Reference article:
Top 60 Linux Interview Questions and Answers - howtouselinux
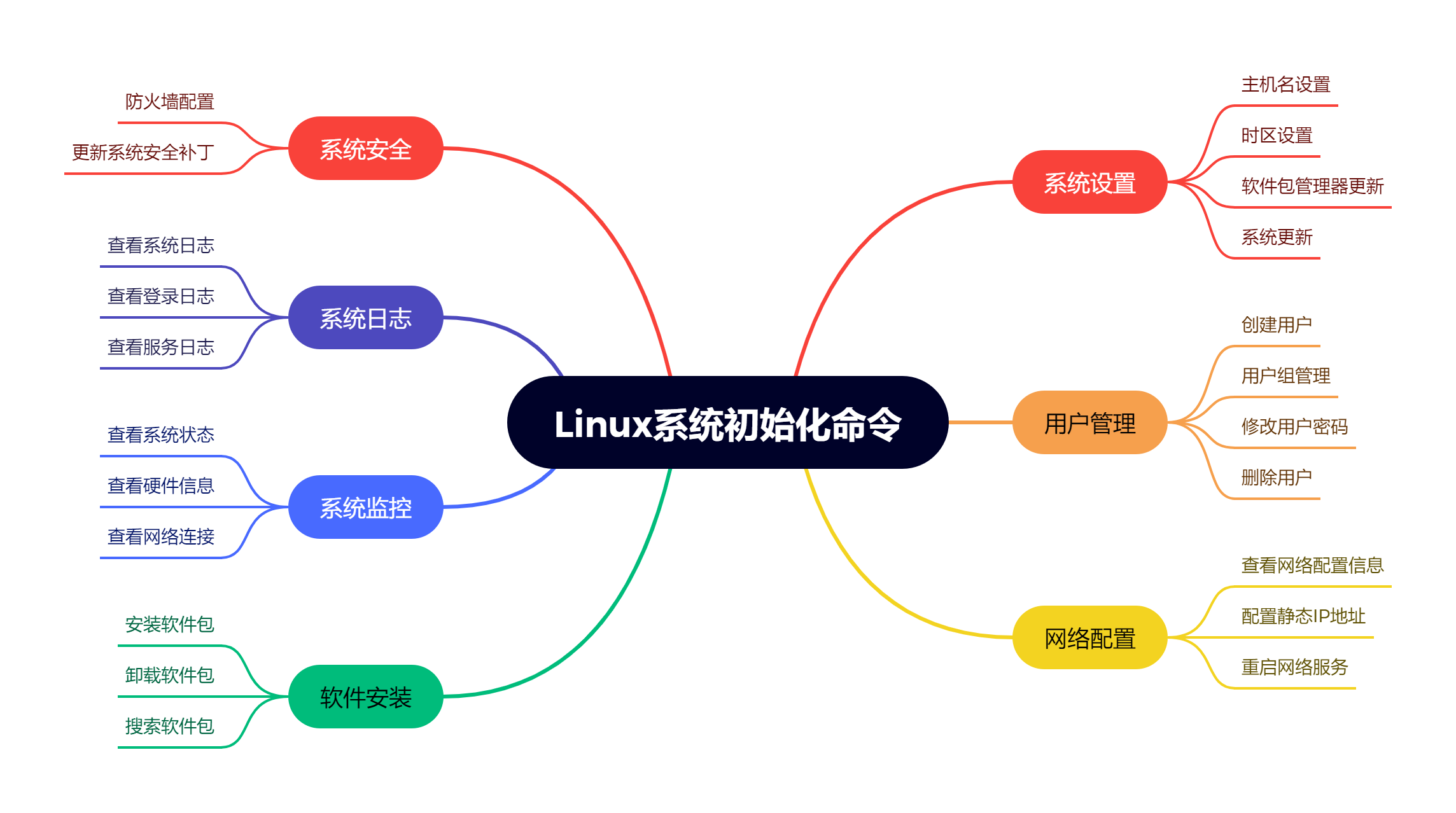
When managing and maintaining a Linux system, there are some commonly used commands that can help you with system initialization and configuration. These commands cover a variety of tasks, including system setup, user management, software installation, and network configuration, among others.
This article will provide you with a cheat sheet of Linux system initialization commands for easy reference and use when needed.
system settings
hostname setting
hostname: Display the current host name.hostnamectl set-hostname <new_hostname>: Set a new hostname.
time zone setting
timedatectl set-timezone <timezone>: Set the time zone of the system.
Package Manager Updates
apt update: Update APT package list (for Debian/Ubuntu).yum update: Update YUM package list (for CentOS/RHEL).dnf update: Update DNF package list (for Fedora).
system update
apt upgrade: Upgrade all packages in the system (for Debian/Ubuntu).yum upgrade: Upgrade all packages in the system (for CentOS/RHEL).dnf upgrade: Upgrade all packages in the system (for Fedora).
User Management
create user
adduser <username>: Create a new user.useradd <username>: Create a new user (advanced option).
User Group Management
groupadd <groupname>: Create a new user group.usermod -aG <groupname> <username>: Add the user to the specified user group.
Modify user password
passwd <username>: Change user password.
delete users
userdel <username>: Delete the specified user (the user's home directory will not be deleted).userdel -r <username>: Delete the specified user and its home directory.
Network Configuration
View network configuration information
ifconfig: Displays configuration information for a network interface (obsolete).ip addr show: Display the configuration information of the network interface.ip route show: Display the information of the network routing table.
Configure a static IP address
nano /etc/network/interfaces: Edit network interface configuration files (for Debian/Ubuntu).vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<interface>: Edit network interface configuration file (for CentOS/RHEL).
restart network service
systemctl restart networking: Restart network services (for Debian/Ubuntu).systemctl restart network: Restart the network service (for CentOS/RHEL).
Software Installation
install package
apt install <package>: Install the specified package (for Debian/Ubuntu).yum install <package>: Install the specified package (for CentOS/RHEL).dnf install <package>: Install the specified package (for Fedora).
uninstall package
apt remove <package>: Uninstall the specified package (for Debian/Ubuntu).yum remove <package>: Uninstall the specified software package (for CentOS/RHEL).dnf remove <package>: Uninstall the specified package (for Fedora).
search package
apt search <keyword>: Search for the specified keyword in the APT package list (for Debian/Ubuntu).yum search <keyword>: Search for the specified keyword in the YUM package list (applicable to CentOS/RHEL).dnf search <keyword>: Search for the specified keyword in the DNF package list (for Fedora).
System monitoring
Check system status
top: View system resource usage and process information in real time.
View hardware information
lscpu: Display CPU information.lsblk: Display block device information.free: Display system memory usage.df -h: Displays the disk space usage of the file system.
check network connection
netstat -tuln: Display all network connections and listening ports.
system log
view system log
tail -f /var/log/syslog: View system log files in real time.
View login log
last: Display the information of the most recently logged in user.
View service log
journalctl -u <service>: View the logs of the specified service (applicable to systemd systems).
system security
firewall configuration
ufw enable: Enable Uncomplicated Firewall (for Debian/Ubuntu).firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=<port>/tcp --permanent: Allow specific ports through FirewallD (for CentOS/RHEL).
Update system security patches
apt upgrade: Upgrade all packages in the system, including security patches (for Debian/Ubuntu).yum update --security: Update security-related packages in the system (for CentOS/RHEL).dnf updateinfo list security: List available security update information (for Fedora).