1. Alternate execution of tasks with the same priority
2. Under the default scheduling mechanism, high priority tasks are executed first. If the high-priority task does not voluntarily give up execution, other low-priority tasks will not be executed.
3. Using the same task function, multiple tasks can be created. Each task has its own stack space, so each task can not affect each other.
4.
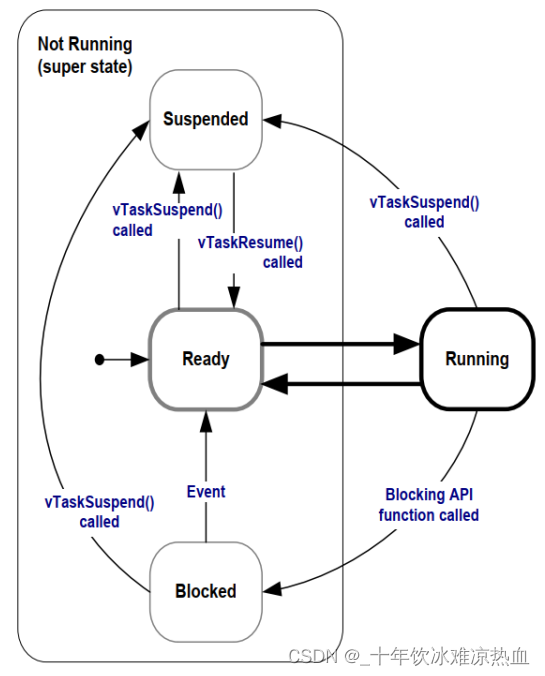
Event: interrupt, other tasks
4.1) Blocked state (Blocked): waiting for something to happen
When the mother communicates with her colleagues in front of the computer, if the colleague has not responded, then the mother's work will be stuck, blocked, and in a blocked state (Blocked). The point is this: the mother is waiting .
1) Time-related events
You can wait for a while: I wait for 2 minutes
You can also wait until an absolute time: I wait until 3 pm
2) Synchronous event: This event is generated by other tasks or interrupt programs
Example 1: Task A waits for Task B to send data to it
Example 2: Task A waits for the user to press a key
There are many sources of synchronization events (these concepts will be elaborated later):
queue
Binary semaphores
counting semaphores
Mutexes
Recursive mutexes, recursive locks (recursive mutexes)
event groups
task notifications
4.2) Suspended state (Suspended): pure rest
In an everyday example, the mother is in front of the computer communicating with a colleague, the mother can pause:
It's annoying, I'll stop for a while
The leader said: you pause
To exit the suspended state, it can only be operated by others :
Other task calls: vTaskResume
Interrupt routine call: xTaskResumeFromISR
4.3) Ready status (Ready)
This task is fully prepared and ready to run: it's just not its turn yet. At this time, it is in the ready state (Ready).
5. The concept of synchronization and mutual exclusion
In team activities, colleague A writes the report first, and then manager B can take it to report to the leader. Manager B must wait for colleague A to finish
Into a report, there is a dependency between A and B, and B must slow down, which is called synchronization. Colleague A has already used the conference room during team activities.
Manager B also wants to use it, even if manager B is the leader, he has to wait, this is called mutual exclusion.