Super Score Mission Statement
Super-resolution task: recovering high-resolution images from low-resolution images. For example, the original resolution is 128 128 (meaning that the image consists of 128 128 pixels) and the super division is 256*256. On the basis of the original data, a higher resolution display is realized by increasing the number of pixels. (The so-called higher resolution refers to displaying an image with more pixels.)
Today the teacher talked about another idea of understanding spatial resolution: the ability to distinguish two different points in space.
Super resolution image display
1. Selection of storage image format
1)png
Lossless compression format, can be displayed at the original resolution
2)jpg
Lossy compression format that loses the resolution of the original image
3) svg
Vector graphics, which use mathematical formulas to describe images without distortion at any magnification.
Summarize
For the super-resolution task, if you want to better compare the image performance of different super-resolution multiples, you can choose to save the original resolution image and the real resolution image at the target resolution you want to super-resolution.
detail
How can the original low-resolution image be displayed in a higher-resolution form?
The ultimate goal:

the goal achieved by super-resolution is shown in the figure above, to obtain a clearer image than the original blurred image.
Both super-resolution and low-resolution are based on the same canvas size.
Isn't this canvas size pixel-relative?
The current implementation method: both the original 128 resolution image and the super-extracted 256 image are displayed with 256 pixels. For 128 missing pixels, the nearest neighbor method is used to fill them up.
The problem with this method: the display quality of 128 is artificially reduced, so that only the effect of the nearest neighbor interpolation and the super-resolution method used can be compared. But it will not achieve the difference between comparing images with different resolutions at the same size as shown in the above figure.
The method I want to use: specify the canvas size and display different resolutions. This kind of problem is that when the resolution is relatively high, the difference cannot be displayed.
The way to achieve the goal: fix the canvas size, use different pixel sizes for different resolutions, and the size is closest to the original situation
You can choose the existing commonly used super-resolution methods, bicubic interpolation, nearest neighbor interpolation, etc. The unsupervised super-resolution task requires an image display superior to any of the previous ones.
This involves upsampling the original low-resolution image up to a high-resolution image. We specify to use nearest neighbor interpolation.
The understanding of the nearest neighbor interpolation
From each pixel point in the original image, grow a point
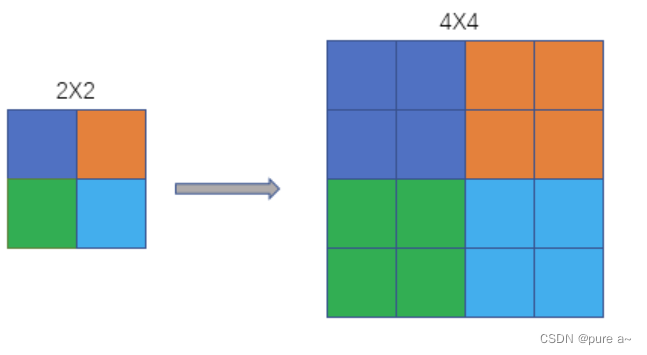
from the pixel center of the low-resolution image to expand the magnification times of each pixel point outward.
From the perspective of interpolation:
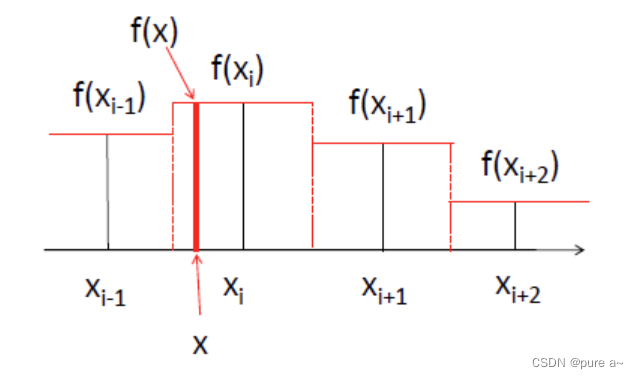
the position and pixel value of the original pixel point are regarded as a piecewise function.
The improvement of image resolution indicates the number of pixels displayed in a unit size.
The more pixels displayed in a unit size, the better?
But in medical images, we want the voxel value to be as small as possible for comparison, so it should be compared with the effect of zero-filling outside the k-space
Reference paper: Deep Learning Single-Frame and Multiframe SuperResolution for Cardiac MRI 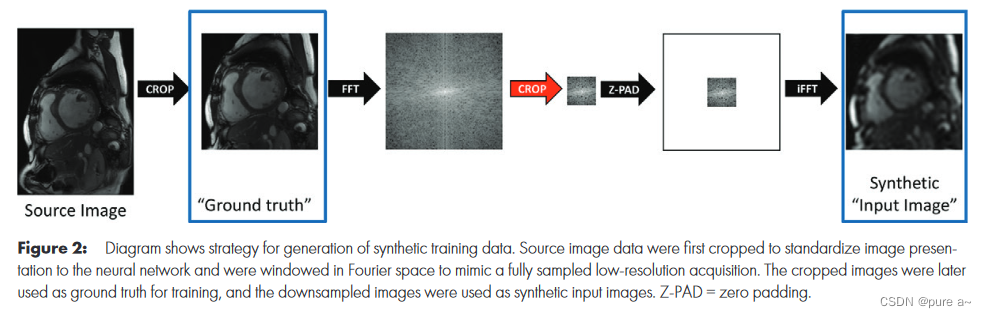
Why can use the nearest neighbor interpolation of the original image, and compare the results of the super-resolution image in the form of the specified resolution display
1. The nearest neighbor interpolation is the least loss of original data Behavior
2. Otherwise, it is necessary to reduce the size of the higher-resolution image for comparison with the lower-resolution image. The method of reducing the resolution will lose image accuracy.
Therefore, using the above method can achieve effect comparison under the premise of ensuring the resolution.