading and other services, with a large amount of capital flow, any design flaws, system flaws, system failures, human operations, security vulnerabilities and other factors will cause direct or indirect capital losses. Capital loss prevention and control is to introduce a variety of capital analysis and control methods during the entire life cycle of the project to prevent capital loss failures or control the impact of capital loss failures.
So in daily work, how to carry out specifically? It can be done mainly from the following three aspects:
1.1 Mechanism process construction
At the beginning of a business project, we should assess the risk level of project funds, such as high-risk needs to focus on & invest, how much resources need to be invested in medium-risk, and how to guarantee low-risk.
After the risk assessment of project funds, the product architecture design needs to include technical risk design, such as idempotent, distributed data consistency, multi-active in different places, etc.
Then for high capital risk projects, we need to develop a special capital risk system, focusing on capital flow, information flow and logistics flow in Dewu, such as what is the high-security link of the business, and what are the risk points of capital loss, etc. .
The next step is to arm the output risk points of asset loss. The form of arming is mainly checking and monitoring. Checking is the mainstay, and monitoring is the bottom line, because the risk points of asset loss output previously may be missed, and monitoring is a means of sensing business abnormalities. . In daily life, we can also carry out risk mining & check rule verification through chaos engineering.
Finally, we need to respond to the asset loss risk alarm, and pull up the emergency team to check and confirm the risk and repair it.
1.2 Personnel formation construction
Capital loss prevention and control is not undertaken by a certain role, but requires structure, R&D, quality and SRE to prevent and control and embed it into the daily work process. From the perspective of organizational structure, we need to establish at least three lines of defense, namely the R&D line of defense , The quality defense line and the SRE defense line are mutually supportive and combined to achieve the purpose of asset loss prevention and control. Of course, each role has its own focus at each stage of the project. For example, SRE is responsible for the online stability of the business, so the investment in online asset loss prevention and control is relatively large.
1.3 Multi-system prevention and control
From the perspective of the timeliness of discovering capital loss risks, it can be divided into real-time verification (T+0), near-real-time verification (T+M), and offline verification (T+H, T+1). Each verification method has its own advantages. There is no alternative for the business scenarios that are configured. For example, real-time verification is applicable to configuration changes that do not fall into the database, and offline verification is applicable to scheduled business tasks. When arming in actual business scenarios, it is necessary to analyze the business characteristics, and then use the appropriate verification system tools. In terms of organizational division of labor, R&D focuses on offline verification, testing focuses on near real-time verification, and SRE focuses on real-time verification. Of course, the boundaries do not have to be so clear in actual work. You can choose the appropriate tool system for the risk points you see.
From the perspective of whether the verification affects business operation, it can be divided into bypass verification and main road verification. The result of bypass verification does not affect business operation, but only reveals risks, while main road verification has the ability to affect business operations. For example, The main road verification technology is used for the capital loss circuit breaker, and the business operation is interrupted after the verification alarm is issued. At present, the existing A and B platforms of the company belong to the bypass checking system.
After deploying the verification rules, how do we test the effectiveness of the deployment? At the same time, due to the iterative development of the business, the verification rules for the previous deployment need to be adjusted to adapt to the new business logic. In other words, how do we keep the verification rules fresh? This requires the support of chaos engineering loss drills. Asset loss drills are further divided into lossy drills and non-destructive drills. For example, when conducting online lossy drills, the amount data is often added/subtracted by 0.01 to check whether the check rules for arming are found. In this way, even if actual asset losses occur, the drill budget can still be maintained. However, it is necessary to carefully evaluate the scope of influence when engaging in online destructive drills. The key to non-destructive exercises for asset loss prevention and control lies in the cloning of the production database, so that data tampering during the exercise will not affect online business operations.
2 Asset loss prevention and control technology system
When we are doing asset loss prevention and control, the most important step is risk identification, which is the source of asset loss verification and deployment. It can be said that if there is no risk identification, there will be no subsequent verification and deployment. Risk identification can be obtained through manual analysis and intelligent system derivation. From the construction and development stage, manual analysis is usually the first method adopted. On this basis, intelligent system derivation is developed through algorithm derivation + expert experience. The following is based on the perspective of manual analysis. Here is an example of how to prevent and control the asset loss of a simplified version of the Dewu system. As shown in the figure below, the left side is the product transaction business link, which includes the user's order transaction and operation configuration product:
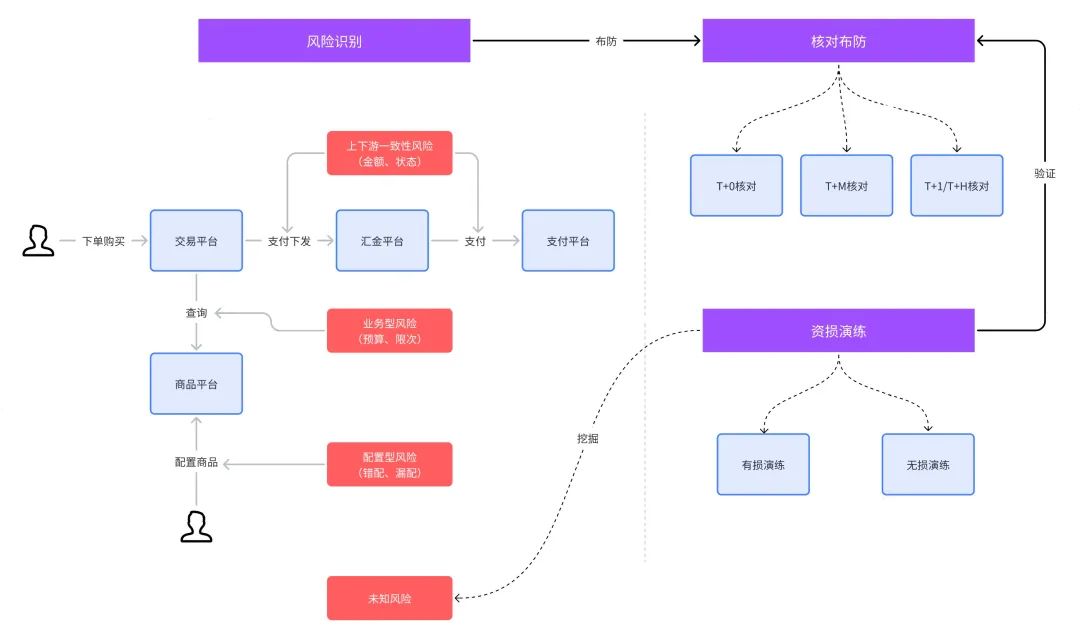
Because the trading platform has the amount and status of the order transaction, and the Huijin platform is connected to various payment channels and is the actual executor of the payment, there is a risk of consistency between the upstream and downstream order amounts and status.
If the product purchased by the user is participating in a marketing activity, the transaction platform will query the specific activity logic of the product operation platform, such as the budget of the marketing activity and the logic of the limit of coupon usage. There may be business risks in the activity budget and coupon usage.
Operation personnel configure a certain marketing activity, and there are configuration risks such as mismatch and missing configuration in key parameters such as product and price.
The risks mentioned above usually need to be identified after analyzing the PRD, technical implementation documents or code CR. Next, let’s see how we can deploy them.
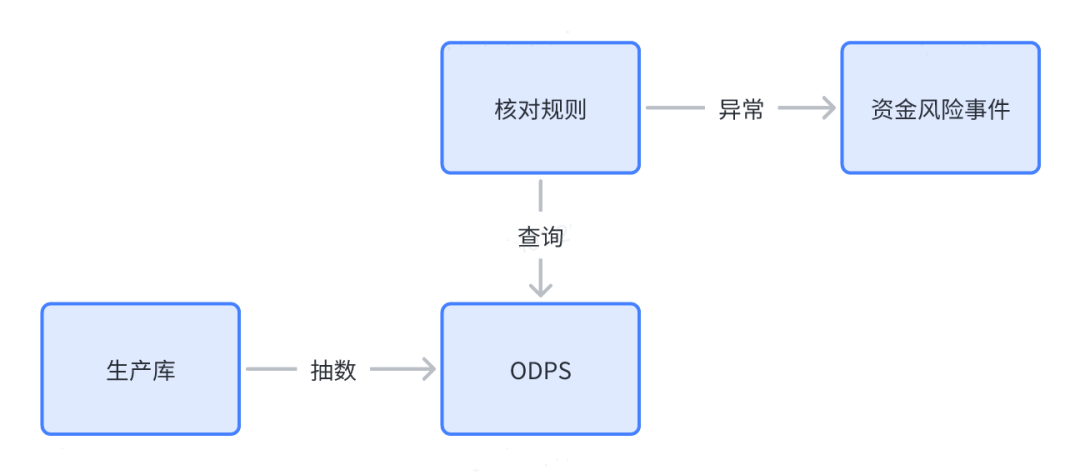
2.1 T+1/T+H check
In the evolution process of the entire fund prevention and control system, offline verification should be said to be the first verification method developed in the industry. At first, like many banks, it relied on manpower to reconcile the current amount with the general ledger throughout the day, and then through automatic In this way, the full database table is exported and then calculated for verification. At present, ODPS is mainly used to realize T+1 and T+H offline verification. Its advantage is that it does not affect the business production library, and because it is scheduled to run at regular intervals, it takes a long time for business timing tasks and other data backtracking The scene is quite suitable.
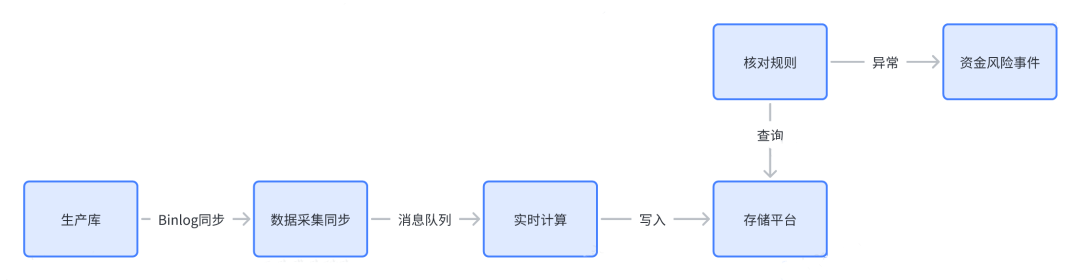
2.2 T+M check
Minute-level asset loss checks can be realized through the database Binlog. This check method has a very good ability to discover the consistency risks of upstream and downstream businesses. It can also be used for uncovered asset loss risks when combined with the non-destructive drill capabilities of Chaos Engineering. Therefore, T+M verification is applicable to business scenarios involving consistency risks and blocking of database fields.
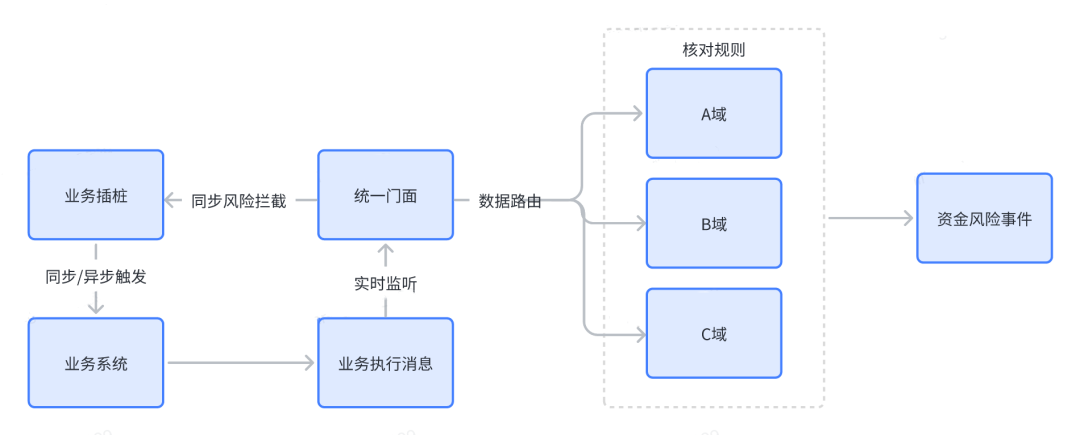
2.3 T+0 check
With the development of business, higher requirements are put forward for asset loss verification, and we need to develop real-time verification capabilities. For example, it is possible to implement synchronous/asynchronous triggering by means of business instrumentation, and at the same time monitor business execution messages in real time, and then route the data to specific business domains to perform verification logic. This verification method is a heavy weapon in the field of asset loss prevention and control, and is suitable for business type risk, configuration type risk, and meet complex business verification scenarios at the same time. At present, SRE is already building a T+0 real-time verification system.
2.4 Asset Loss Drill
Asset loss drills can verify the validity of the check rules for deployment, and can also be used to uncover uncovered asset loss risks. Therefore, asset loss drills are an important part of the asset loss prevention and control system. There are three key points in the capital non-destructive exercise:
The rules for asset loss prevention and control are all implemented for business data
The data of loss prevention and control non-destructive exercise comes from the production environment
The non-destructive exercise data is essentially isolated from the production environment data
The following figure shows the preliminary non-destructive exercise plan for funds:

3 Dewu business practice
As an SRE that supports the Dewu business, it has led the work of guaranteeing the security of Dewu's performance funds. Due to the long business chain and large risk exposure of Dewu's performance, we have carefully considered the stability of the business and the risk of asset loss and practiced the aforementioned related The concept of asset loss prevention and control.
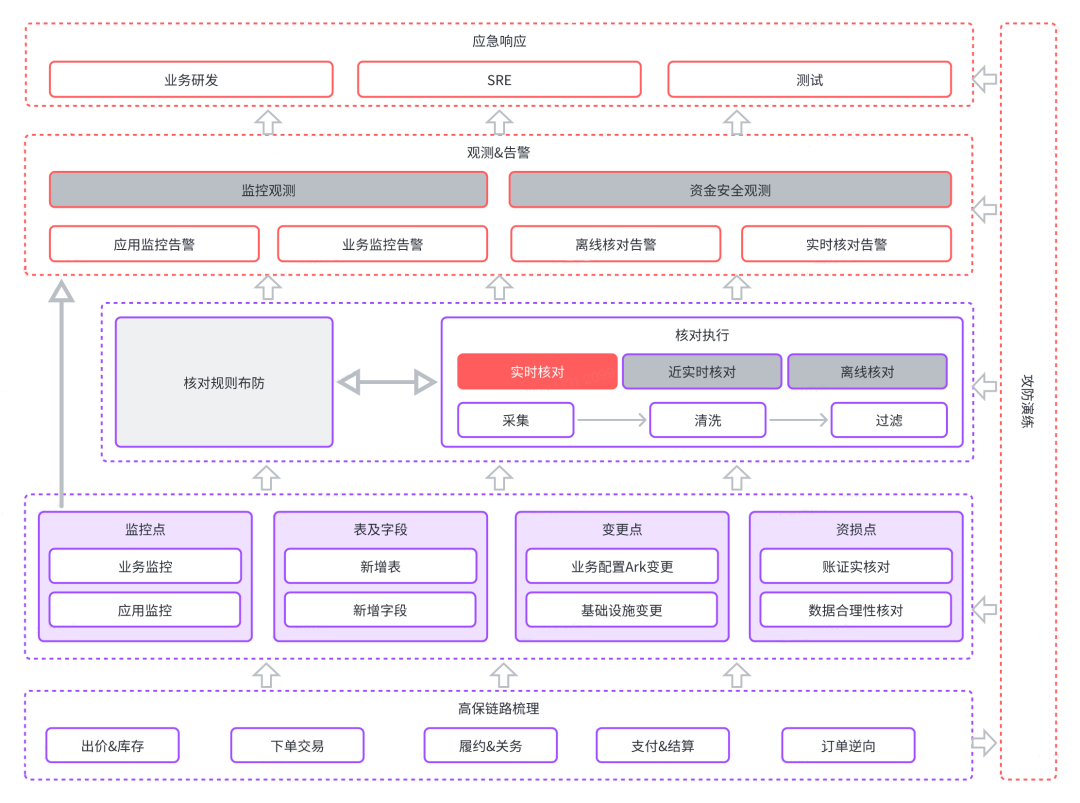
3.1 High-security link combing
Bidding, ordering, payment, delivery, settlement, marketing, and reverse seven business domains define high-security business links, and output asset loss points, change points, new tables and fields, and related monitoring points.
3.2 Tool selection
Relying on the existing tool platform for deployment, the cost-optimized solution.

3.3 Rule Arming
Capital loss prevention and control is implemented through verification rules, and at the same time, alarm rules are configured for business monitoring, and the validity of the rules is verified through chaos engineering drills.
3.4 Observe alarms
a. Emergency response
b. Automatic inspection
i. Daily automatic inspection of important indicators is pushed to the corresponding work group
3.5 Walkthrough
a. Keep relevant rules fresh
b. Mining of unexposed risks
3.6 Real-time verification system construction
a. The business instrumentation bypasses the check first, and then blocks the check.
4 Summary & Outlook
During the period of Dewu's implementation of asset loss prevention and control, as SRE has been promoting the concept: asset loss prevention and control requires the cooperation of research and development, testing, and SRE. In the future, we will focus on the following three aspects for asset loss prevention and control:
Risk analysis--At present, we are mainly based on expert experience. In the future, we will achieve automated risk output through data coloring and blood relationship analysis.
Multi-system prevention and control--Improve the construction of asset loss prevention and control system, abstract general prevention and control capabilities and expandable fine-grained prevention and control capabilities, so that the checking tool system is compatible with business scenarios.
Drilling for asset loss—In a large-scale business system, it is not realistic to rely solely on people to attack, and it must be driven by intelligent and data-based methods. For the same fault, we let it replay on hundreds or thousands of systems, so that we can very efficiently realize large-scale risk mining, verify the effectiveness of risk prevention and control rules, and keep the deployed rules fresh.
*Text/Yuerong
This article is an original article of Dewu Technology. For more exciting articles, please see: Dewu Technology Official Website
It is strictly forbidden to reprint without the permission of Dewu Technology, otherwise legal responsibility will be investigated according to law!
Redis 7.2.0 was released, the most far-reaching version Chinese programmers refused to write gambling programs, 14 teeth were pulled out, and 88% of the whole body was damaged. Flutter 3.13 was released. System Initiative announced that all its software would be open source. The first large-scale independent App appeared , Grace changed its name to "Doubao" Spring 6.1 is compatible with virtual threads and JDK 21 Linux tablet StarLite 5: default Ubuntu, 12.5-inch Chrome 116 officially released Red Hat redeployed desktop Linux development, the main developer was transferred away Kubernetes 1.28 officially released