SAN(Storage Area Networks)
- SAN advantage benefits
- SAN components components
- SAN connection optionsconnective options
- FC protocol FC addressing protocol addressing\
- FC topology topologie
Advantages and disadvantages of SAN
fiber channel fiber channel
SAN components
FC three kinds of interconnection
FC port type
fabric
Business Needs and Technological Challenges - Feelings Are Not the Point
- real-time information just-in-time info
- information infrastructure, business integration integration of info infrastructure with business processes
- Flexible flexible flexible resilient
DAS is inefficient for the above processing
What is SAN
- Dedicated high speed network of servers and shared storage devices
- block level data access block level data access
- Resource integrationresorce consolidation
- centralizedd storage, management
- Scalability
- Theoretical limit 15 million devices
- secure access secure access
Understanding fibre channel
- high-speed network technology
- Optical fiber cables Front connection
- Serial copper cables Serial copper cables (back end)
The latest FC achieves 16Gb/s
The server is connected to 2 different networks
- front end
- Back-end
Users and application clients connect to Servers and applications through IP network, and then connect to storage and application data through FC SAN
FC SAN Evolution (see p8 for details)
- SAN Islands FC Arbitrated Loop
- Interconnected SANs FC Switched Fabric Interconnected SAN FC Switched Fabric
- Note that switched fabric is the original fabric of the exchange structure fabric
- Enterprise SANs FC Switched Fab Enterprise SAN FC Switched Fab
Components of SAN
Node ports
example
- hosts
- storage
- tape library
ports are available in
- Host HBAs
- front-end adapter in storage
- transmit Tx link and receive Rx link in each port
HBA automatically executes low-level interface functions low-level interface functions automatically , minimizing the impact of minimize impact on performance on host performance
Cabling
- SAN implementation use: Imolemantation use
- short distance copper cable
- long distance fiber optic cable
- Two Types of Fiber Optic Cables
- single mode
- can carry a single beam
- Distance up to 10 km
- multimodal
- Can carry multiple beams at the same time
- Distance up to 500 meters
- single mode
Components of SAN: Cabling (Connector
- SC duplex connection duplex GBIC
- LC Dual Regulatory Connection SFP
patch panel connector
- ST simplex connector 单工
Components of SAN: Interconnecting devices
- Hubs
- Switches and
- Director
Components of SAN: Storage array
- Storage consolidation, centralized consolidation, centralization
- Properties of an array
- availability redundancy
- performance
- business continuity
- multiple host connection
SAN management software
- a suite of tool to manage interface between hosts and storage arrays
- SAN Environment Integrated Management
- Web GUI and CL
SAN interconnectivity Options
p2p
- direct connection between devices
- limited connectivity limited connectivity
FC-AL
Fiber Channel Arbitrated Loop Fiber Channel Arbitrated Loop
- Arbitrate to gain control through arbitration
- hubs connection
- Up to 127 devices
See 17 for details
FC-SW
fabric connect
- dedicated broadband
- 15 million devices
- higher availability
ISL Inter-switch link inter switch link
- ISL uses electronic ports to interconnect two or more FC switches
- Route host-to-storage data and fabric management traffic from one switch to another
- ISL is also the expansion mechanism of SAN
Type port
- FLOGI fabric login
- N F
- PLOGI port login
- between N and N
- Nport establishes a session with another Nport
- PRLI
- Between NN
- Share information about the type of upper layer protocol being used
- The device is identified as a SCSI initiator or target
Lesson Summary
Key topics covered in this lesson:
FC SAN and its components
SAN Interconnectivity Options
Port types and inter switch lin
Lesson: Fibre Channel Architecture
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:
Describe layers of FC
Describe FC protocol stack
Discuss FC addressing
Define WWN addressing
Discuss structure and organization of FC Data
FC Architecture Overvie
- channel tech
- Provides high performance with low protocol overhead
- FCP - SCSI-3 over FC network
- Subtained transmission bandwidth with over long distances
- 8GB/s
- For details on the fifth floor, see 25
- FC4 SCSI HIPPI ESCON ATM IP
- FC2 Farming/Flow Control
- FC1 Encode/Decode
- FC0
- FC-3 is not yet implemented
Fibre Channel Protocol Stack
| FC layer | Function | SAN relevant features specified by FC lay |
|---|---|---|
| FC-4 | Mapping interface | Mapping high-level protocols |
| FC-3 | Common services | not realized |
| FC-2 | Routing, Flow Control | Frame structure, ports, FC address buffer credits |
| FC-1 | Encode/decode | 8b/10b encoding, bit and frame synchronization |
| FC-0 | physical layer | media cables connector |
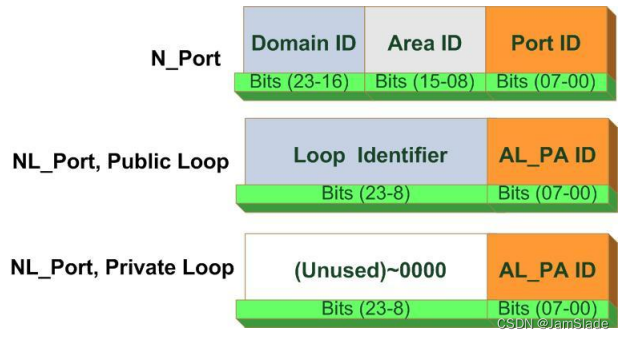
Fiber Addressable Channel
- FC address is assigned during fabric (structure) login
- SAN internal node communication
- Similar to the IP address of a NIC
- Format:
- 24 bits
- dynamic allocation
- The content of three bytes depends on the N port type
- For Nport or public Nport
- The switch maintains the mapping from WWNs to FC addresses through the Name Server
World Wide Names
- unique unique 64-bit identifier
- Static to Port—used to physically identify a port or node in a SAN
- Similar to the MAC address of a NIC
Structure and organization of FC data
FC data includes:
- Exchange operation
- Two N_ports can identify and manage a set of information units
- map to sequence
- sequence (order
- Contiguous set of frames sent from one port to another
- frame
- basic unit of data transfer
- Each frame can contain up to 2112 bytes of payload
Lesson Summary
Key topics covered in this lesson:
Fibre Channel Protocol Stack
Fibre Channel Addressing
Data Organization: Frame, Sequence and Exchang
Lesson: FC Topologies and Management
Define FC fabric topologies
Describe different types of zoning分区
Core-Edge Fabric
p32
- Can be two or three layers
- single core layer
- one or two edge layers
- In a two-tier topology, storage is usually connected to the Core
- Benefits
availability high availability
scalability medium scalability
connectivity medium to maximum connectivity
Mesh
- Global partial or global full mesh
- switch connected to each other
- Hosts, storage can be located anywhere in the structure
- host, storage localized to a single switch
Fabric Management: Zoning
Zoning Components
p 35
Types of Zoni
Key topics covered in this lesson:
FC SAN Topologies
– Core-Edge
– Mesh
Fabric management by zoning