
Install the Python program
Official website Python download address: Python Releases for Windows | Python.org
You can install version 3.7, and there may be minor changes in version upgrades. The following will be learned with python3.7 as an example
After downloading the installation package, double-click the brainless installation
Frequently asked questions for novices:
1. The symbols use Chinese characters
2. Code indentation
3. The built-in function in python is wrong
After the installation is complete, use the tools that come with python to learn programming

basic grammar learning
dir(__builtins__) #View built-in functions in python
>>> dir(__builtins__)
['ArithmeticError', 'AssertionError', 'AttributeError', 'BaseException', 'BlockingIOError', 'BrokenPipeError', 'BufferError', 'BytesWarning', 'ChildProcessError', 'ConnectionAbortedError', 'ConnectionError', 'ConnectionRefusedError', 'ConnectionResetError', 'DeprecationWarning', 'EOFError', 'Ellipsis', 'EnvironmentError', 'Exception', 'False', 'FileExistsError', 'FileNotFoundError', 'FloatingPointError', 'FutureWarning', 'GeneratorExit', 'IOError', 'ImportError', 'ImportWarning', 'IndentationError', 'IndexError', 'InterruptedError', 'IsADirectoryError', 'KeyError', 'KeyboardInterrupt', 'LookupError', 'MemoryError', 'ModuleNotFoundError', 'NameError', 'None', 'NotADirectoryError', 'NotImplemented', 'NotImplementedError', 'OSError', 'OverflowError', 'PendingDeprecationWarning', 'PermissionError', 'ProcessLookupError', 'RecursionError', 'ReferenceError', 'ResourceWarning', 'RuntimeError', 'RuntimeWarning', 'StopAsyncIteration', 'StopIteration', 'SyntaxError', 'SyntaxWarning', 'SystemError', 'SystemExit', 'TabError', 'TimeoutError', 'True', 'TypeError', 'UnboundLocalError', 'UnicodeDecodeError', 'UnicodeEncodeError', 'UnicodeError', 'UnicodeTranslateError', 'UnicodeWarning', 'UserWarning', 'ValueError', 'Warning', 'WindowsError', 'ZeroDivisionError', '__build_class__', '__debug__', '__doc__', '__import__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'abs', 'all', 'any', 'ascii', 'bin', 'bool', 'breakpoint', 'bytearray', 'bytes', 'callable', 'chr', 'classmethod', 'compile', 'complex', 'copyright', 'credits', 'delattr', 'dict', 'dir', 'divmod', 'enumerate', 'eval', 'exec', 'exit', 'filter', 'float', 'format', 'frozenset', 'getattr', 'globals', 'hasattr', 'hash', 'help', 'hex', 'id', 'input', 'int', 'isinstance', 'issubclass', 'iter', 'len', 'license', 'list', 'locals', 'map', 'max', 'memoryview', 'min', 'next', 'object', 'oct', 'open', 'ord', 'pow', 'print', 'property', 'quit', 'range', 'repr', 'reversed', 'round', 'set', 'setattr', 'slice', 'sorted', 'staticmethod', 'str', 'sum', 'super', 'tuple', 'type', 'vars', 'zip']1. Variables
name = '张三'create variable procedure
Variable declaration first, variable assignment second
Variable name rules:
1. Variables are case-sensitive. If you use variables with different case, python will consider them as multiple variables.
2. It is not allowed to start with a number, not only python, but most languages are not allowed
3. Do not start with a special symbol, you can start with an underscore _
define different statements
>>> name = '张三'
>>> print (name)
张三
>>> age = 17
>>> print (age)
17
>>> description="hello world!"
>>> print (description)
hello world!
>>> description_two="'hello world!'"
>>> print (description_two)
'hello world!'2. escape
| symbol | illustrate |
|---|---|
| \\ | backslash (\) |
| \' | apostrophe(') |
| \" | Double quotes(") |
| \a | ring the bell |
| \b | backspace |
| \n | line break |
| \r | carriage return |
| \t | horizontal tab |
| \v | vertical tab |
| \f | Form feed |
| \ooo | ooo is octal |
| \xhh | hh is hexadecimal |
3. Variables and strings
>>> print(520+1314)
1834
>>> print('520'+'1314')
5201314
>>> print(520+1314)
1834
>>> print('520'+'1314')
5201314From this few lines of code, it can be seen that the sum of numbers is added when numbers are added, but the addition of strings is also called concatenation. Multiplication is used in strings to print multiple times, and strings can only be concatenated using the + symbol. Used with *, the string is the difference in type
4. Variable type escape
1.int()
You can convert numeric strings to int integers, but some letters or text will report an error
>>> age = '18'
>>> type (age)
<class 'str'>
>>> age_1 = int(age)
>>> type (age_1)
<class 'int'>2.abs()
Convert numeric type to absolute value
>>> abs(-100)
1003.float()
convert integer to float
>>> float(1)
1.04.bool()
>>> bool(100)
True
>>> bool(-1)
True
>>> bool(0)
False
>>> bool('false')
True
>>> bool(False)
False5. Operators
arithmetic operator
| operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| < | Determine whether the left side is smaller than the right side |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| > | more than the |
| >= | greater or equal to |
| == | Judging whether it is equal |
| != | Is it not equal |
| is | Check if the ids of two objects are equal |
| is not | Determine if the ids of two objects are not equal |
>>> 1 > 2
False
>>> 3 <= 5
True
>>> 3 == 3
True
>>> 3 != 3
FalseLogical Operators
| operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| and | Both left and right are true, the result is true |
| or | One of the left or right is true, the result is true |
| not | If true, the result is false, if false, the result is true |
6. Loop structure
for loop
结构:
for 变量 in 可迭代对象:
statement()Loop value:
>>> for i in "Curry":
print (i)
C
u
r
r
yrange() iteration function
语法:
range(stop)
range(start,stop)
range(start,start,step)range usage:
>>> for i in range(5):
print (i)
0
1
2
3
4
>>> for i in range(2,5):
print(i)
2
3
4
>>> for i in range(1,5,2):
print(i)
1
3
>>> for i in range(5,0,-1):
print(i)
5
4
3
2
1while loop
格式:
while 条件:
条件为true的执行语句
第二种方式:
while 条件:
代码块
else:
当条件为假执行此代码块Other loop items:
brack; //结束当前循环
continue; //跳出当前一层循环7. Basic common modules
1.random random number module
>>> import random
>>> print (random.randint(1,10))
42.decimal precision floating point number module
>>> import decimal
>>> 0.1 + 0.2
0.30000000000000004
>>> a = decimal.Decimal('0.1')
>>> b = decimal.Decimal('0.2')
>>> print (a+b)
0.33.len() to get the length
>>> len('Curry')
5
>>> test=[1,2,3,4,5,'Curry']
>>> len(test)
68. Types in python
-
floating point
-
integer
-
string
-
plural
-
Boolean
9. Business logic
flow chart
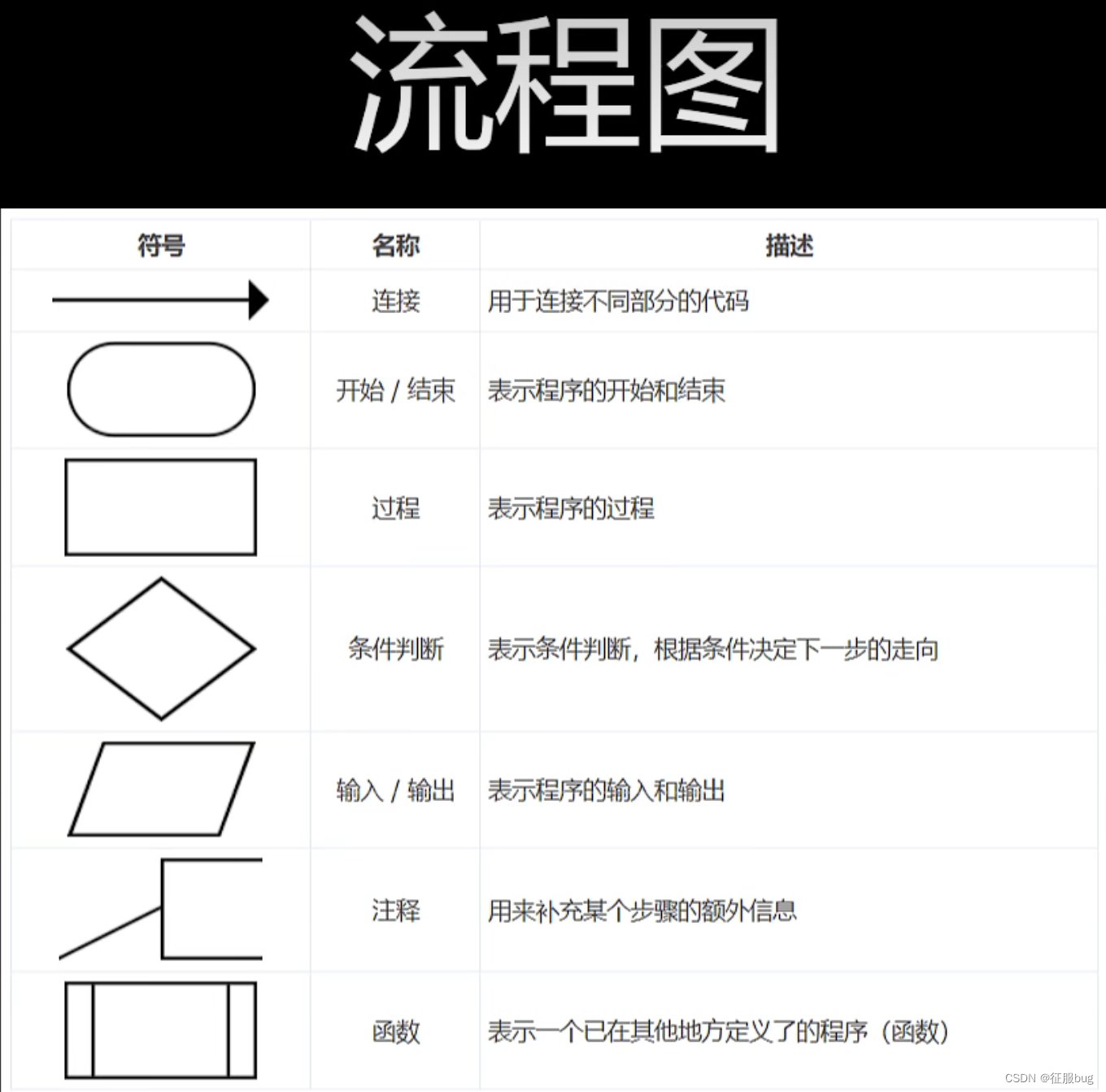
mind Mapping
10. The Great Judgment Branch
1. Single judgment
if 条件:
代码块2. Double branch judgment
if 条件:
代码块
else:
代码块3. Multi-branch judgment
if 条件:
代码块
else if:
代码块
else if:
代码块
else:
代码块4. Special way of writing judgment
格式:为true代码块 if 条件 else 为false结果
>>> if 0 < 1:
print ("True")
else:
print ("False")
True
>>> print ("True") if 0 < 1 else print ("False")
True