
At present, thousands of industries are in a critical period of digital transformation, and data has become an important factor of production for enterprises, and is even called enterprise assets by industry insiders.
As the cornerstone of data processing, databases are playing an important role in digital transformation.
With the acceleration of technological innovation and the wide application of industries, the domestic database industry is also undergoing earth-shaking changes.
worth a look
▼▼▼
Driven by technological innovation and user needs,
Cloud-native databases are becoming a trend
So far, database technology has been developed for more than 60 years. The first company in the world to develop a database management system (DBMS) came from the United States, known as General Electric (GE), in 1961. The first company in the world to develop a commercial relational database system (Multics Relational Data Store) also came from the United States. It was the well-known Honeywell in 1976. In the following decades of development, the "Romance of the Three Kingdoms" has been staged in the database field. The three giants of Oracle, IBM and Microsoft American database dominate the global database industry, presenting a pattern of extreme concentration in the traditional database market.
Not only is the traditional database market centralized, but its core technology also adopts a centralized architecture, which has become the backbone for supporting key business application loads of enterprises in industries such as finance, energy, and telecommunications in the mainframe era.
Since 2000, with the rise of the Internet, cloud computing has gradually moved towards in-depth application in the industry. As a result, a large number of innovators in the database industry have emerged, thanks to the cost-effective performance of x86 hardware clusters, and the wave of "going to IOE" in China is getting higher and higher. Since then, distributed databases have entered the stage of history. Especially after 2010, the development of open source databases has been surging, showing a new trend of replacing traditional databases in more and more application scenarios, and its technology adopts a distributed architecture, and at the same time continuously improves the functions of the cloud management platform to further help The flexibility of data analysis and the high efficiency of delivery demonstrate the value of cloud-based distributed databases. Of course, we should thank open source databases such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, as well as the contributions of public clouds.
But this is not enough. With the vigorous development of emerging technologies such as mobile Internet, cloud computing, big data, Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence, user data has changed. Not only has the amount of data increased greatly, but the types of data have also become diversified. At the same time, enterprises' migration to the cloud has accelerated the surge in the amount of data on the cloud. In terms of database applications, they have to face three new challenges.

First, computing and storage hardware resources are not fully utilized, and it is difficult to achieve high concurrent load capacity of database applications. In order to achieve high availability of data, previous distributed databases generally adopt the "one master and many slaves" mode. In the case of failure to achieve full read-write separation, the slave node cannot undertake the write task, but can only undertake the read task of the read-write separation. That is to say, modifying data on the master node will be synchronized to the slave node, and the slave node can read data, but cannot write modified data. Because the CPU load of the slave node is not high, it cannot share the writing pressure of the master node, and the computing resources are idle and wasteful, which naturally reduces the availability of the entire cluster. Adopting the "one master and multiple slaves" mode not only has low computing resource utilization, but also low storage utilization. In the "one master and multiple slaves" mode, one piece of data is stored in multiple redundant copies, which will inevitably lead to low utilization of the cluster's storage space, and pre-stored redundancy. This also makes it difficult to realize on-demand allocation of storage, and it is difficult for data to flow efficiently between nodes. Not only is the storage utilization rate low, but there is also the hidden danger of single-point performance bottlenecks.
Second, the flexibility is insufficient, and the elastic expansion and contraction capacity is stretched. The traditional distributed database adopts the "storage-computing integration" architecture. Although the fusion and bundling of computing and storage can eliminate unnecessary data flow, it is very effective for the early application of data-intensive enterprises. However, after the large increase in the amount of enterprise data, the traditional The performance of a single database in a distributed database is insufficient. Sharding of about 500G cannot solve the fundamental problem, and the gap between computing and storage will become wider and wider. Severe challenges have arisen in database elastic scalability, and relying on the number of stack nodes to improve performance and reliability will inevitably increase enterprise costs. From the perspective of the design concept, the server local disk deployment method is adopted, and the database and the local disk belong to the same failure domain, which severely limits hardware upgrades and capacity expansion.
Third, the operation and maintenance management is too complicated to realize a one-stop database service. The system deployment of a distributed database with a "storage-computing integration" architecture requires professional DBA support in order to achieve landing deployment. Computing and storage are bound, and automatic switching cannot be realized. Once a server failure occurs, data needs to be manually restored, which not only reduces availability but also takes time and effort, let alone the realization of a one-stop database service.
Since the distributed database with the "integrated storage and computing" architecture can no longer fully meet the needs of enterprise development and business applications, these challenges will inevitably lead to new advancements in database technology, and distributed transformation has become the first choice.
In this regard, the cloud-native database that separates storage and computing has attracted the attention of the industry. It combines the flexibility of cloud computing, the ease of use of open source databases, and the simplicity of intelligent and efficient operation and maintenance. Development is highly adaptable.
Going deep into the reasons, Global Cloud Watch further analyzed that, on the one hand, it is due to the trend of technological development. After years of development, the database has shown a development trend from traditional databases to distributed databases on the cloud and then to cloud-native databases. On the other hand, it is also driven by the acceleration of user business innovation and application requirements, making cloud-native databases present unprecedented development magic.
As Gartner predicts, by 2023, 75% of the world's databases will run on the cloud. Driven by the two-way drive of technological innovation and user needs, cloud-native databases are gradually becoming a trend.
meet the challenge,
Why are cloud vendors more powerful in developing cloud-native databases?
It is very interesting that to deal with the three new challenges of the database, different database manufacturers have their own development paths.
Traditional database vendors rely on the advancement of cloud strategies to realize database migration to the cloud, and also introduce innovative technologies such as support for containerization, but it always makes people feel that cloud native is not thorough enough; emerging open source database vendors cooperate with public clouds and launch based on their own business development needs. Cloud-native databases; public cloud vendors have natural Cloud Native cloud-native advantages, have a fundamental strategy for upgrading cloud-native databases, and have the thoroughness of distributed transformation.
From a global perspective, very representative cloud-native databases such as Amazon Cloud Technology’s Aurora, Google’s Spanner, Microsoft’s Socrates, etc.; from a domestic perspective, very representative cloud-native databases such as Alibaba Cloud’s PolarDB, Tencent Cloud’s CynosDB of Huawei Cloud, TaurusDB of Huawei Cloud, TeleDB of Tianyi Cloud, etc. In addition, judging from the performance of these domestic and foreign public cloud vendors in recent years, the database has become another important cloud business contributor after virtual machines, CDN, and storage, and the differentiation of database competition not only has a direct impact on the public cloud IaaS business. At the same time, it also allows public cloud vendors to see more sources of profit. It can be seen that public cloud vendors are more powerful in developing cloud-native databases and have become their main promoters. Among them, the operator cloud represented by Tianyi Cloud has also become an important force that cannot be ignored to promote the database into the cloud-native era.
In August 2022, TeleDB will once again realize the upgrade of cloud-native database capabilities, further consolidating the core competitiveness of Tianyi Cloud as the "leading cloud" in China's cloud computing industry. Therefore, we also clearly see that Tianyi Cloud is "particularly heavy-handed" in promoting the development of cloud-native databases, and the two major technological killers are at the same time.
The killer feature is to break the industry's perception and realize the containerization of the database.
Previously, some people in the industry believed that database containerization was difficult to ensure strong data consistency. At the same time, there were many technical challenges in failover, elastic expansion, and data security. The view that databases were not suitable for containerization was also prevailing. Although it is well known that the containerization trend of applications has risen very early, the containerization of databases has been "seeing each other late".
In recent years, Kubernetes has gradually become the de facto standard for container technology, which has objectively accelerated the wide application and popularization of cloud-native technology, thereby driving the continuous growth of cloud-native data volume. Transformation and upgrading are particularly prominent. Naturally, this also drives these industries to have an urgent demand for cloud-native database services.

To break the industry's perception, to realize the migration and deployment of distributed databases from physical machines to cloud to container platforms, it is necessary to deal with the challenges of strong consistency, as well as the challenges of stability and availability. Tianyi Cloud is not only keenly aware of these technical challenges, but also implements containerized TeleDB high-availability cluster management based on the self-developed TeleDB Operator's custom controller and custom resource CRD. Based on the Kubernetes API, it provides unified support for PaaS and CI (continuous integration), and provides services for the database cluster management platform through Stateful Set, Service, Pod, PVC, etc.
Tianyi cloud TeleDB cloud-native database adopts a layered architecture design as a whole, which simplifies the complexity of database containerization. At the same time, the mutual interference between multiple cluster instances is reduced as much as possible, and the autonomy of each Cluster Instance cluster instance is realized. After the database is containerized, the deployment and installation become very simple. Based on the e-surfing cloud self-developed technology to realize the efficient creation of database clusters, the agile delivery capability and ease of use are greatly improved, the deployment density is also improved, and hardware resources can be effectively used. At the same time, it also has the ability of elastic expansion, which strengthens the automatic scheduling. What concerns users' data engineers the most is that not only cluster instance nodes realize fault autonomy, but also precipitate operation and maintenance knowledge into codes, which further liberates operation and maintenance and realizes unified database management and operation and maintenance services. After a series of "ruthless" containerization upgrades, TeleDB will definitely bring cost reduction and efficiency enhancement to enterprise digitalization, and bring out the innovative value of cloud-native databases.
The second killer feature is innovation and transformation to realize the separation of storage and calculation of distributed databases.
E-surfing Cloud breaks the previous conventional distributed database storage and computing integrated architecture, fundamentally solves the problems of waste of computing and storage resources and poor availability, and fully exerts the high-performance value of distributed databases.
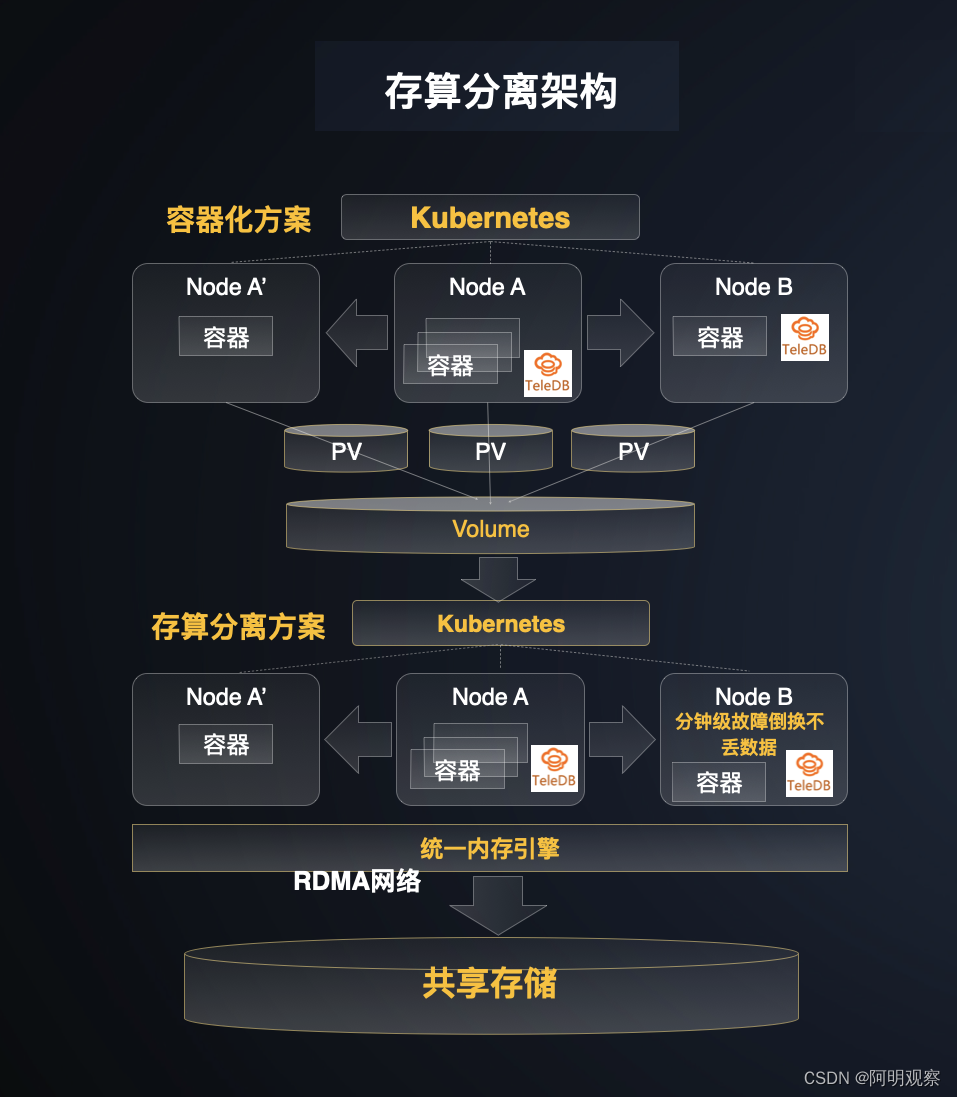
Global Cloud Observation analysis found that the industry adopts a storage-computing separation model for distributed databases, and generally builds resource pools for two dimensions of computing and storage to achieve two-tier decoupling of computing and storage. However, E-surfing Cloud has fully utilized the advantages of the storage-computing separation architecture, further deepened the statelessness of computing nodes, separated the memory engine layer, realized memory pooling, and formed a three-layer decoupling of computing, memory, and storage.
Through RDMA technology, memory resources are further unified to form a shared memory pool, which not only improves the flexibility of the memory engine, but also improves memory utilization. In this way, multi-node multi-read and multi-write capabilities are realized, and the problem that slave nodes cannot perform data editing and writing operations in the previous "one master and multi-slave" mode has been completely solved, and the concurrency performance of database applications has been significantly improved.
Computing nodes realize shared memory and shared data storage, and multiple copies are normalized, which better realizes the consistency of multiple copies of distributed database data, and greatly improves the availability.
After the database is containerized, the memory and stored data are shared globally, and the computing nodes are completely stateless, which not only improves the deployment density, but also solves the problems of data loss and long failover time that were very troublesome for users before.
It can be seen that the value brought by the realization of distributed database containerization is very obvious, and it is also imperative. It not only greatly improves the reliability of cloud-native database applications for users, but also brings visible practical value to the cost reduction and efficiency increase that many users are currently concerned about.
Focus on future opportunities,
Forging the Innovation Cornerstone of Enterprise Digital Transformation
Opportunities are born out of competition, and the future of the database industry remains the same. Focusing on future development opportunities, compared with foreign database giants, cloud-native-driven domestic databases are on the same starting line as global database giants.
Tianyi Cloud not only solves the technical pain points of distributed database containerization through self-developed technological innovation, but also realizes the three-layer decoupling of computing, memory and storage in terms of separation of storage and computing.
At the same time, Tianyi Cloud has a natural large-scale application scenario of big data, which is of great significance to the deepening of database technology innovation. After all, the database not only needs technical iteration, but also needs practical application to drive its innovation and improvement.
According to reports, the TeleDB cloud-native database version of Tianyi Cloud has been practiced in the relatively difficult telecommunications field. After Fujian Telecom adopted the TeleDB cloud-native database solution, it demonstrated its innovative advantages over the original solution. In the previous solution, there were hidden dangers of data loss due to disk failure and downtime, low database deployment density, low resource utilization, complex delivery and low efficiency, and lack of elastic scalability.
Practice has proved that the TeleDB cloud-native database of e-surfing cloud helps Fujian Telecom's digital development, bringing application values such as efficient resource utilization, rapid deployment and delivery, and flexible expansion with high flexibility, especially in terms of high reliability, cost reduction and efficiency increase outstanding performance.
To achieve high reliability, the RTO can be reduced from minutes to 30 seconds. Using multi-read multi-write clusters, through EDP technology, optimize the failover process, effectively reduce the amount of log playback, and cooperate with high-frequency CKPT to achieve fast failover, which greatly optimizes the target recovery time (RTO) of the database. In terms of data protection mechanism, a mature solution of enterprise-level storage is adopted to ensure that data will not be lost under extreme conditions, and the availability has been improved from 4 9s to 6 9s.
Aiming at reducing costs and increasing efficiency, and re-innovating the separation of storage and computing, the three major resource pools of computing, memory, and storage are decoupled to better utilize the computing power of the CPU and improve the utilization of hardware resources. At the same time, it realizes the ability to write multiple times and read multiple times, completes the normalization of multiple copies of the original one-master-multiple-slave architecture, and globally shares one data, which greatly reduces the cost of shared storage.
It can be seen that through the successful implementation of the TeleDB cloud native database case of Fujian Telecom, we can see the advantages and value of TeleDB upgrade. Next, Tianyi Cloud will also expand the application breadth and depth of TeleDB cloud native database in finance, Internet, operators and other industries , and join hands with partners and industry customers to accelerate into the cloud-native era and reshape the new pattern of the domestic database industry.
Facing the future, in the process of seizing the historical development opportunities of domestic databases, Tianyi Cloud is constantly strengthening its innovative resilience in the database field, further increasing investment in independent research and development on the road to cloud-native future innovation, focusing on in-depth independent innovation, HTAP Cloud-native databases and databases with multiple engines share the same architecture. With stronger cloud-native capabilities, it is believed that e-surfing cloud will be able to win the leading position in the competition of many database manufacturers, forging the innovative cornerstone of enterprise digital transformation, and empowering the sustainable development of digital economy.
(by Aming)
- END-
you
How
What?
look
?
Comments at the end of the article are welcome!
[Global Cloud Observation|Technology Explanation] Focus on the analysis of technology companies, use data to speak, and show you how to understand technology. This article and the author's reply only represent personal opinions and do not constitute any investment advice.