1. Introduction to Cloud Computing
1. First understanding of cloud computing and its advantages
1.1 Common Cloud Computing Services
Cloud file storage, cloud music, cloud backup, and more.
1.2 Advantages of Cloud Computing
①On-demand self-service
IT industry needs and customer service consultation, understand the cloud computing services that suit you.
② Extensive network access
As long as you are connected to the Internet, you can use cloud computing services.
③Resource pooling
Mask underlying hardware differences.
④Fast elastic expansion and contraction
Cloud computing IT service specifications can be configured according to demand; capacity can be quickly expanded.
⑤ Measurable services
Use technical means to realize the unification of units and accurate measurement of value; it can accurately control and allocate resources for customers' businesses; for customers, they can clearly see the usage of their purchased services.
2. Definition, development history and classification of cloud computing
2.1 Definition of Cloud Computing
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines:
Cloud computing is a model that can obtain required resources (such as networks, servers, storage, applications, services) from a shared pool of configurable computing resources anytime, anywhere, conveniently, and on demand. Rapid provisioning and release with minimal effort to manage resources and interaction with service providers .
In layman's terms, "cloud" is a metaphor for the network and the Internet, that is, the abstraction of the Internet and the underlying infrastructure required to build the Internet. "Computing" refers to computing services (including various functions, resources, storage) provided by a sufficiently powerful computer. "Cloud Computing" can be understood as: a sufficiently powerful computer can be used to provide services to users through the Internet, and the usage of such services can be described using a unified unit.
2.2 Origin and Development of Cloud Computing
① History of Internet development
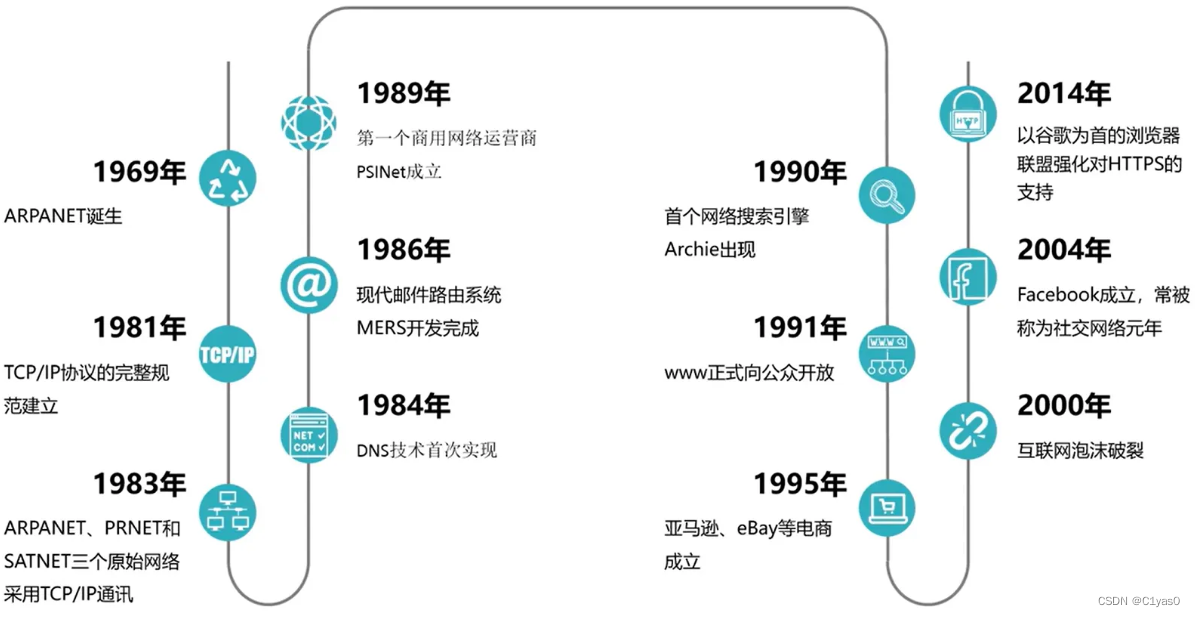
② History of Computing Development
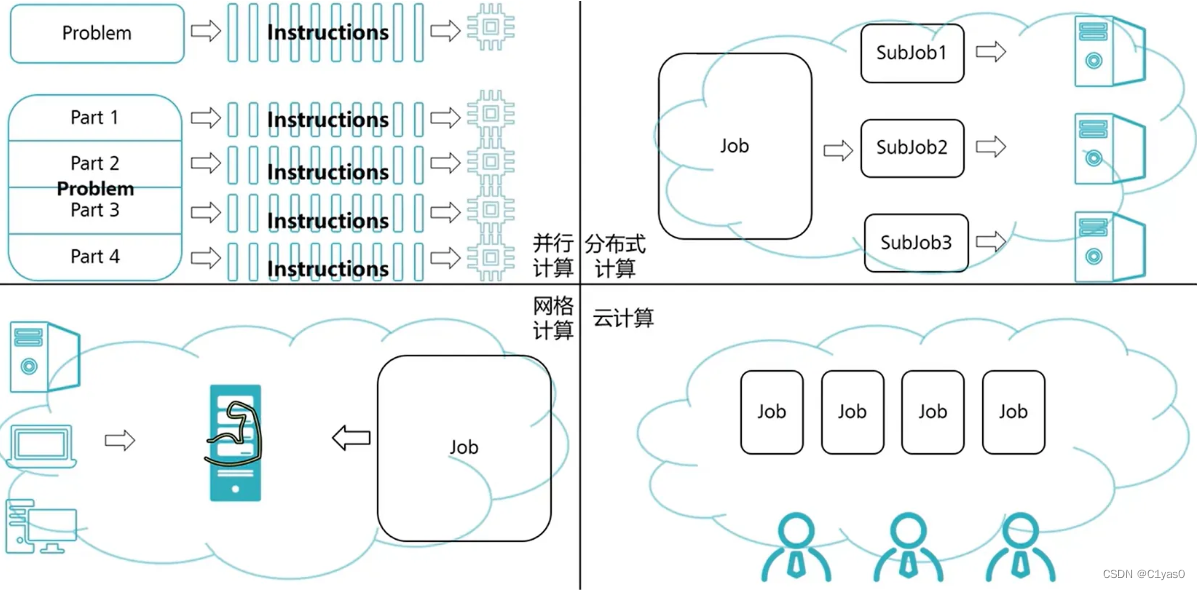
Serial Computing—>Parallel Computing—>Distributed Computing—>Grid Computing—>Cloud Computing
Parallel computing: Divide a large problem into multiple parts that can be solved simultaneously, convert each part into scattered instructions, and then hand over each instruction to its own CPU for processing.
Features: save computing cost; solve problems that cannot be solved by serial computing
Distributed computing: CPUs for parallel computing can come from the same computer or from different computers under the same network. Distributed computing belongs to the scientific field of computers that study distributed systems. Distributed systems disperse all components on computers belonging to different networks. These computers communicate and cooperate with each other through a unified message mechanism. Computer components distributed in different networks Collaborate with each other to achieve common goals.
Features: Rare resources can be shared; load balancing can be achieved on multiple computers through distributed computing; programs can be placed on the most suitable computer
Grid Computing: Use a wide range of scattered computing resources to complete common tasks. Create a virtual and dynamic collection of resources, enabling users to use resources in a safe and coordinated manner.
Cloud Computing: An emerging method of sharing technical architecture, connecting huge resource pools together to provide various IT services.
③Development of cloud computing

Cloud computing 1.0: The focus is on computing virtualization. Through virtualized cluster scheduling software, more IT applications can be attached to fewer IT nodes, thereby improving resource utilization. Users need to apply and administrators to configure.
Cloud Computing 2.0: The stage of resource service and management automation for infrastructure cloud tenants and cloud users. Users can select configurations on the web, and administrators can approve them.
Cloud Computing 3.0: The application architecture supported by enterprise IT has changed from a vertically expanded application layered architecture system to a distributed stateless architecture, enabling IT to take a new step in supporting enterprise business agility, intelligence, and resource utilization. steps.
2.3 Classification of Cloud Computing
① Classification of operating modes: public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, industry cloud
Public cloud: Users pay to obtain public cloud resources, which are maintained by the service provider.
Private cloud: A cloud service platform built within the enterprise, managed internally by the enterprise, with limited access.
Hybrid cloud: Enterprises place some services in public clouds, where public clouds and private clouds are usually separated by firewalls.
Industry cloud: a paid or free cloud that provides services to users for special industries.
②Classification of service models: Iaas, Paas, SaaS
