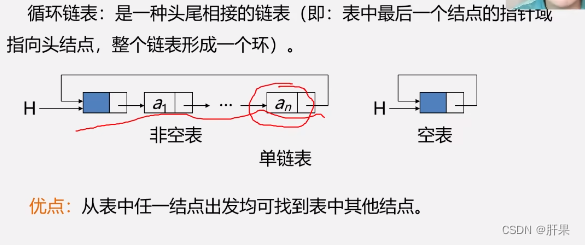
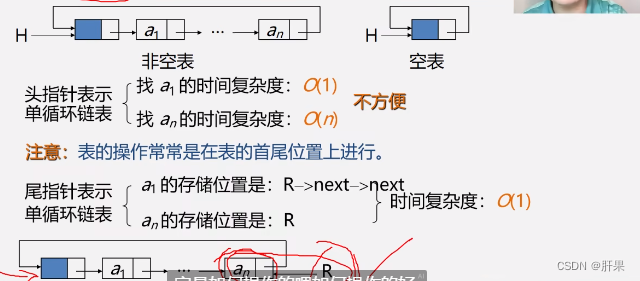
circular linked list

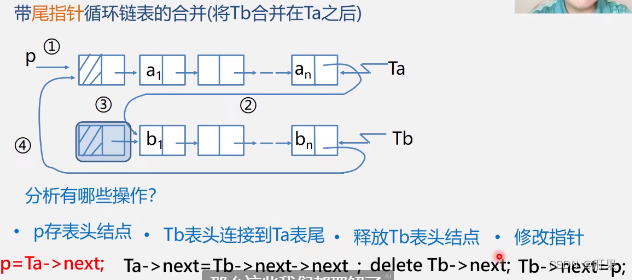
Merge of Circular Linked List with Tail Pointer

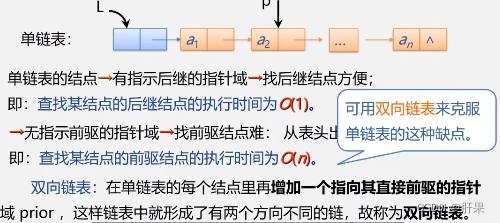
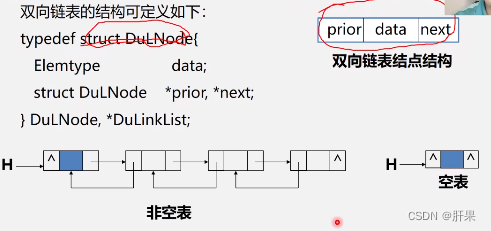
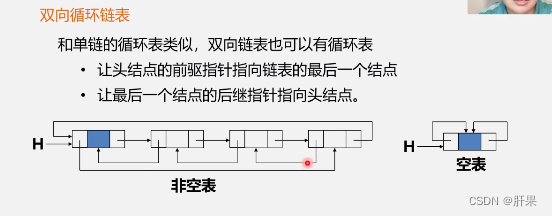
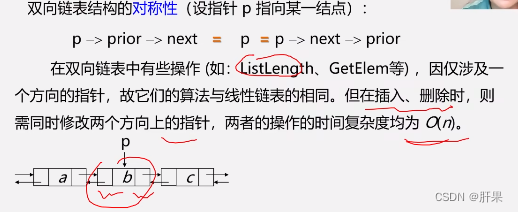
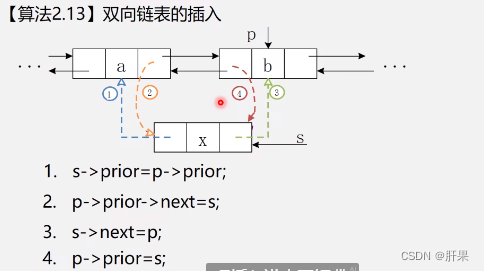
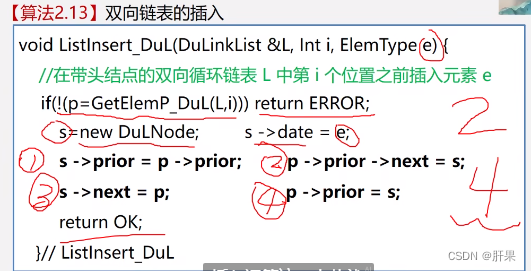
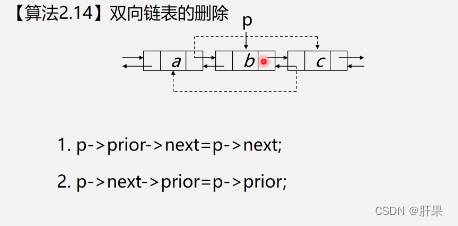
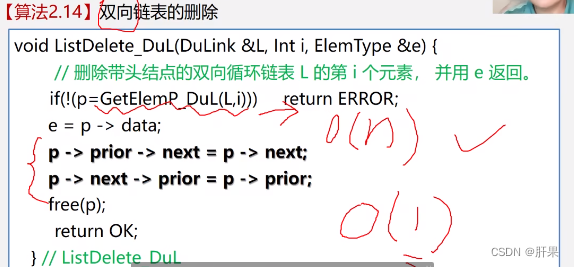
Doubly linked list
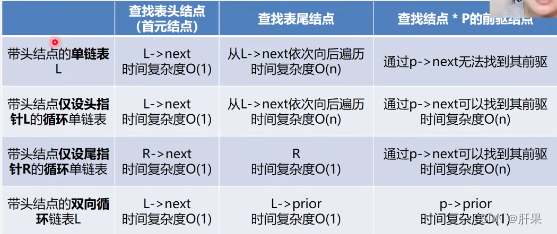
Time Efficiency Comparison of Singly Linked List, Circular Linked List and Doubly Linked List
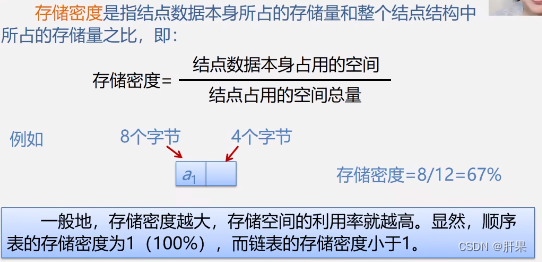
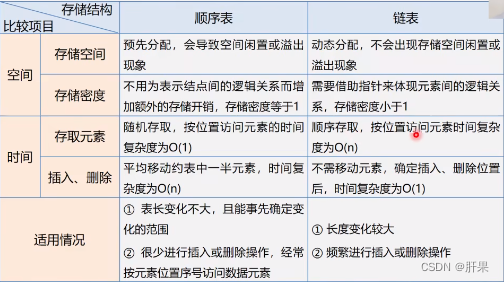
Comparison between sequenced list and linked list
Advantages of chain storage structure
1. The node space can be dynamically applied and released;
2. The logical order of the data elements is indicated by the pointer of the node, and there is no need to move the data elements when inserting and deleting.
Disadvantages of chain storage structure
1. The storage density is small, and the pointer field of each node needs to occupy additional storage space. When the data field of each node occupies a small number of bytes, the proportion of the storage space occupied by the pointer field appears to be very large.
2. The chain storage structure is a non-random access structure. The operation on any node needs to find the node from the head pointer according to the pointer chain, which increases the complexity of the algorithm.
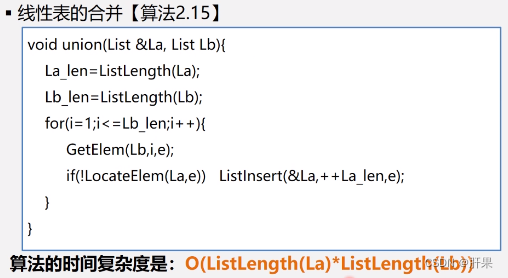
Linear table application


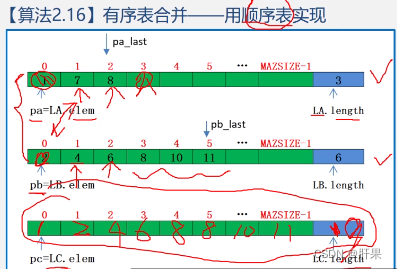
Implemented in C language:
#include <stdio.h>
void mergeArrays(int arr1[], int size1, int arr2[], int size2, int mergedArray[]) {
int i, j, k, duplicate;
// 将arr1的元素插入合并数组
for (i = 0; i < size1; i++) {
mergedArray[i] = arr1[i];
}
k = size1;
// 将arr2中非重复元素插入合并数组
for (i = 0; i < size2; i++) {
duplicate = 0;
for (j = 0; j < size1; j++) {
if (arr2[i] == arr1[j]) {
duplicate = 1;
break;
}
}
if (!duplicate) {
mergedArray[k++] = arr2[i];
}
}
}
int main() {
int arr1[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int size1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int arr2[] = {
4, 5, 6, 7, 8};
int size2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
// 计算合并数组的最大长度
int maxSize = size1 + size2;
int mergedArray[maxSize];
mergeArrays(arr1, size1, arr2, size2, mergedArray);
// 输出合并并去重后的数组
for (int i = 0; i < size1 + size2; i++) {
printf("%d ", mergedArray[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}



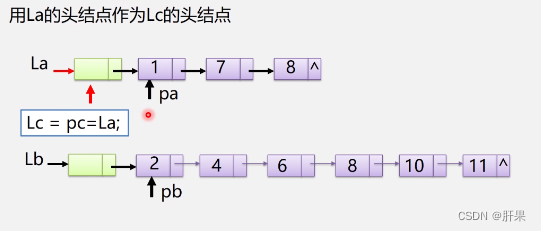
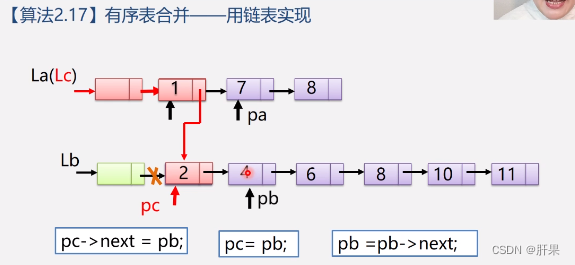
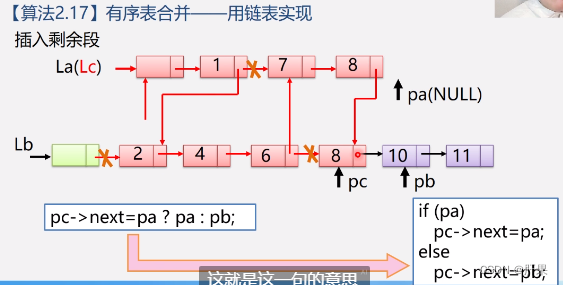
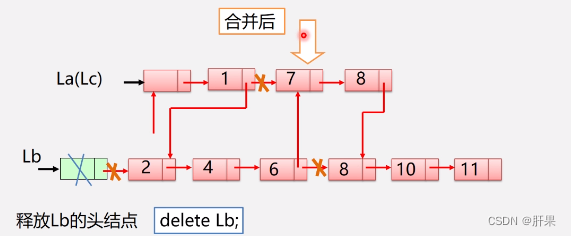

The implementation code is as follows:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Mylist
{
int m_int;
Mylist* myl;
};
int main()
{
Mylist* la = new Mylist;
la->myl = new Mylist;
la->myl->myl = new Mylist;
la->myl->myl->myl = new Mylist;
la->myl->myl->myl->myl = NULL;
la->myl->m_int = 1;
la->myl->myl->m_int = 7;
la->myl->myl->myl->m_int = 8;
Mylist* lb = new Mylist;
lb->myl = new Mylist;
lb->myl->myl = new Mylist;
lb->myl->myl->myl = new Mylist;
lb->myl->myl->myl->myl = new Mylist;
lb->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl = new Mylist;
lb->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl = new Mylist;
lb->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl = NULL;
lb->myl->m_int = 2;
lb->myl->myl->m_int = 4;
lb->myl->myl->myl->m_int = 6;
lb->myl->myl->myl->myl->m_int = 8;
lb->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl->m_int = 10;
lb->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl->myl->m_int = 11;
Mylist* pc = la;
Mylist* lc = la;
Mylist* pa = la->myl;
Mylist* pb = lb->myl;
while (pa&&pb)
{
if (pa->m_int <= pb->m_int)
{
pc->myl = pa; pc = pa; pa = pa->myl;
}
else
{
pc->myl = pb; pc = pb; pb = pb->myl;
}
}
pc->myl = pa ? pa : pb;
delete lb;
pc = lc;
while (pc->myl)
{
cout << pc->myl->m_int << " ";
pc = pc->myl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Case Analysis and Implementation
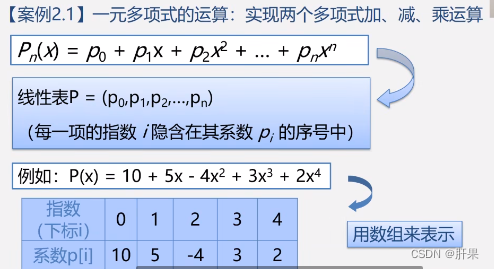
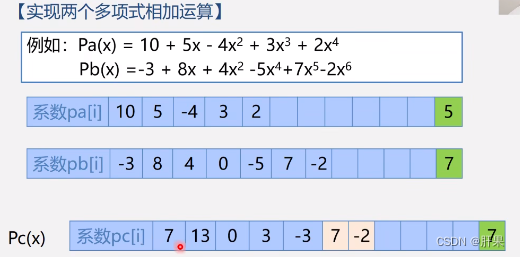
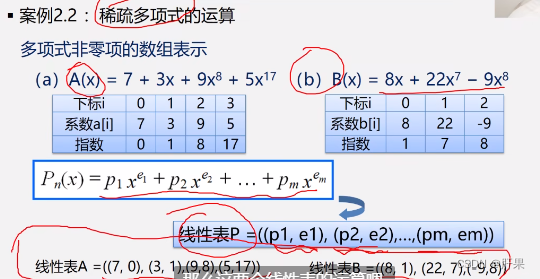

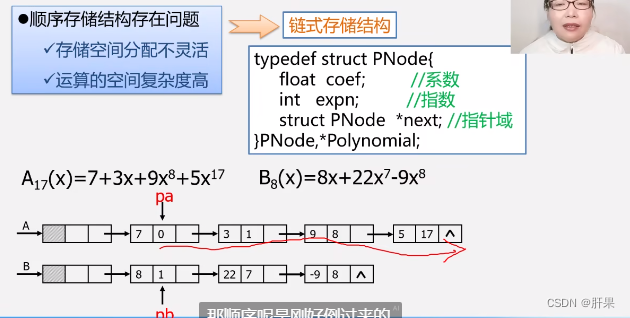


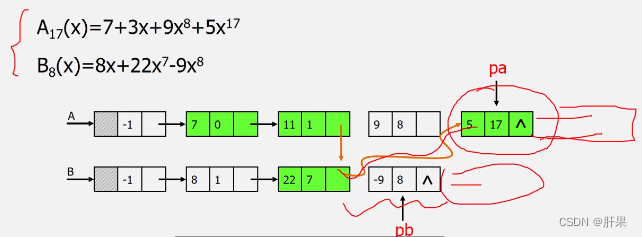
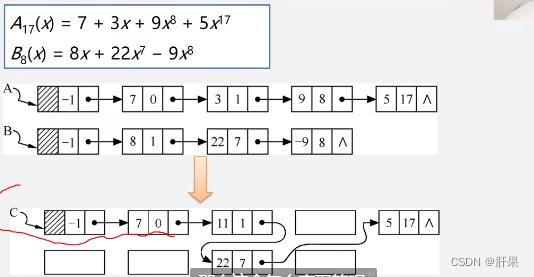
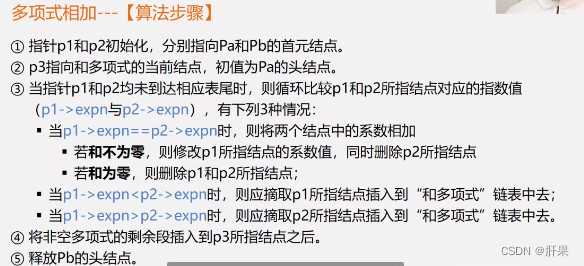
Implementation code:
Originally thought it was very simple, all written in the main function, the result...
The author of this code will avoid the situation of program errors and memory leaks as much as possible. If there are still deficiencies, you are welcome to point them out.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Poly
{
int c;
int e;
Poly* pnext;
};
int main()
{
cout << "本程序用链表方式实现两个一元多项式相加" << endl;
cout << "由低阶到高阶依次输入一元多项式的系数和指数" << endl;
cout << "用空格分隔,回车结束:(系数为0不需要输入)" << endl;
cout << "比如:y(x)=3x^0+4x^1+x^3 输入:3 0 4 1 1 3" << endl;
cout << "提示:输入任意非数字键退出" << endl;
int input;
int ctmp = 0;
int etmp = 0;
int tmp = 0;
int pta = 0;
int ptb = 0;
Poly* Pahead = new Poly;
Pahead->pnext = NULL;
Poly* Pa = Pahead;
Poly* Pbhead = new Poly;
Pbhead->pnext = NULL;
Poly* Pb = Pahead;
Poly* temp = NULL;
Poly* Pc = NULL;
while (true)
{
Pa = Pahead;
Pa = Pa->pnext;
while (Pa)
{
//cout << "Pa删除一项" << endl;
temp = Pa->pnext;
delete Pa;
Pa = temp;
}
Pa = Pahead;
Pb = Pbhead;
Pb = Pb->pnext;
Pahead->pnext = NULL;
while (Pb)
{
//cout << "Pb删除一项" << endl;
temp = Pb->pnext;
delete Pb;
Pb = temp;
}
Pb = Pbhead;
Pbhead->pnext = NULL;
cout << "下面请输入第一个一元多项式一共有几项" << endl;
cout << "=>";
while (true)
{
cin >> input;
if (cin.fail())
{
cin.clear();
cout << "已退出,欢迎再次使用。" << endl;
Pa = Pahead;
Pb = Pbhead;
if (Pahead != NULL)
{
//cout << "删除Pahead。" << endl;
Pa = Pahead;
while (Pa)
{
temp = Pa->pnext;
delete Pa;
Pa = temp;
}
}
if (Pbhead != NULL)
{
//cout << "删除Pbhead。" << endl;
Pb = Pbhead;
while (Pb)
{
temp = Pb->pnext;
delete Pb;
Pb = temp;
}
}
return 0;
}
if (input <= 0)
{
cout << "请至少输入一项" << endl;
continue;
}
if (input > 100)
{
cout << "最大不要超出100项……这么多的多项式爱因斯坦见了都得捂脸……" << endl;
continue;
}
pta = input * 2;
break;
}
cout << "下面请输入第一个一元多项式" << endl;
cout << "=>";
while (pta--)
{
cin >> input;
if (cin.fail())
{
cin.clear();
cout << "已退出,欢迎再次使用。" << endl;
Pa = Pahead;
Pb = Pbhead;
if (Pahead != NULL)
{
//cout << "删除Pahead。" << endl;
Pa = Pahead;
while (Pa)
{
temp = Pa->pnext;
delete Pa;
Pa = temp;
}
}
if (Pbhead != NULL)
{
//cout << "删除Pbhead。" << endl;
Pb = Pbhead;
while (Pb)
{
temp = Pb->pnext;
delete Pb;
Pb = temp;
}
}
return 0;
}
if (tmp == 0)
{
ctmp = input;
++tmp;
continue;
}
else
{
etmp = input;
Pa->pnext = new Poly;
Pa->pnext->c = ctmp;
Pa->pnext->e = etmp;
Pa = Pa->pnext;
Pa->pnext = NULL;
--tmp;
}
}
int availableChars = (int)cin.rdbuf()->in_avail();
if (availableChars)
{
cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n');
}
cout << "第一个一元多项式:" << endl;
cout << "y(x)=";
Pa = Pahead;
cout << Pa->pnext->c << "x^" << Pa->pnext->e;
Pa = Pa->pnext;
while (Pa->pnext)
{
cout << "+";
cout << Pa->pnext->c << "x^" << Pa->pnext->e;
Pa = Pa->pnext;
}
cout << endl;
//第二个
Pb = Pbhead;
cout << "下面请输入第二个一元多项式一共有几项" << endl;
cout << "=>";
while (true)
{
cin >> input;
if (cin.fail())
{
cin.clear();
cout << "已退出,欢迎再次使用。" << endl;
Pa = Pahead;
Pb = Pbhead;
if (Pahead != NULL)
{
//cout << "删除Pahead。" << endl;
Pa = Pahead;
while (Pa)
{
temp = Pa->pnext;
delete Pa;
Pa = temp;
}
}
if (Pbhead != NULL)
{
//cout << "删除Pbhead。" << endl;
Pb = Pbhead;
while (Pb)
{
temp = Pb->pnext;
delete Pb;
Pb = temp;
}
}
return 0;
}
if (input <= 0)
{
cout << "请至少输入一项" << endl;
continue;
}
if (input > 100)
{
cout << "最大不要超出100项……这么多的多项式爱因斯坦见了都得捂脸……" << endl;
continue;
}
ptb = input * 2;
break;
}
cout << "下面请输入第二个一元多项式" << endl;
cout << "=>";
while (ptb--)
{
cin >> input;
if (cin.fail())
{
cin.clear();
cout << "已退出,欢迎再次使用。" << endl;
Pa = Pahead;
Pb = Pbhead;
if (Pahead != NULL)
{
//cout << "删除Pahead。" << endl;
Pa = Pahead;
while (Pa)
{
temp = Pa->pnext;
delete Pa;
Pa = temp;
}
}
if (Pbhead != NULL)
{
//cout << "删除Pbhead。" << endl;
Pb = Pbhead;
while (Pb)
{
temp = Pb->pnext;
delete Pb;
Pb = temp;
}
}
return 0;
}
if (tmp == 0)
{
ctmp = input;
++tmp;
continue;
}
else
{
etmp = input;
Pb->pnext = new Poly;
Pb->pnext->c = ctmp;
Pb->pnext->e = etmp;
Pb = Pb->pnext;
Pb->pnext = NULL;
--tmp;
}
}
availableChars = (int)cin.rdbuf()->in_avail();
if (availableChars)
{
cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n');
}
cout << "第二个一元多项式:" << endl;
cout << "z(x)=";
Pb = Pbhead;
cout << Pb->pnext->c << "x^" << Pb->pnext->e;
Pb = Pb->pnext;
while (Pb->pnext)
{
cout << "+";
cout << Pb->pnext->c << "x^" << Pb->pnext->e;
Pb = Pb->pnext;
}
cout << endl;
//求和
Pa = Pahead->pnext;
Pc = Pahead;
Pb = Pbhead->pnext;
while (Pa&&Pb)
{
if (Pa->e < Pb->e)
{
Pc->pnext = Pa; Pc = Pa; Pa = Pa->pnext;
}
else if (Pa->e > Pb->e)
{
Pc->pnext = Pb; Pc = Pb; Pb = Pb->pnext;
}
else
{
if ((Pa->c + Pb->c) == 0)
{
temp = Pb;
Pb = Pb->pnext;
delete temp;
temp = Pa;
Pa = Pa->pnext;
delete temp;
}
else
{
Pc->pnext = Pa; Pc = Pa; Pa = Pa->pnext;
Pc->c += Pb->c;
temp = Pb;
Pb = Pb->pnext;
delete temp;
}
}
}
Pc->pnext = Pa ? Pa : Pb;
Pbhead->pnext = NULL;//必须设置为NULL,要不然下次对Pbhead进行释放时会造成野指针
cout << "二个一元多项式之和为:" << endl;
Pc = Pahead;
cout << "y(x)+z(x)=";
if (!Pc->pnext)//存在两个多项式相加为零的情况!
{
cout << 0 << endl;
Pc = Pahead;
continue;
}
cout << Pc->pnext->c << "x^" << Pc->pnext->e;
Pc = Pc->pnext;
while (Pc->pnext)
{
cout << "+";
cout << Pc->pnext->c << "x^" << Pc->pnext->e;
Pc = Pc->pnext;
}
cout << endl;
Pc = Pahead;
}
return 0;
}
Output result:
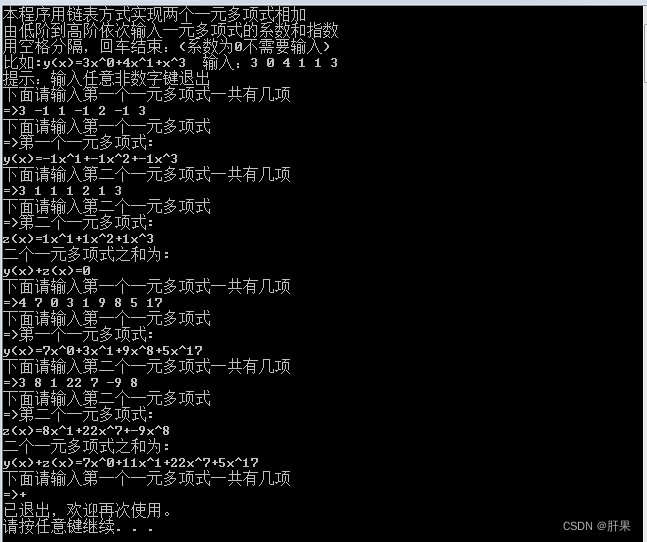
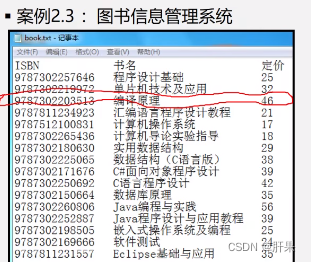
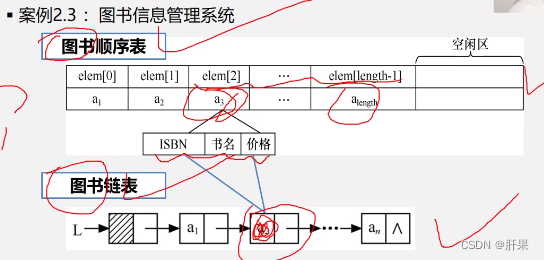
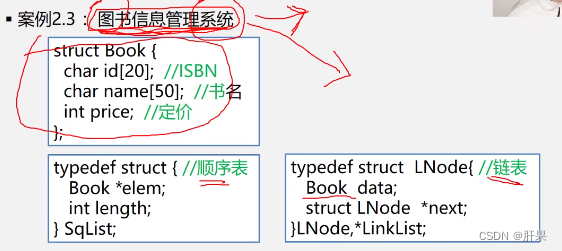
The implementation of the case is similar to the resource management system written on the 106th day, so I won't repeat it here.